Search Results
Results for: 'narrow synaptic cleft'
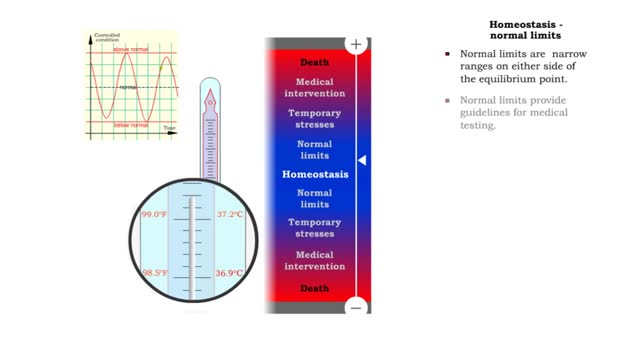
Homeostasis (range of body conditions, normal limits, mild stresses & severe stresses)
By: HWC, Views: 10876
Homeostasis: • Provides relative stability of the internal environment. • Results from constant adjustments. • Regulated by regulatory processes. • Requires system interplay. • Normal limits. • Temporary stresses. • Disruptions requiring medical intervention. • D...
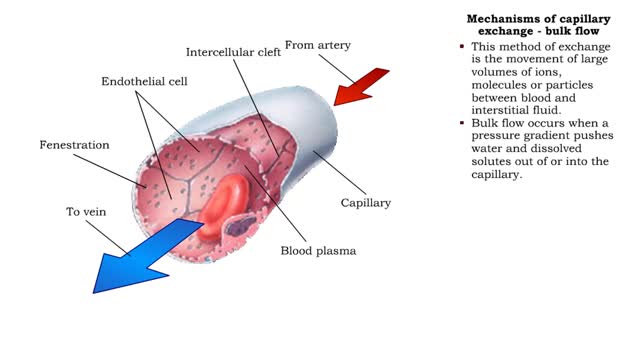
Mechanisms of capillary exchange (transcytosis & bulk flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10720
■ This method of capillary exchange is mainly used to transport small amounts of large, lipid-insoluble (water soluble) molecules, such as large proteins. ■ Substances, packaged in vesicles, move through endothelial cells via endocytosis and exocytosis. ■ This method of exchange is th...
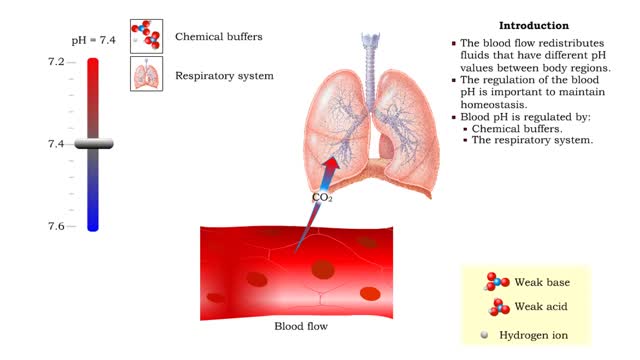
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 10909
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
By: Administrator, Views: 14103
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the or...
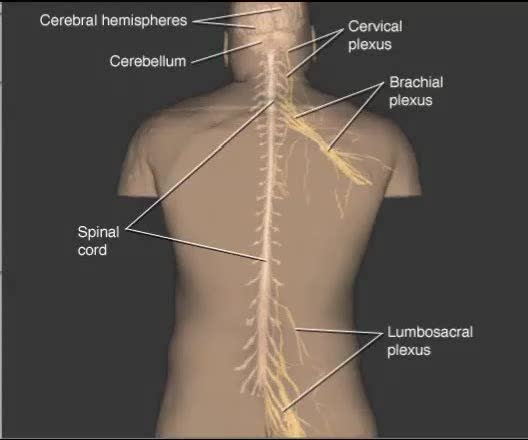
Components of the Nervous System
By: Administrator, Views: 539
The nervous system is the part of an animal that coordinates its actions by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue...
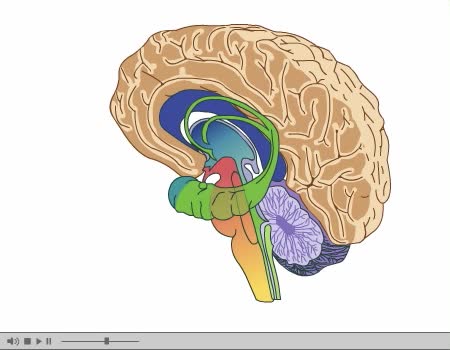
Brain Anatomy Animation (Part 2 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 15363
Its nervous tissue consists of millions of nerve cells and fibers. It is the largest mass of nervous tissue in the body. The brain is enclosed by three membranes known collectively as the meninges: dura mater arachnoid pia mater The major structures are the: cerebrum cerebellum dienc...
Advertisement