Search Results
Results for: 'parasympathetic impulses'
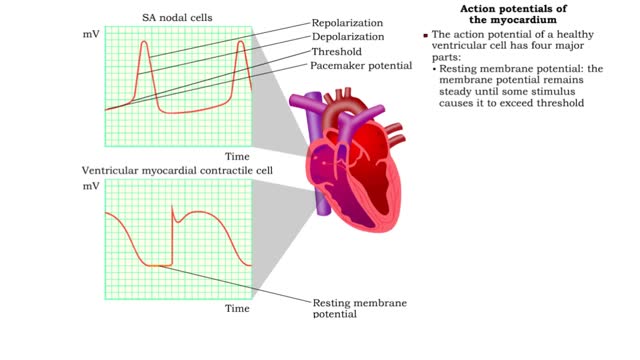
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 11243
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
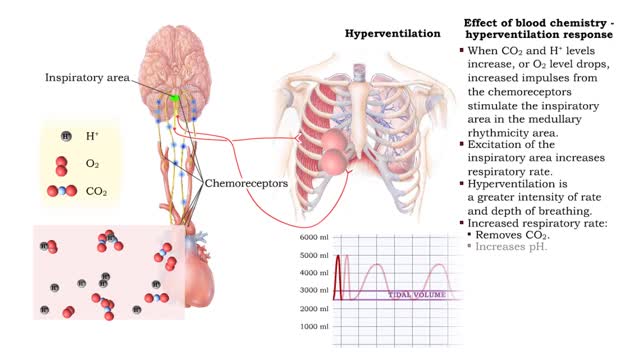
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 10994
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
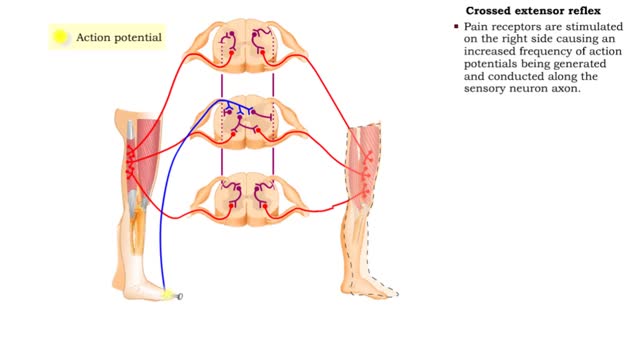
Flexor reflex & Crossed extensor reflex
By: HWC, Views: 11262
• The flexor reflex is a response to pain. This reflex is polysynaptic, ipsilateral, and intersegmental. • Pain receptors are stimulated causing increased frequency of action potentials to be generated and conducted along the sensory neuron axon. • The sensory impulses excite several ass...
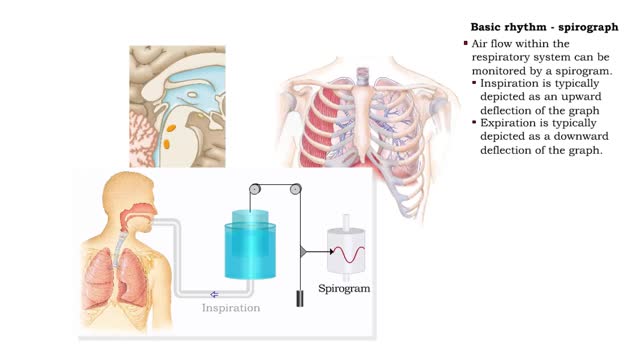
Basic rhythm - control centers in medulla oblongata, spirograph and normal tidal cycle
By: HWC, Views: 11202
• Normal ventilation is rhythmic and involves continuous cycles of inspiration and expiration. • Various regions of the brain closely regulate this rhythmic pattern of ventilation. • The rhythmicity area in the medulla regulates the basic rhythm of ventilation. • The medullary rhy...
By: Administrator, Views: 14491
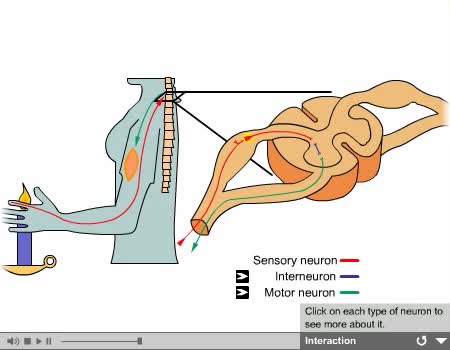
Interneurons: - Are called central or associative neurons. - Located entirely within the central nervous system. - They function to mediate impulses between sensory and motor neurons.
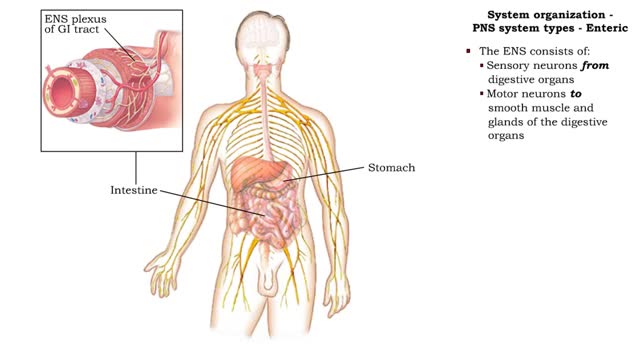
System organization - PPM system types (Somatic, Autonomic & Enteric) and Reflex arc types
By: HWC, Views: 11543
• The PNS consists of all nervous tissue outside of the CNS. • It is divided into three functional components: • Somatic nervous system (SNS) • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Enteric nervous system (ENS) • The SNS consists of: • Sensory neurons from skeletal muscles ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14624
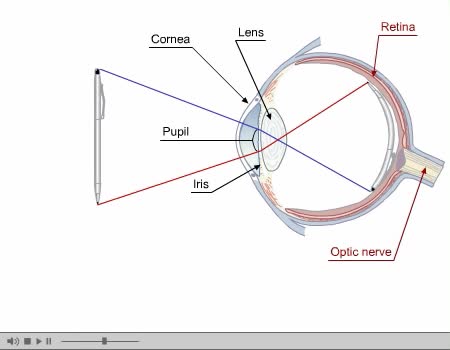
Eye Composed of special anatomical structures that work together to facilitate sight: Cornea Pupil Lens Vitreous body Light stimulates sensory receptors (rods and cones) in the retina or innermost layer of the eye. Vision is made possible through the coordinated actions of nerves that co...
By: Administrator, Views: 14381
Cardiac dysrhythmias are a problem with the rate or rhythm of your heartbeat caused by changes in your heart’s normal sequence of electrical impulses. Your heart may beat too quickly, called tachycardia; too slowly, bradycardia; or with an irregular pattern. Dysrhythmias can range from complete...
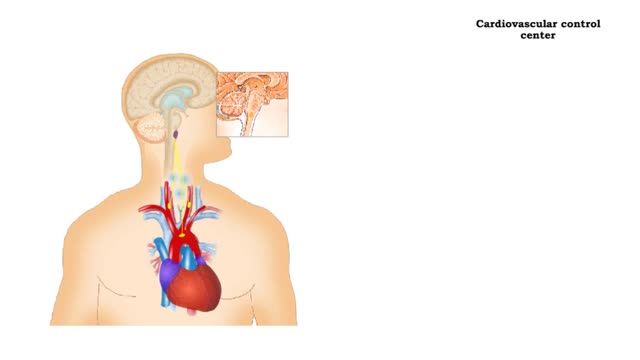
Negative Feedback Regulation of Blood Pressure
By: HWC, Views: 11299
stimulus • Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. Baroreceptors • The aortic arch carries blood to the body. • The common carotids ca...
Advertisement