Search Results
Results for: 'solute concentration'
By: HWC, Views: 11799
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
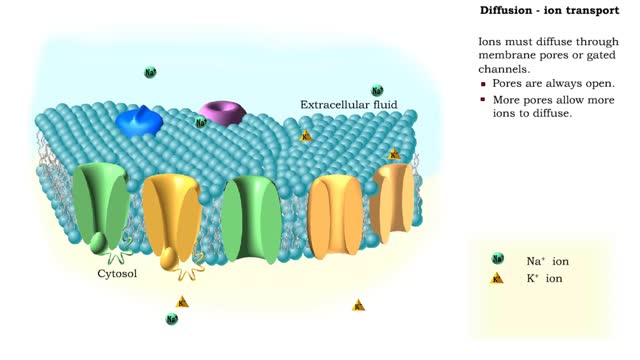
Simple Diffusion - Ion transport
By: HWC, Views: 11724
In the process of diffusion, a substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until its concentration becomes equal throughout a space. Ions must diffuse through membrane pores or gated channels. Pores are always open. More pores allow more ions...
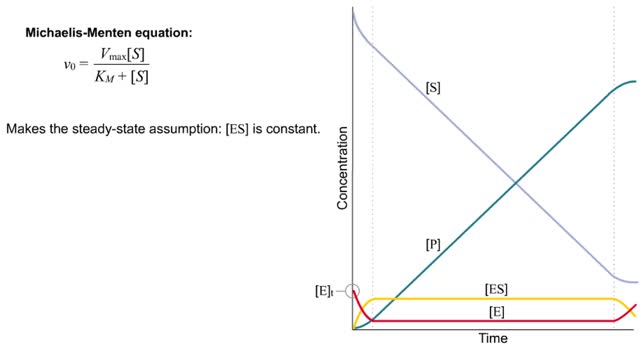
Michaelis–Menten equation & Kinetic parameters
By: HWC, Views: 11525
The Michaelis–Menten equation is the rate equation for a one-substrate enzyme-catalyzed reaction. This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v0), the maximum reaction rate (Vmax), and the initial substrate concentration [S] through the Michaelis constant KM—a measure of the substrat...
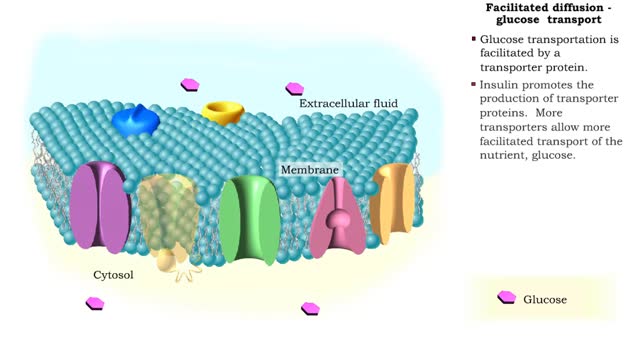
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11949
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
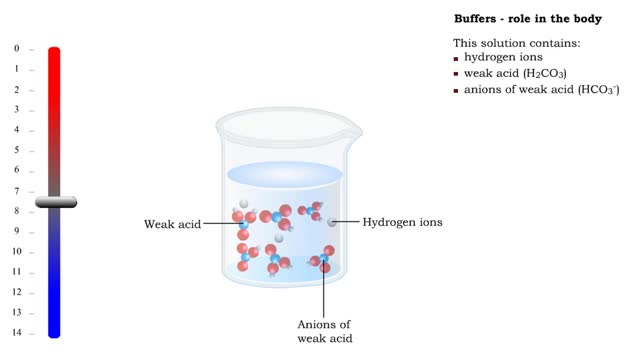
Buffers definition and the role of buffer in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11744
■ Too many H+ break hydrogen bonds and a protein comes apart. ■ Buffers react with excess H+ to protect proteins from breaking down. ■ Buffers consist of weak acid plus anions of that weak acid. This solution contains: • hydrogen ions • weak acid (H2CO3) • anions of we...
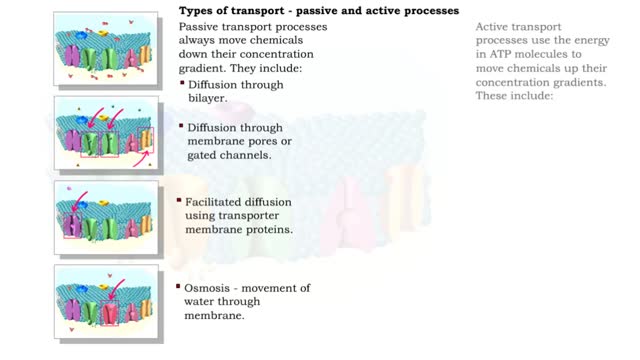
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 12012
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
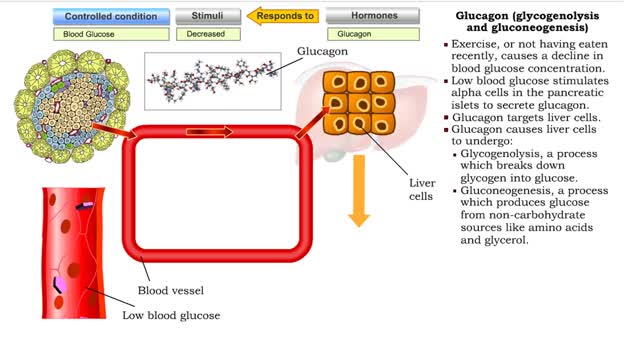
Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11544
• Exercise, or not having eaten recently, causes a decline in blood glucose concentration. • Low blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete glucagon. • Glucagon targets liver cells. • Glucagon causes liver cells to undergo: • Glycogenolysis, a proce...
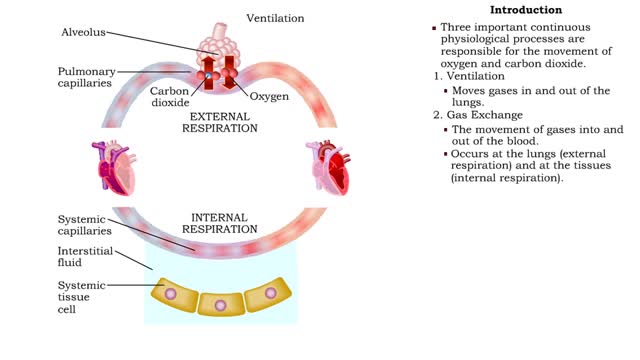
By: HWC, Views: 11732
• The respiratory system is responsible for the movement of gases involved in cellular metabolism. • Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is generated during the aerobic breakdown of glucose and other fuel molecules in order to produce ATP. • Three important continuous physiological pro...
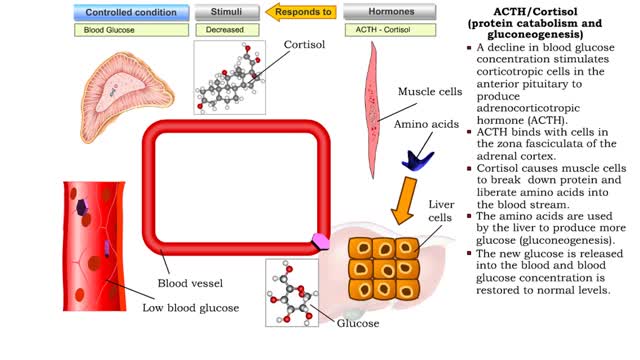
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11635
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
Advertisement