Search Results
Results for: 'solute concentration'
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 11367
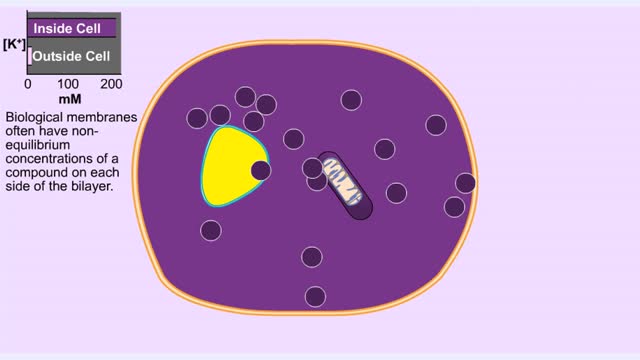
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
By: HWC, Views: 11832
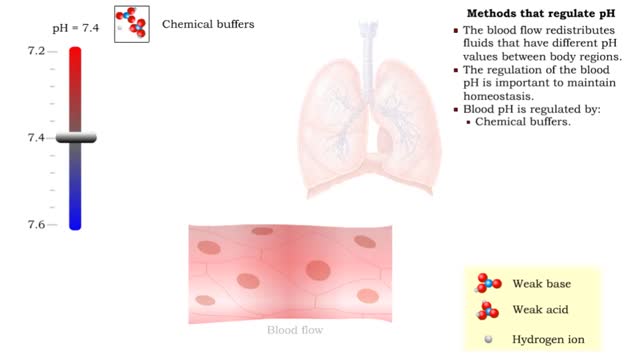
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
Hydrogen bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11981
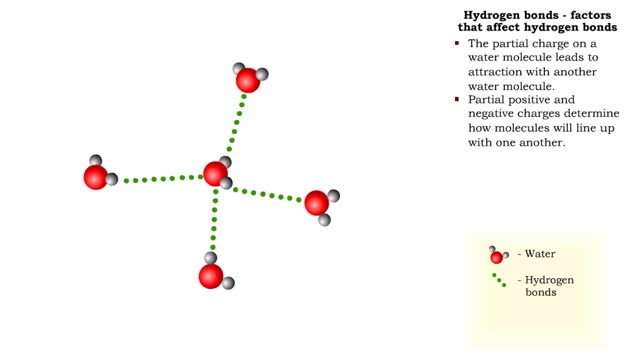
A hydrogen bond is the electromagnetic attraction between polar molecules in which hydrogen is bound to a larger atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This is not a sharing of electrons, as in a covalent bond. Instead, this is an attraction between the positive and negative poles of charged atoms. ...
Chemical Buffers - protein buffer, phosphate buffer system and bicarbonate buffer system
By: HWC, Views: 11926
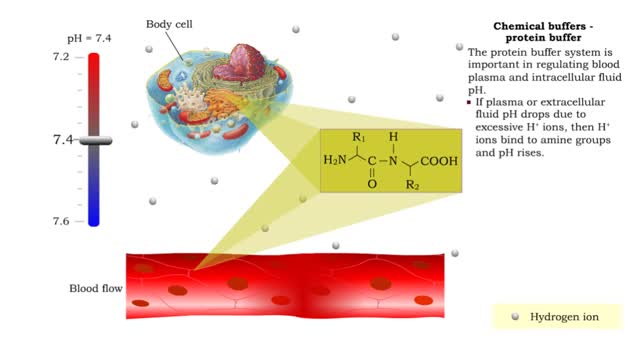
• There are a variety of chemicals in body fluids that prevent the fluids from undergoing large changes in. • These chemicals buffer or regulate fluctuations in H+ concentration. • Chemical buffers: • Bind to H+ ions when there are too many in a solution so pH remains normal. •...
By: HWC, Views: 11818
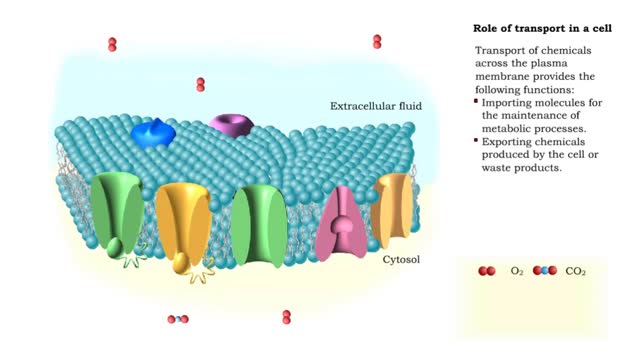
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
By: Administrator, Views: 15002
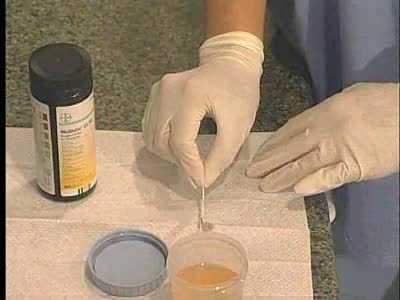
A urinalysis is a test of your urine. A urinalysis is used to detect and manage a wide range of disorders, such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease and diabetes. A urinalysis involves checking the appearance, concentration and content of urine. Abnormal urinalysis results may point to ...
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11860
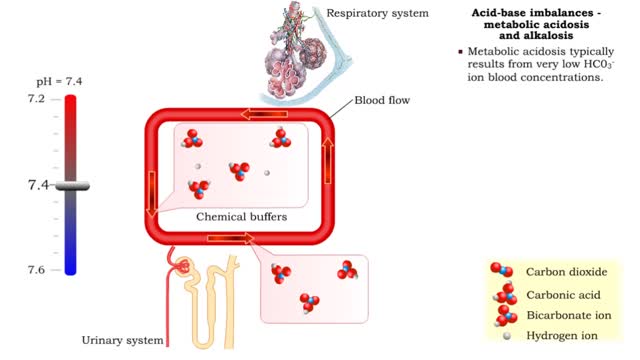
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 12047
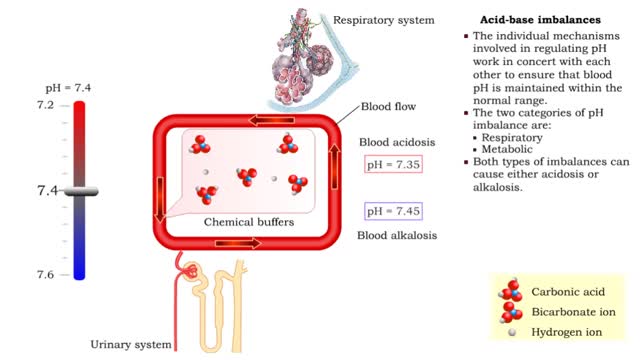
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11845
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
Advertisement