Search Results
Results for: 'solute concentration'
By: HWC, Views: 12072
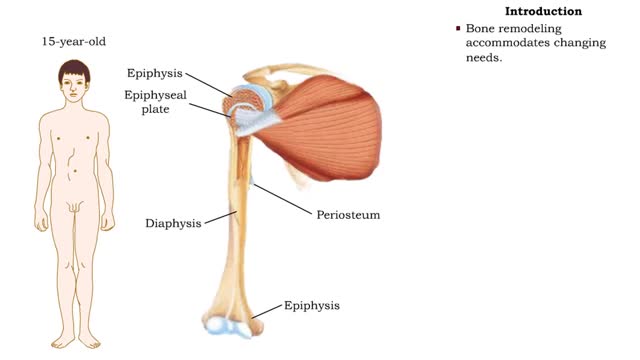
• After birth, bones grow in thickness and length. • Bones grow in diameter via appositional growth at the periosteum. • Epiphyseal plates enable lengthwise growth of long bones, such as the humerus, by interstitial growth. • Bone remodeling accommodates changing needs. • While th...
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
By: HWC, Views: 12215
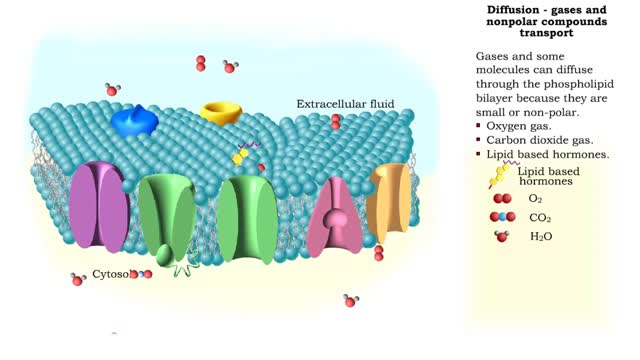
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11856
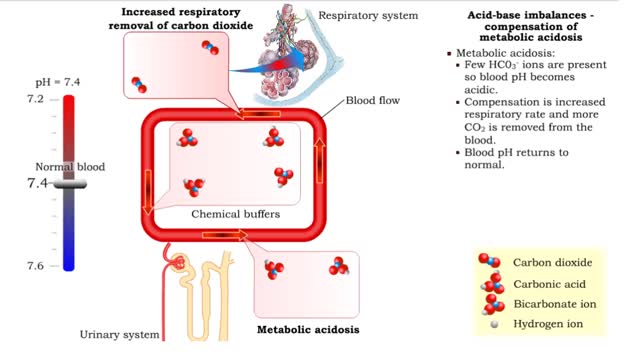
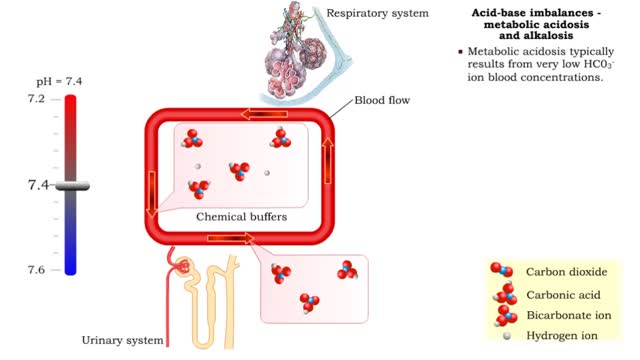
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
By: HWC, Views: 12522
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11949
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
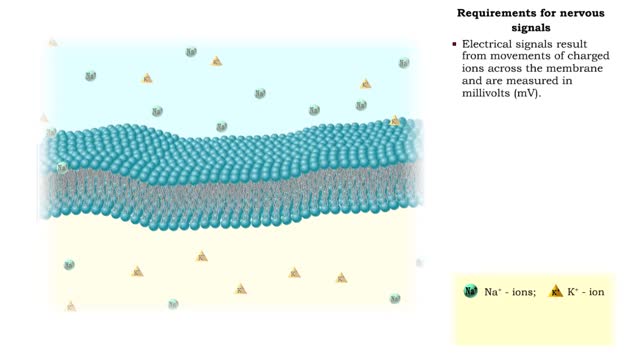
Requirements for nervous signals
By: HWC, Views: 11562
• The function of neurons is to allow communication between cells, thereby maintaining homeostasis. • Electrical signals, called membrane potentials, travel along the membranes of the neurons. • Voltage variability and distance traveled determine the type of nervous signal. 1. Graded...
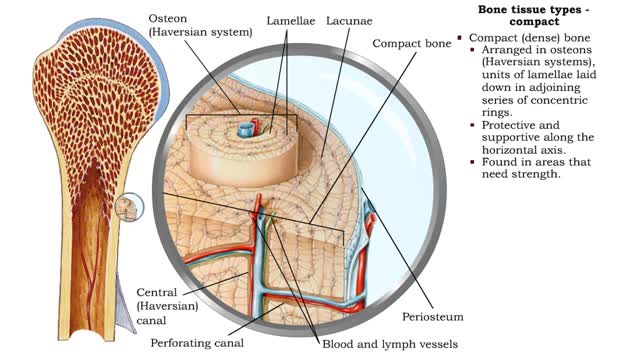
Bone tissue types - compact and spongy
By: HWC, Views: 11739
Bone tissue types • There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy. • All the bones of the skeleton have both kinds of bone tissue. • Compact (dense) bone • Arranged in osteons (Haversian systems), units of lamellae laid down in adjoining series of concentric rings. • P...
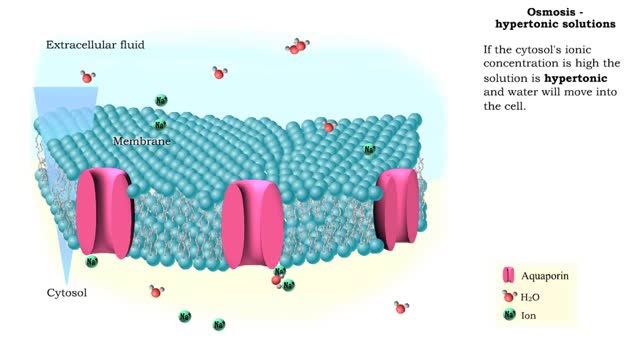
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11799
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
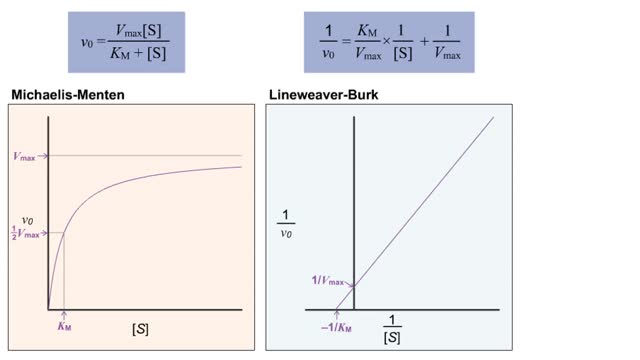
Virtual Enzyme Kinetics & Lineweaver Burk Plot
By: HWC, Views: 11268
• The double-reciprocal (also known as the Lineweaver-Burk) plot is created by plotting the inverse initial velocity (1/V0) as a function of the inverse of the substrate concentration (1/[S]). • This plot is a useful way to determined different inhibitors such as competitive, uncompetitive...
Advertisement