Search Results
Results for: 'epithelial cells'
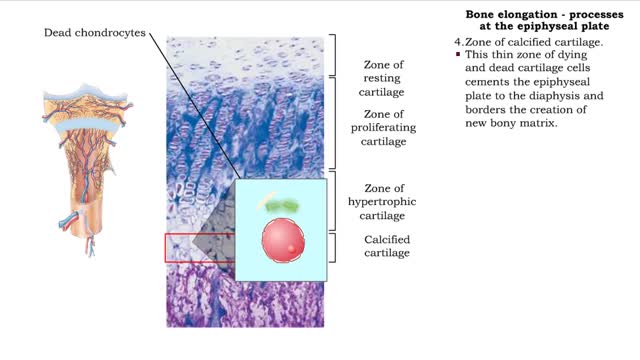
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 10640
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
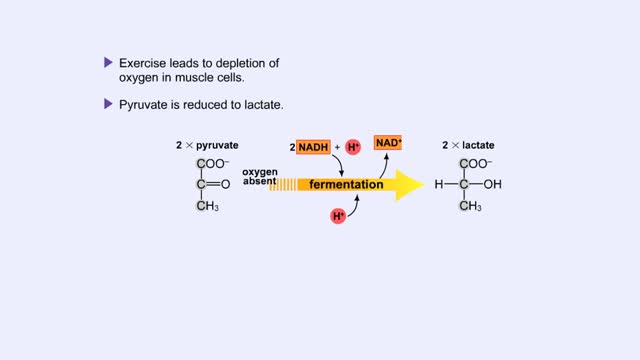
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 9928
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
By: HWC, Views: 11222
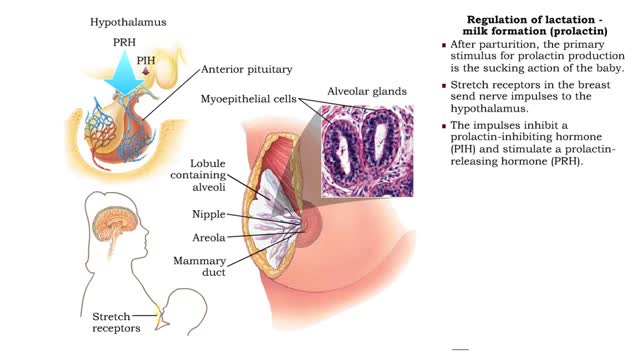
Regulation of lactation - breast preparation • Pregnancy hormones trigger breast changes to prepare for feeding the new baby. • The amount of the hormone prolactin, essential to the initiation of lactation, increases steadily throughout pregnancy. • However, high levels of both estroge...
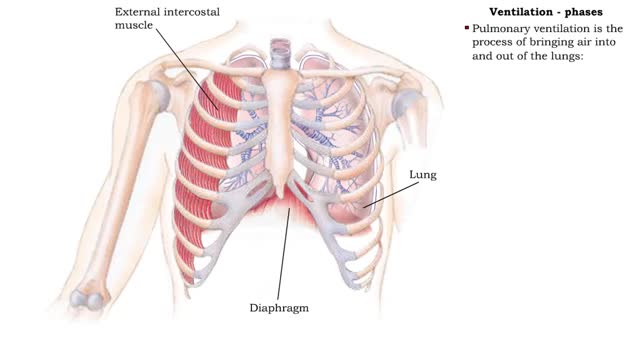
Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC, Views: 10588
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system b...
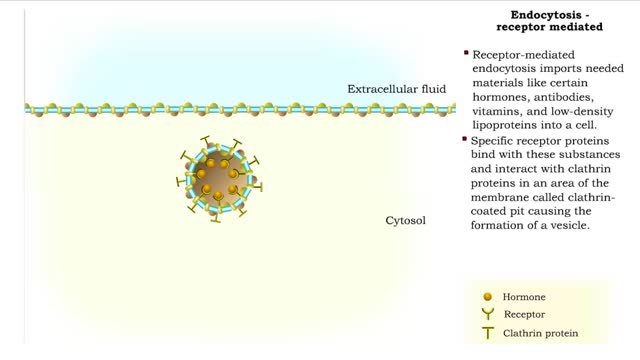
Endocytosis - pinocytosis, receptor mediated and Transcytosis
By: HWC, Views: 10407
Pinocytosis is the process in which a cell "drinks" a tiny droplet Of extracellular fluid, including its solutes. Pinocytosis (Cell Drinking) is the process by which the cell takes in fluids (as well as any small molecules dissolved in those fluids). • The plasma membrane folds inward to...
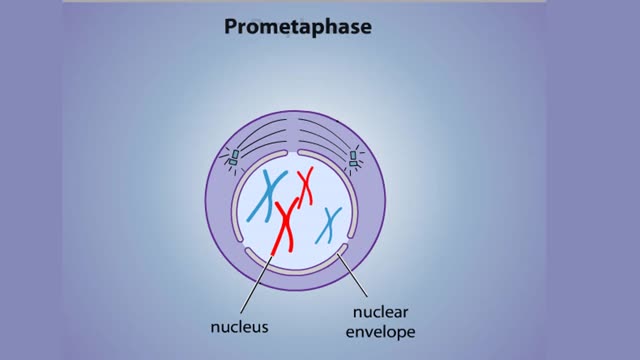
Stages of Mitosis - Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase & Telophase
By: HWC, Views: 10218
In mitosis, the nucleus divides to produce two nuclei that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent nucleus. To prepare for division, the DNA replicates in the preceding interphase. Although the chromosomes are not yet compacted and visible as discrete bodies, we illustrate them ...
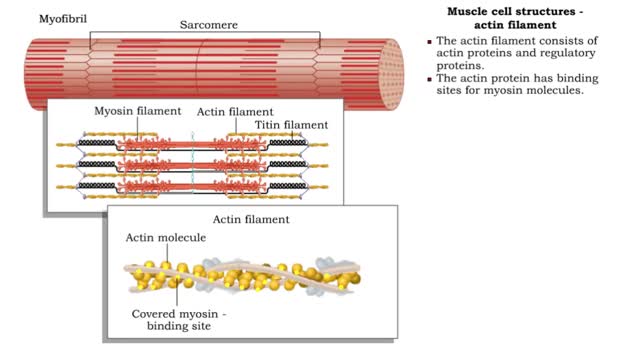
Muscle cell structures - actin, myosin and titin filaments
By: HWC, Views: 10620
Once the muscle cell has been excited it will contract. • A muscle action potential will trigger the release Of Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm. • The Ca2+ ions bind to the regulatory proteins and trigger contraction. • Within skeletal muscle cells are structures that provide the ability...
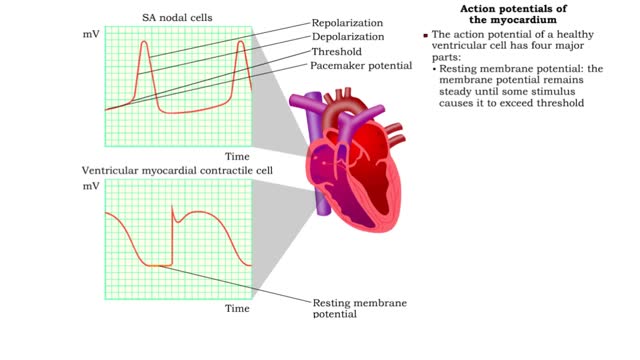
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 10342
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
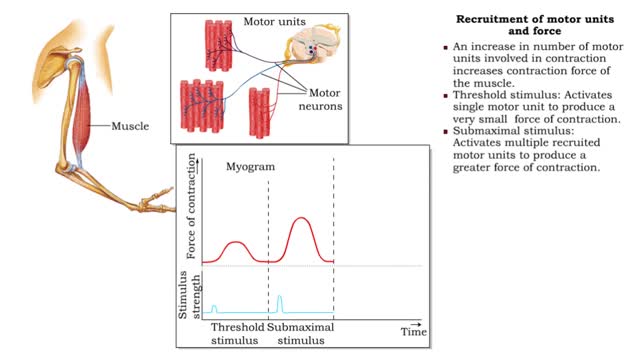
Frequency of stimulation and force (Recruitment of motor units and force)
By: HWC, Views: 10754
• Muscle tension depends on the frequency of stimulation. • Muscle twitch: First stimulus. • Wave summation: When a second stimulus excites a partially relaxed muscle, producing a stronger contraction. • Unfused tetanus: Successive stimulations at the same frequency, producing a se...
Advertisement