Search Results
Results for: 'Enzyme concentration'
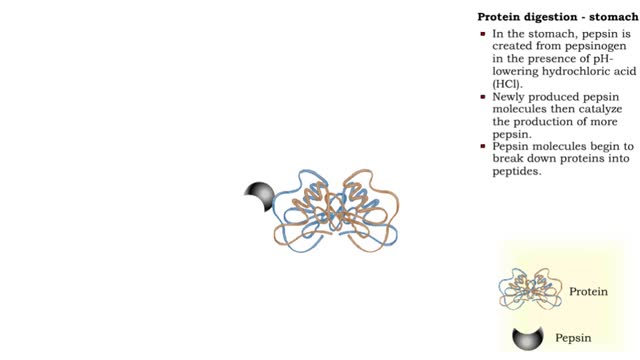
Protein digestion - stomach & small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 10533
• Protein digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine. • The stomach enzyme pepsin initiates the process. • Pancreatic and intestinal brush border enzymes complete the digestive process. • In the stomach, pepsin is created from pepsinogen in the presence of pH-lowering hyd...
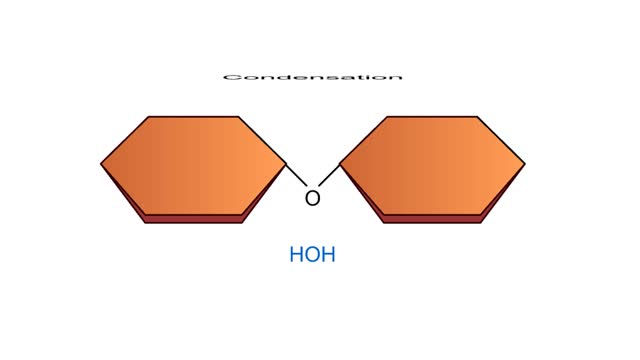
Condensation and Hydrolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4838
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together to form one larger molecule. An enzyme removes a hydroxyl group from one molecule and a hydrogen atom from another, then speeds the formation of a bond between the two molecules at their exposed sites. Typically the discarded atoms join t...
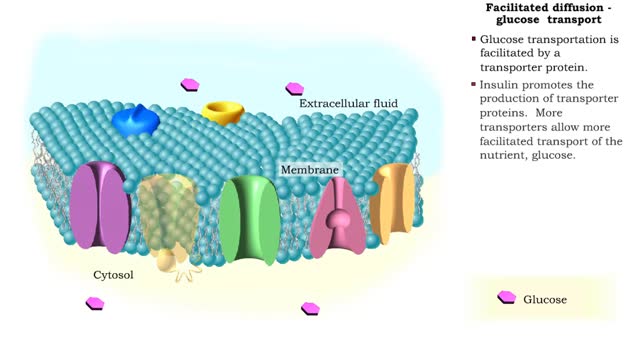
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11284
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
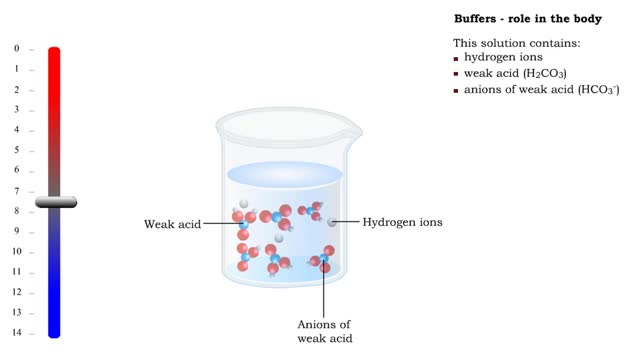
Buffers definition and the role of buffer in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11059
■ Too many H+ break hydrogen bonds and a protein comes apart. ■ Buffers react with excess H+ to protect proteins from breaking down. ■ Buffers consist of weak acid plus anions of that weak acid. This solution contains: • hydrogen ions • weak acid (H2CO3) • anions of we...
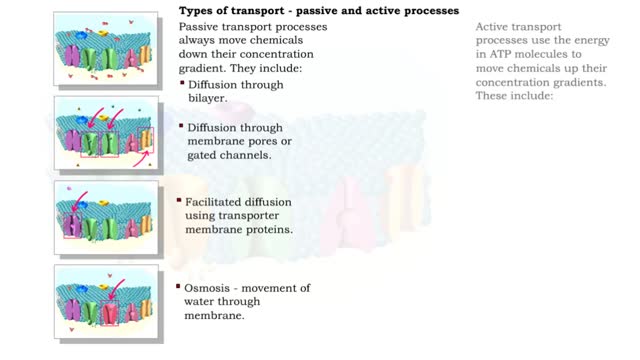
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11343
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
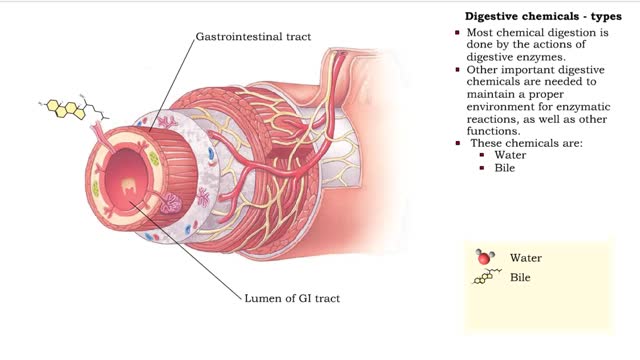
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11062
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
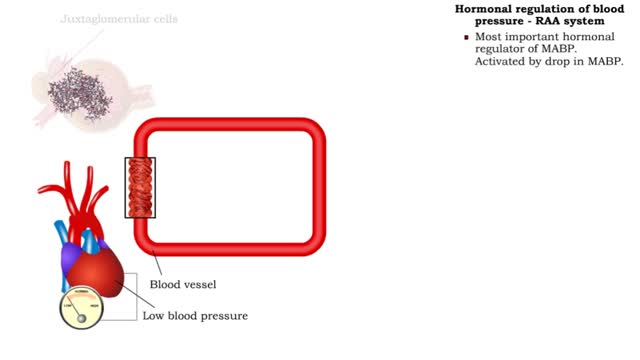
Hormonal regulation of blood pressure - RAA system
By: HWC, Views: 11543
■ Long-term regulation of MABP is under hormonal control. • Hormones that affect blood pressure and volume: the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system, antidiuretic hormone (ADM), and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). ■ Most important hormonal regulator of MABP. Activated by drop in...
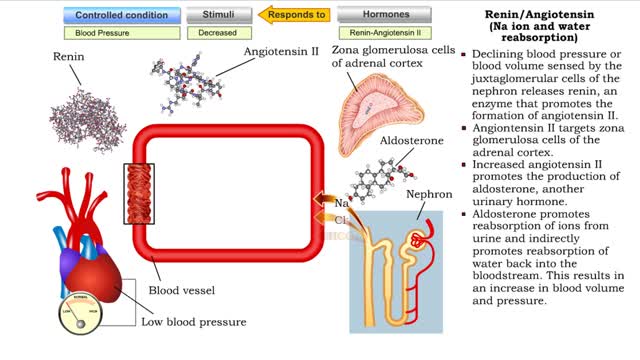
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 11010
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
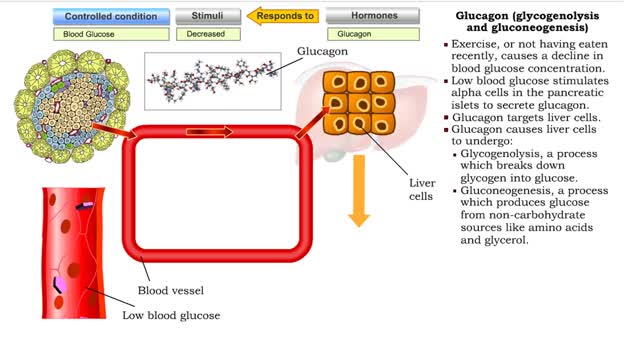
Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10820
• Exercise, or not having eaten recently, causes a decline in blood glucose concentration. • Low blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete glucagon. • Glucagon targets liver cells. • Glucagon causes liver cells to undergo: • Glycogenolysis, a proce...
Advertisement