Search Results
Results for: 'Facilitated diffusion'
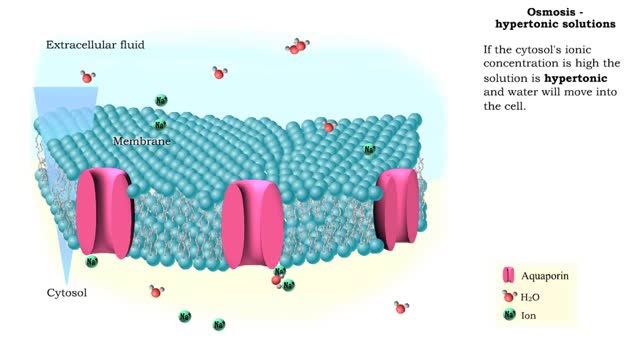
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 9747
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
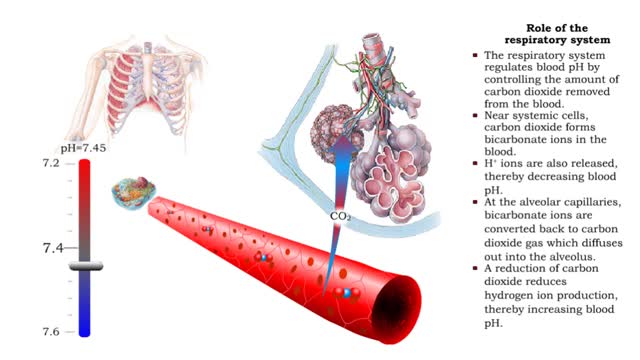
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 10211
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
By: HWC, Views: 9601
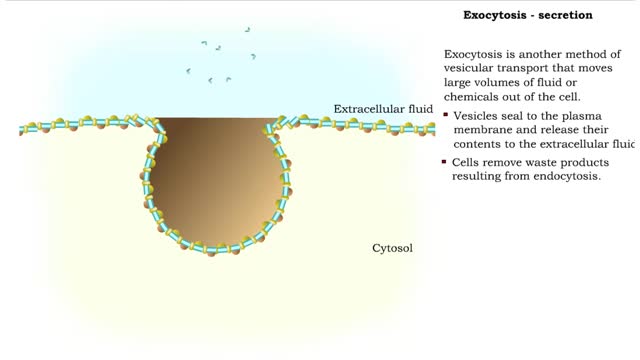
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
Bone processes - resorption and deposition, remodeling and response to stress in adult bones
By: HWC, Views: 9831
• The process of remodeling bone tissues involves bone cells resorbing or depositing minerals into bone tissue. • During resorption, bone cells break down bone tissue and release calcium and other minerals for use by other cells in the body. • Bone cells also rebuild bone tissue by depo...
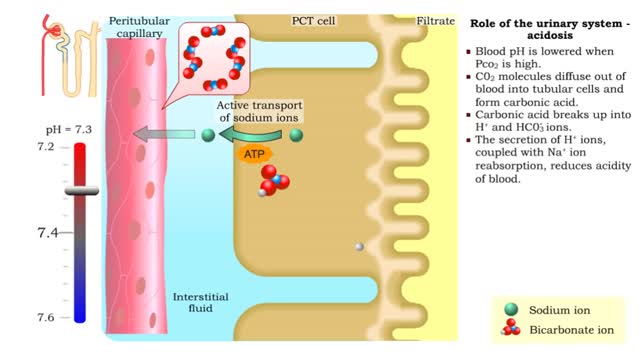
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 9873
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
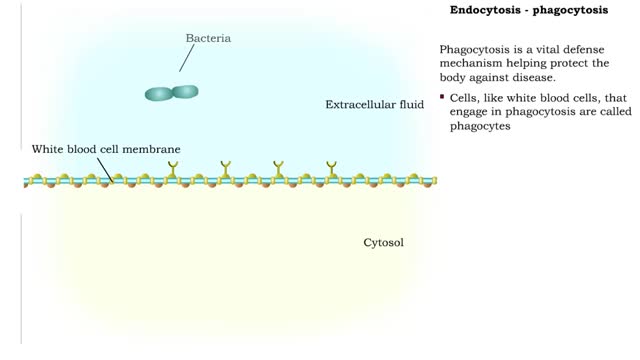
Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
By: HWC, Views: 9716
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secret...
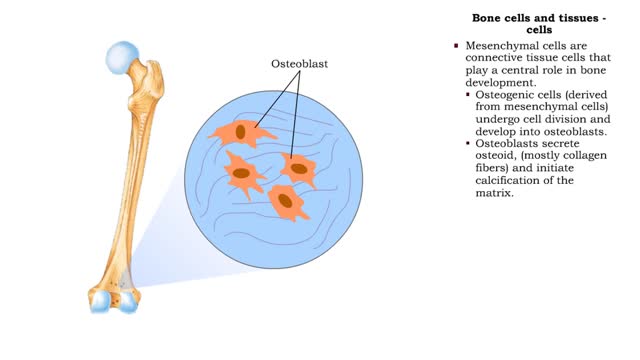
Bone cells and tissues - tissue composition and cells
By: HWC, Views: 10466
Bone tissue consists of bone cells secreting bone matrix. • The extracellular bone matrix is a connective tissue that is hard, yet flexible. • Collagen fibers provide flexibility. • Inorganic mineral salts (primarily calcium phosphate, or hydroxyapatite) provide hardness. • Togethe...
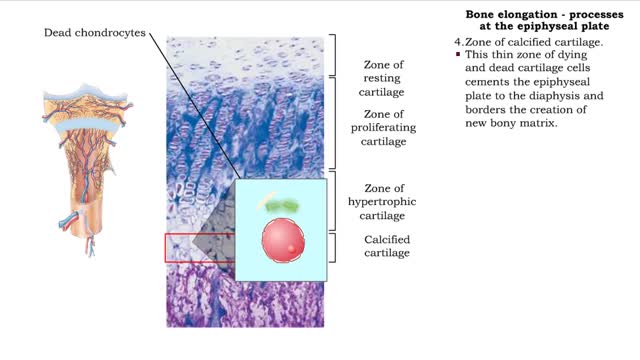
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 9815
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
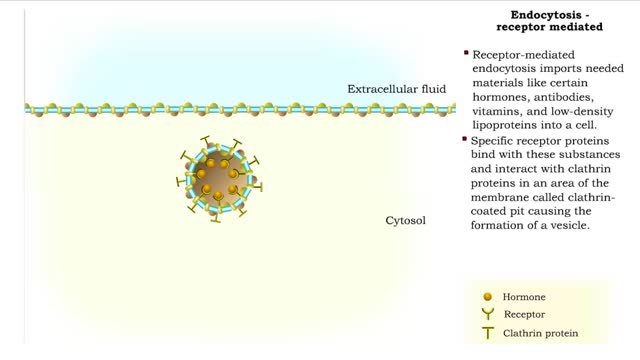
Endocytosis - pinocytosis, receptor mediated and Transcytosis
By: HWC, Views: 9600
Pinocytosis is the process in which a cell "drinks" a tiny droplet Of extracellular fluid, including its solutes. Pinocytosis (Cell Drinking) is the process by which the cell takes in fluids (as well as any small molecules dissolved in those fluids). • The plasma membrane folds inward to...
Advertisement