Search Results
Results for: 'Vascular tissue'
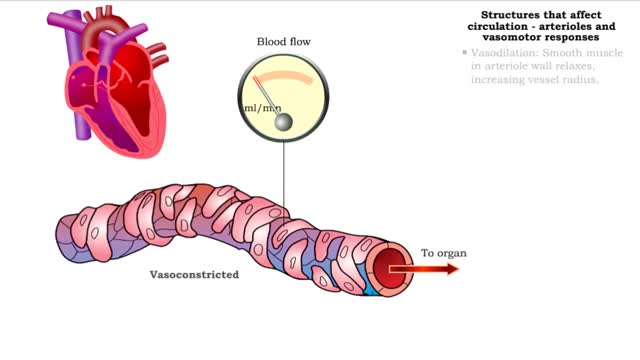
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 11078
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
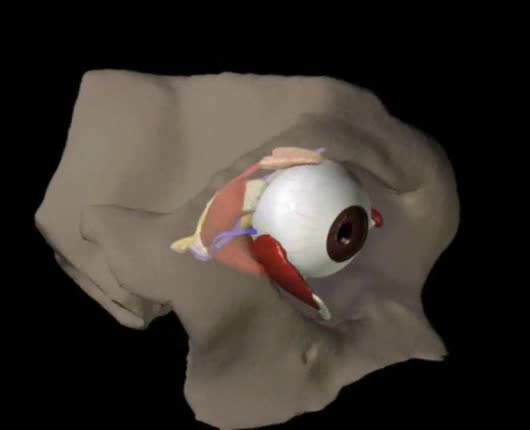
Structures of the Eye Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 2343
Orbit A cone-shaped cavity in the front of the skull that contains the eyeball. Formed by the combination of several bones and is lined with fatty tissue that cushions the eyeball. This cavity has several foramina (openings) through which blood vessels and nerves pass. Largest opening is the ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14301
Inflammation is part of the body's immune response. Infections, wounds, and any damage to tissue would not be able to heal without an inflammatory response. Chronic inflammation can eventually cause several diseases and conditions, including some cancers and rheumatoid arthritis.
By: Administrator, Views: 13822
Pericarditis refers to inflammation of the pericardium, two thin layers of a sac-like tissue that surround the heart, hold it in place and help it work. A small amount of fluid keeps the layers separate so that there's no friction between them.
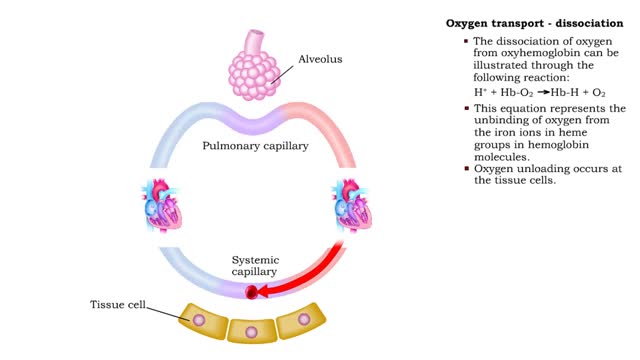
Oxygen transport: association and dissociation & Factors that affect hemoglobin's saturation with O2
By: HWC, Views: 10928
• The production of oxyhemoglobin can be illustrated through the following reaction: 02 + Hb-H --) Hb-02 + H+ • This equation represents the binding of oxygen to the iron ions in heme groups in hemoglobin molecules. • Oxygen binding or loading occurs at the lungs • The dissociatio...
By: Administrator, Views: 14205
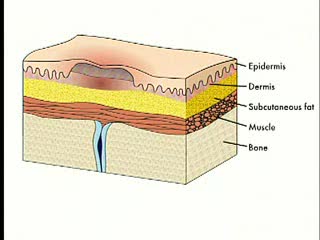
Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, decubiti, decubitous ulcers, pressure injuries, and pressure sores, are localized damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of usually long-term pressure, or pressure in combination with shear or fric...
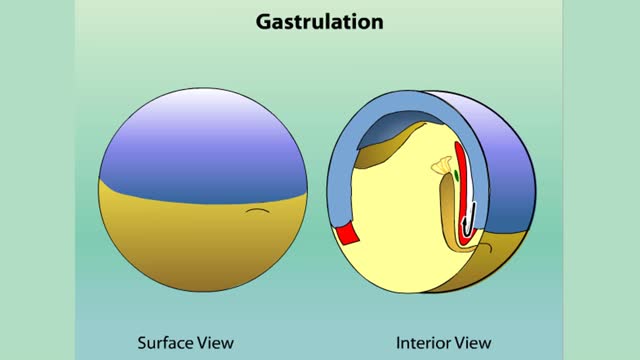
Gastrulation: cross section of the frog
By: HWC, Views: 10133
Gastrulation Most animals enter a phase early in development called gastrulation. In this phase, a tiny ball or disc of cells rearranges to form three embryonic layers of tissue, called germ layers. The germ layers of the embryo—now called a gastrula—are called the endoderm, mesoderm, and eco...
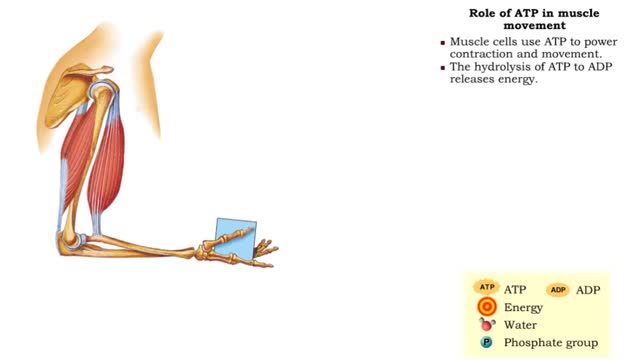
Role of ATP in muscle movement
By: HWC, Views: 11130
• Muscle cells use ATP to power contraction and movement. • The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases • ATP can be regenerated by adding to ADP. • During muscular contraction, ATP molecules: • Energize the myosin head • Detach myosin from actin • ATP must be then regenerat...
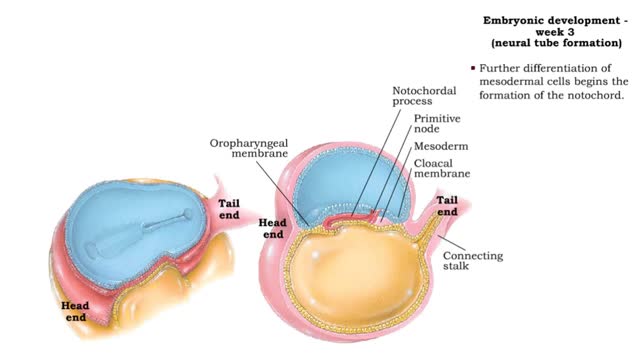
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 11100
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
Advertisement