Search Results
Results for: 'activation energy'
By: HWC, Views: 11955
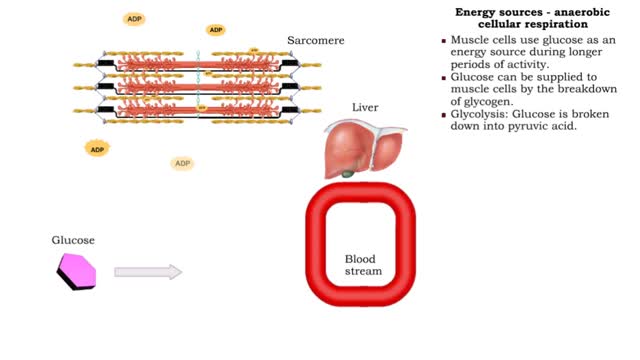
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
Contraction and Relaxation Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14658
Muscles are responsible for movement. The types of movement are: - Locomotion, when chemical energy is changed into mechanical energy. - Propulsion of substances through tubes, as in circulation and digestion. - Changes in the sizes of openings, as in the contraction and relaxation of the iris...
By: HWC, Views: 12294
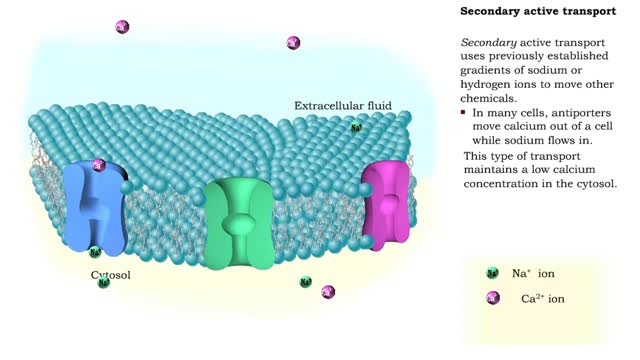
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 10758
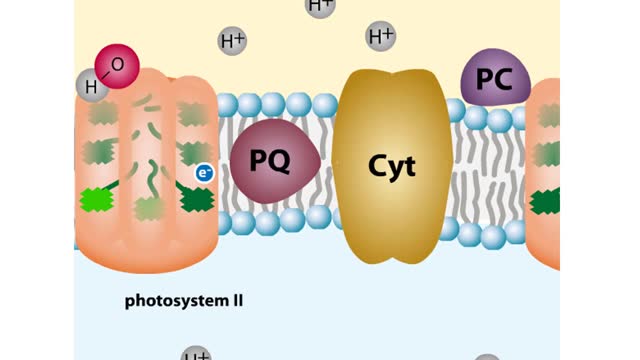
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
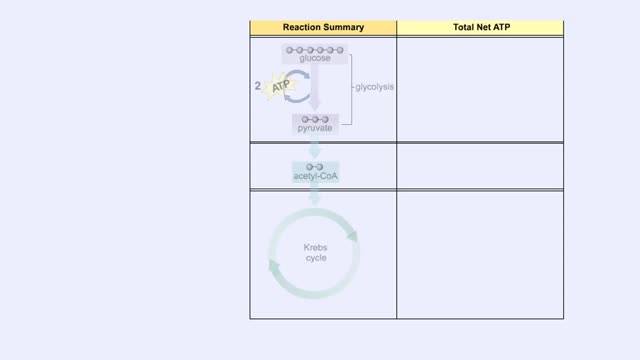
By: HWC, Views: 11992
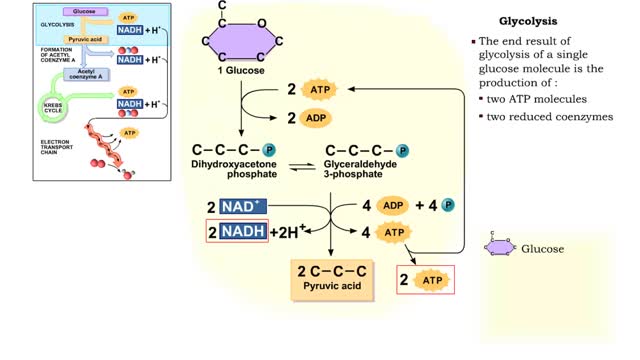
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
By: HWC, Views: 11480
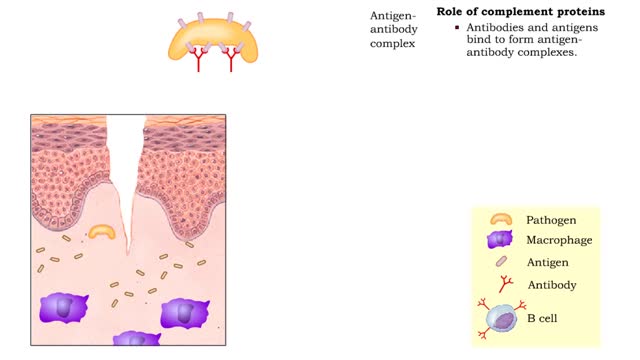
• Non-specific and specific defense mechanisms work through the functions of complement proteins. • As soon as pathogens penetrate the physical barrier of the skin, other resistance mechanisms begin. • Cells, such as macrophages, phagocytize pathogens. • These cells increase exposu...
By: HWC, Views: 5595
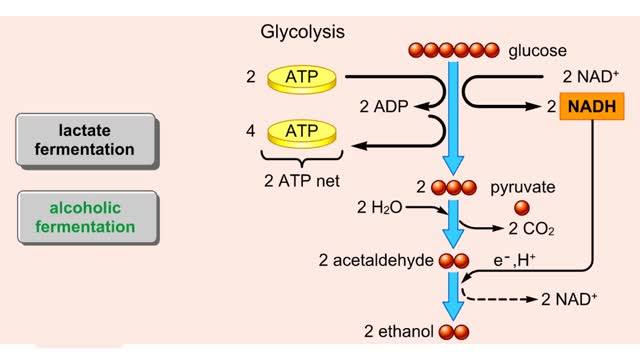
Both lactate fermentation and alcoholic fermentation begin with pyruvate formed by glycolysis. During lactate fermentation, pyruvate molecules accept electrons and hydrogen from NADH. This transfer regenerates NAD± and converts pyruvate to lactate. The net energy yield is the two ATP...
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 12018
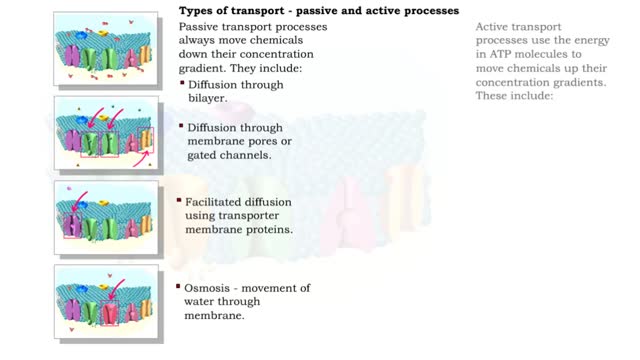
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 11426
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
Advertisement