Search Results
Results for: 'carboxylic acid functional group'
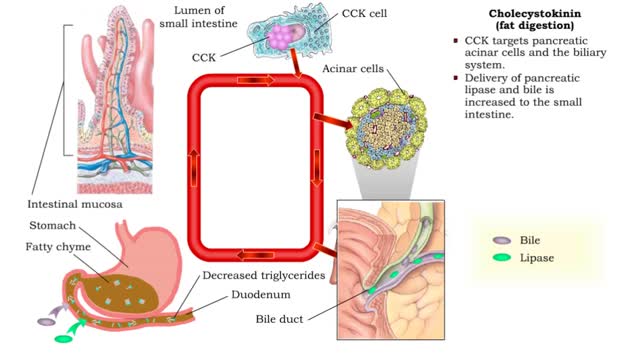
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10828
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
By: Administrator, Views: 14557
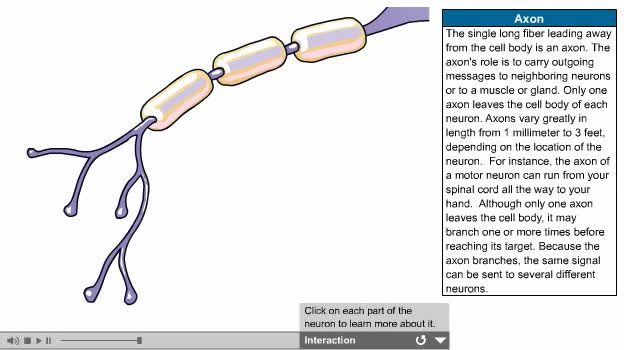
There are several types of neurons, three of which are: Motor neurons, Sensory neurons, Interneurons. The nervous system is usually described as having two interconnected divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS: Includes the brain and spinal...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10700
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
By: HWC, Views: 10830
Acids and bases are found all around your house. For example, if you open your pantry or refrigerator, you might see a lot of acids. Fruit juice, soda pop, vinegar, and milk are all examples of acids. The word acid actually comes from a Latin term meaning ''sour.'' Many materials, like sugar for ...
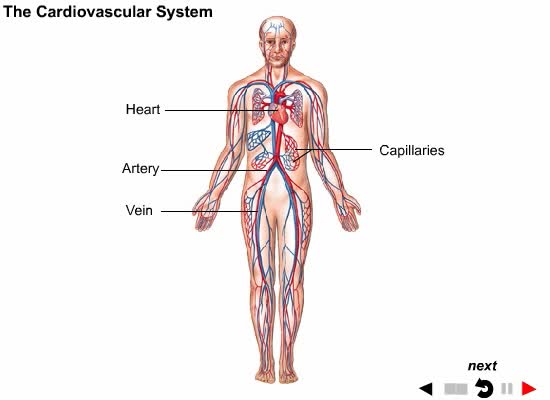
Introduction to Body Systems Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 915
Systems: A group of different organs functioning together for a common purpose.
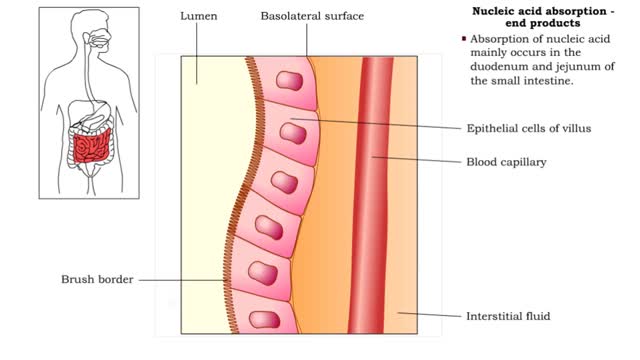
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10763
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10599
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
By: HWC, Views: 7825
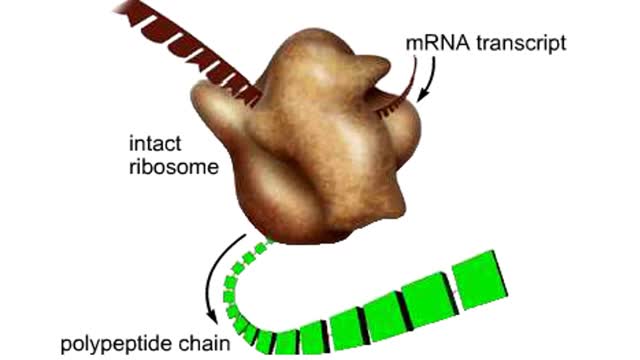
The structure and function of the mammalian ribosome. The mammalian ribosome consists of two subunits, one small and one large. Each subunit is assembled in the nucleus from rRNA and structural proteins. Once assembled, the ribosomal subunits are shipped separately to the cytoplasm. ...
By: HWC, Views: 11146
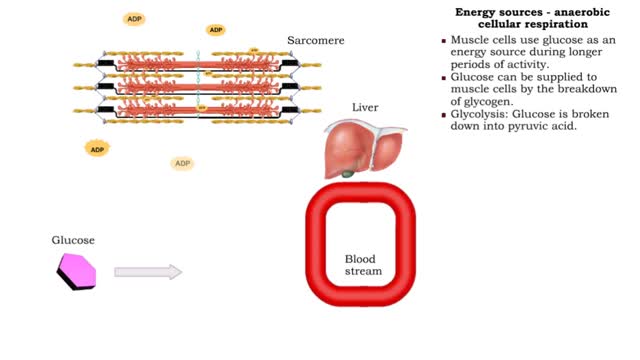
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
Advertisement