Search Results
Results for: 'membrane structure'
By: HWC, Views: 11069
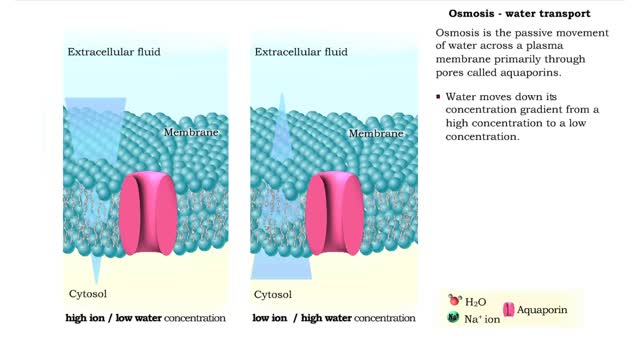
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
By: HWC, Views: 7720
Formation of membrane attack complexes. Complement proteins can activate when they bind to antibodies that are bound to a pathogen. Complement proteins also activate when they bind directly to bacterial surfaces. Cascading reactions yield huge numbers of different types of complement protei...
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 10819
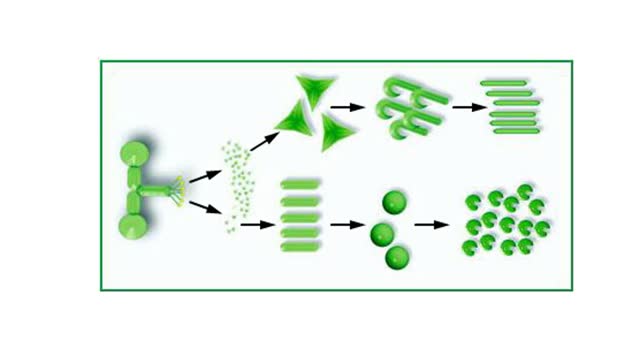
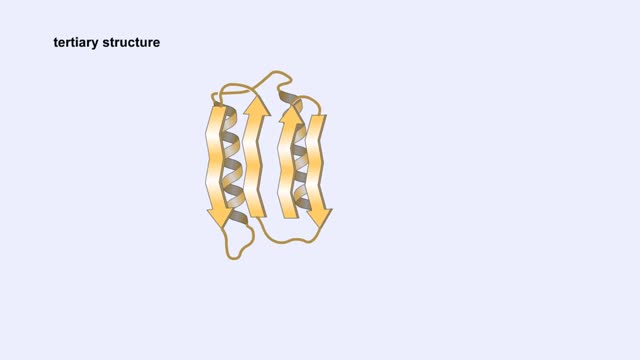
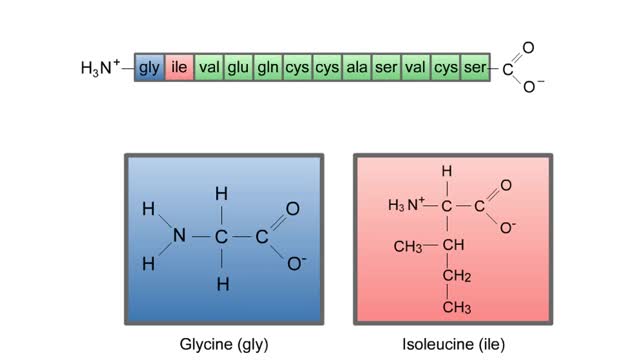
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
By: HWC, Views: 9909
Living things must accomplish a great number of tasks just to get through a day, and these tasks are accomplished by a diverse range of biological molecules. In the range of tasks that molecules accomplish, however, proteins reign supreme. Almost every chemical reaction that takes place in living...
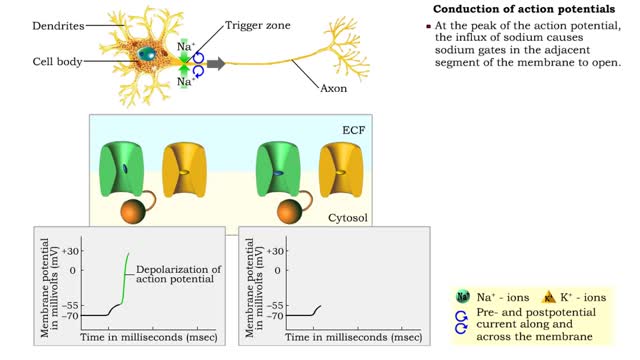
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11069
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
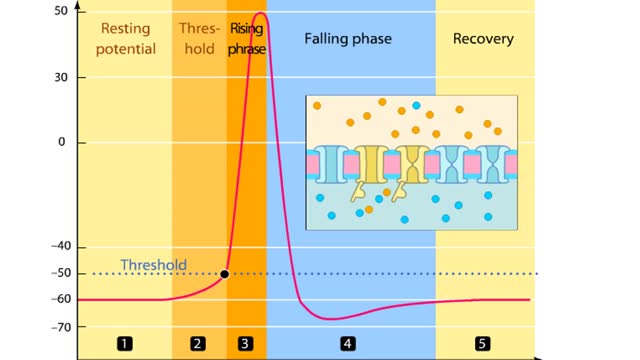
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 10310
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
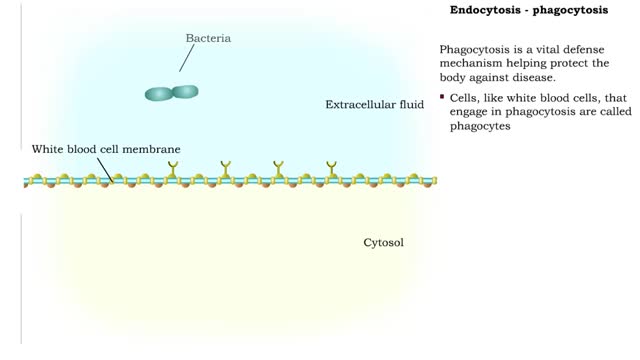
Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
By: HWC, Views: 10953
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secret...
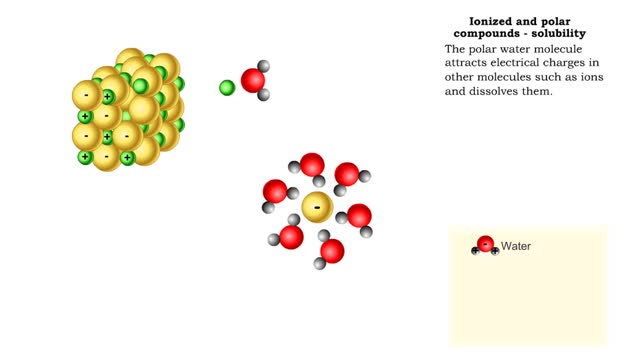
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11041
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
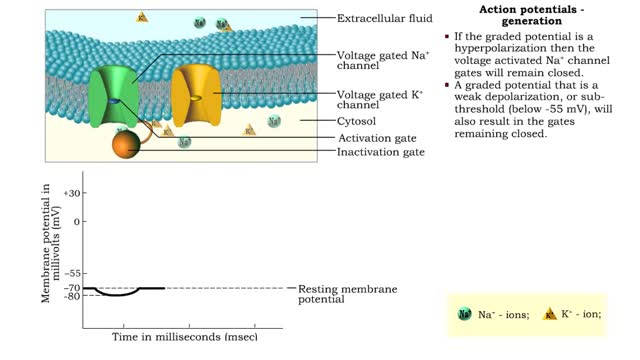
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 10751
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
Advertisement