Search Results
Results for: 'membrane structure'
By: HWC, Views: 8084
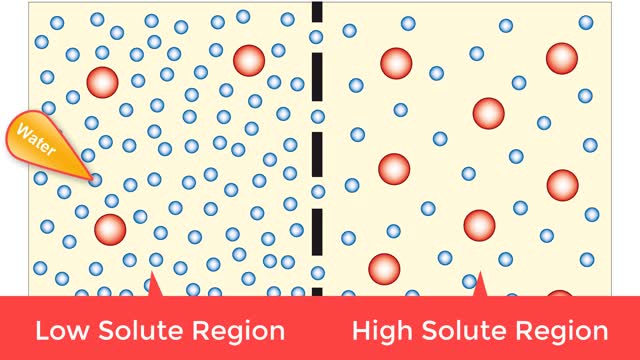
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8590
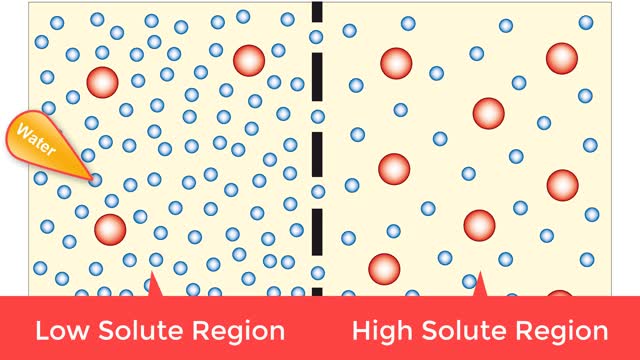
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11410
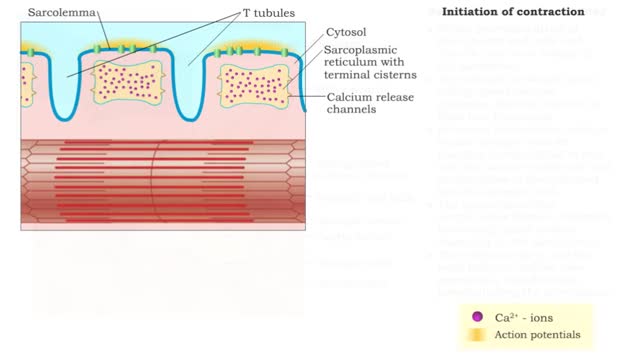
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
By: HWC, Views: 10266
Observe the burning logs of wood. The logs burn to emit heat, light and carbon dioxide. What is left behind is ash. This residue is a new substance with a different molecular structure than the original wood. Similarly when baking the dough into bread, it becomes fluffy and light. There is a ch...
By: HWC, Views: 11348
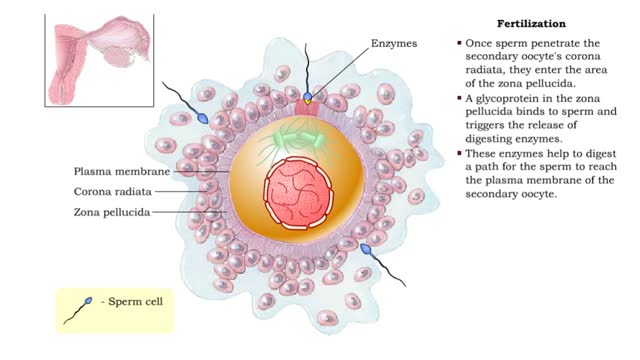
• Fertilization is the process by which the two gametes from the parents fuse their genetic material to form a new individual (zygote). • Fertilization requires that sperm cells swimming through the uterine tube contact a secondary oocyte. • Once sperm penetrate the secondary oocyte's ...
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 11137
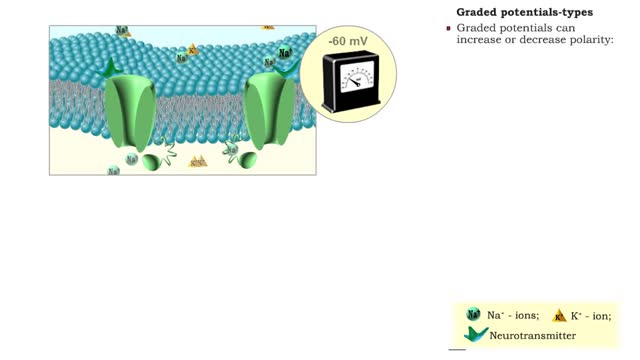
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10721
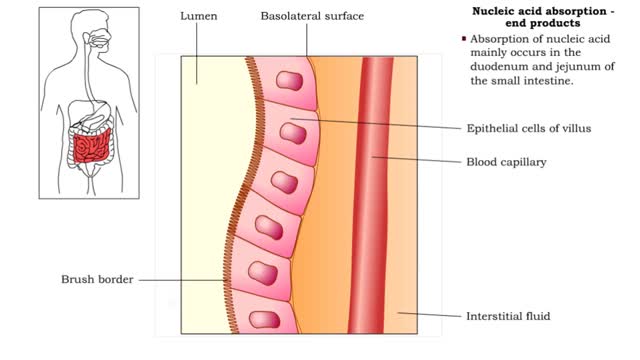
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Proteins
By: HWC, Views: 10419
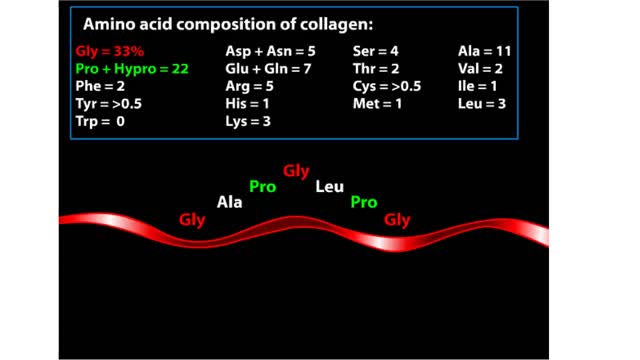
Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The 20 different amino acids used to make all proteins differ only in their side chains, and the properties of these side chains account for the great diversity of protein structure and function. Collagen is an example of how a prote...
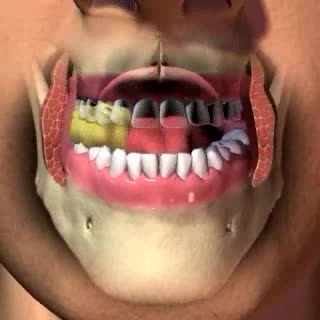
By: Administrator, Views: 14548
The mouth or oral cavity is formed by: - The hard and soft palates at the top or roof - the cheeks - the tongue - the lips Contains the teeth and salivary glands. The gingivae (gums) surround the necks of the teeth. The lingual frenulum is a thin fold of mucous membrane that connects...
Advertisement