Search Results
Results for: 'organic substances'
By: HWC, Views: 12166
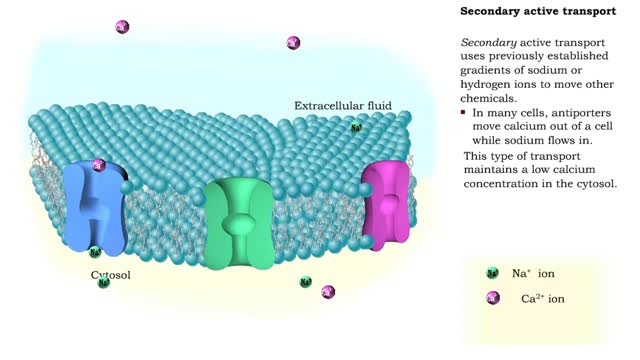
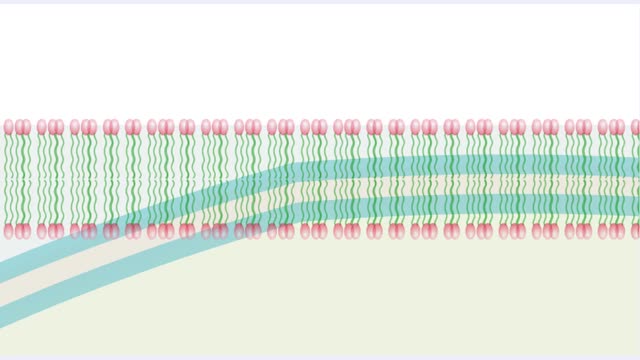
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
By: HWC, Views: 11680
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
Olfaction. or the sense of smell
By: HWC, Views: 9033
Do you ever wonder how you can distinguish thousands of different odors? Olfaction. or the sense of smell, is used by all mammals to navigate, find food, and even find mates. We have millions of olfactory receptors for smelling in our nose. These receptor neurons bind water-soluble or volatil...
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11904
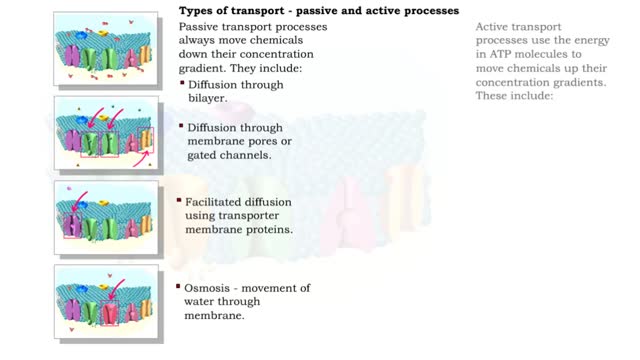
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC, Views: 11740
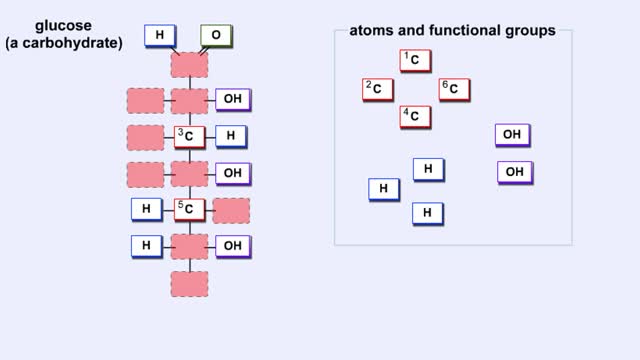
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carb...
Molecules, Membrane Permeability and Structure
By: HWC, Views: 11060
Organisms are not isolated system at equilibrium and need to intake nutrients and electrolytes as remove wastes. Similarly Cells within an organism must also exchange compound by passing them through membrane. The permeability of a membrane is the rate of passive diffusion of molecules th...
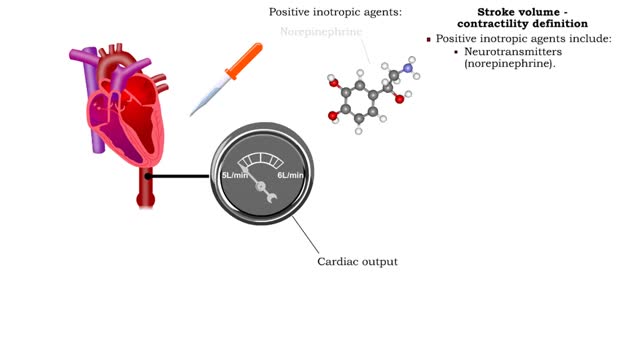
Stroke volume - contractility definition
By: HWC, Views: 11276
Contractility is the forcefulness of contraction of cardiac muscle. • Inotropic agents are substances that increase or decrease contractility (and stroke volume). • Positive inotropic agents increase contractility and will increase stroke volume and cardiac output. • Negative inotropi...
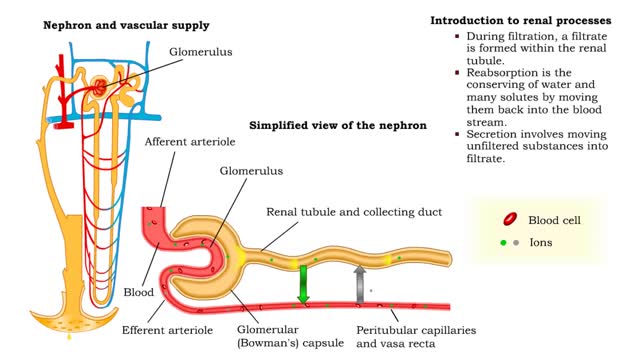
Introduction to filtration - filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 11726
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
By: HWC, Views: 11743
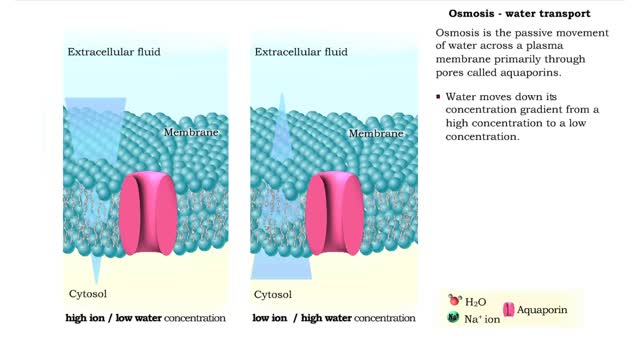
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
Advertisement