Search Results
Results for: 'oxygen molecule'
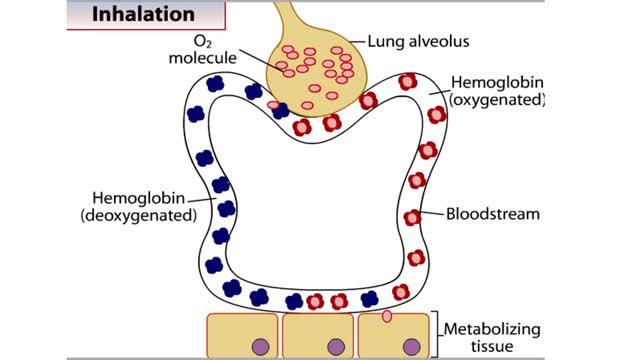
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 10326
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
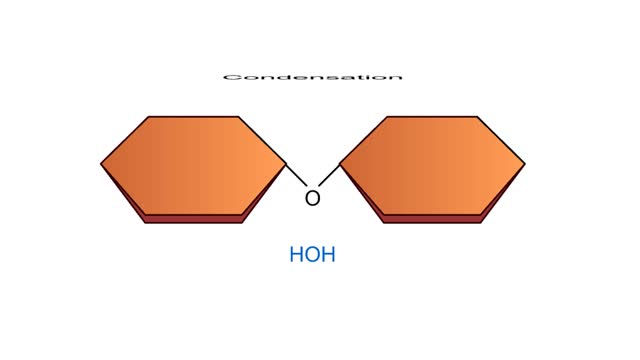
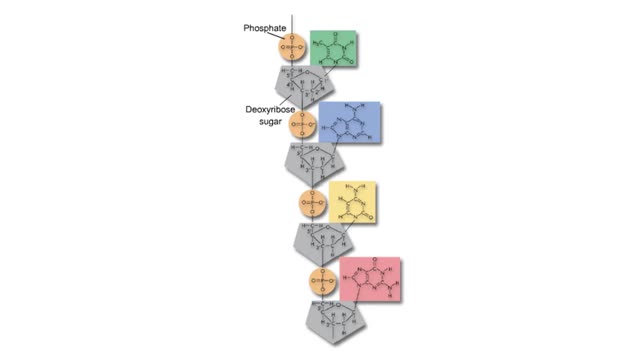
Condensation and Hydrolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4754
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together to form one larger molecule. An enzyme removes a hydroxyl group from one molecule and a hydrogen atom from another, then speeds the formation of a bond between the two molecules at their exposed sites. Typically the discarded atoms join t...
By: Administrator, Views: 482
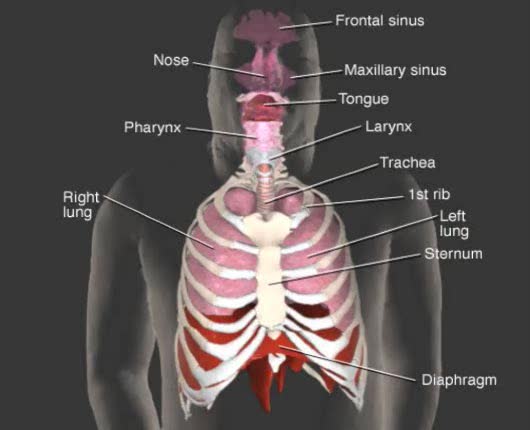
Respiratory system: nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi lungs Respiratory system’s primary function: Furnish oxygen (O2) for use by individual tissue cells and take away their gaseous waste product, carbon dioxide (CO2), through act of respiration. External respiration Lungs are vent...
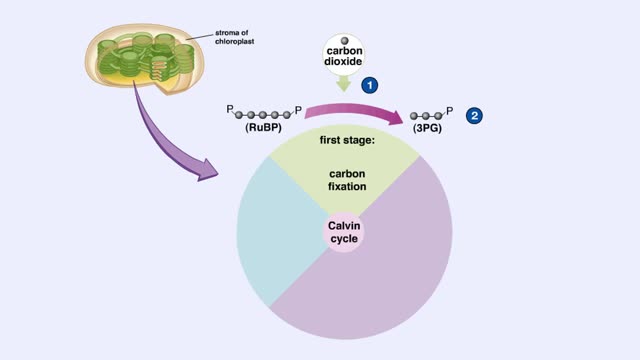
Calvin cycle (The light-independent reactions )
By: HWC, Views: 10746
The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the stroma of the chloroplast. Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through tiny pores or stomata and diffuses into the chloroplast. The first stage of the Calvin cycle is the attachment of a carbon dioxide molecule to a 5-carbon ribulose bi...
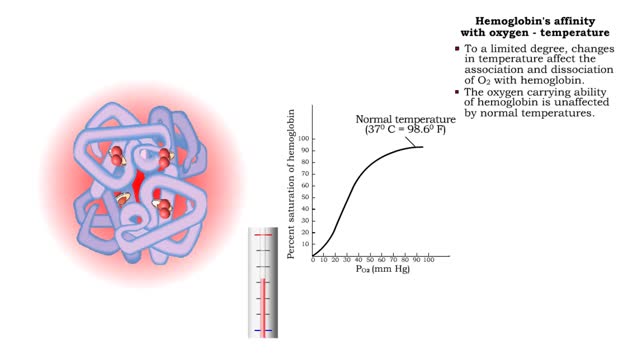
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 10925
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 9970
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
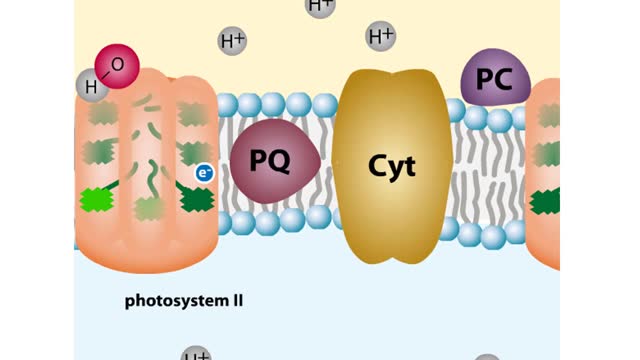
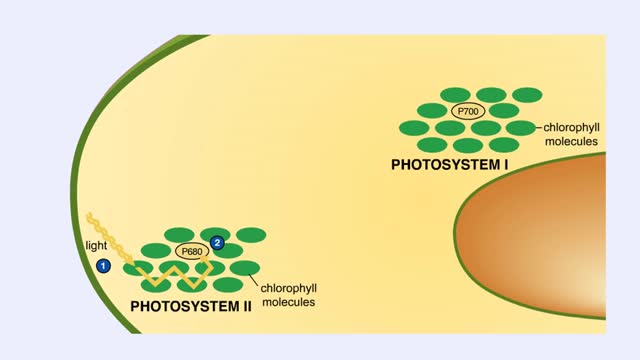
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10517
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
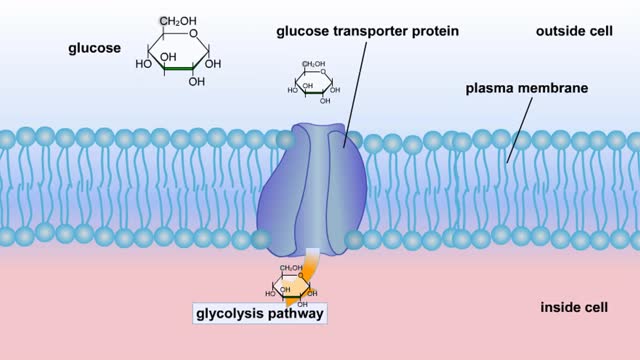
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 10712
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
Advertisement