Search Results
Results for: 'oxygen molecule'
Non-polar compounds - insolubility
By: HWC, Views: 11421
• A non-polar molecule has uniform distribution of electrons. • Non-polar compounds like fatty acids in lipids have a high proportion of carbon and hydrogen. • Lipids possess no charge or partial charge. • Lipids are not attracted to water molecules. • Lipids are not soluble in...
By: Administrator, Views: 14013
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
Brief Summary on Photosynthesis - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 10379
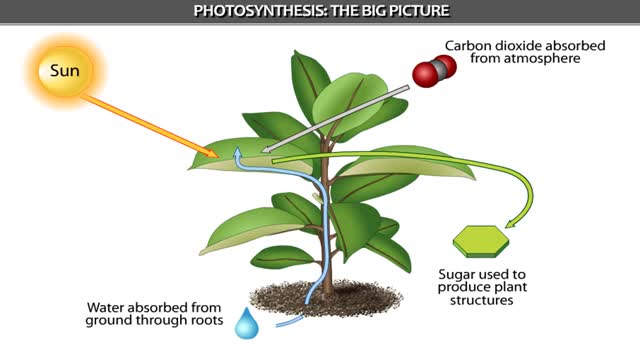
Can increase its weight by 150 pounds as it grows. Where does the new tissue come from? From the soil? From water? Or possibly from the air? The amazing truth is that new material. comes from an invisible gas in the air. In the process of photosynthesis, plants capture carbon dioxide ga...
Labor and Delivery - Infant Cord Apgar
By: Administrator, Views: 470
As soon as your baby is born, a delivery nurse will set one timer for one minute and another for five minutes. When each of these time periods is up, a nurse or physician will give your baby her first "tests," called Apgars. This scoring system (named after its creator, Virginia Apgar) helps t...
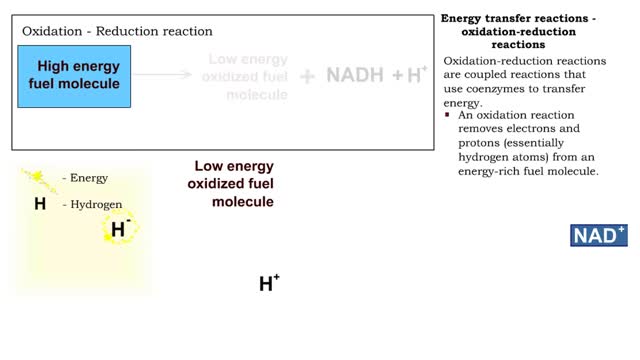
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 11951
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
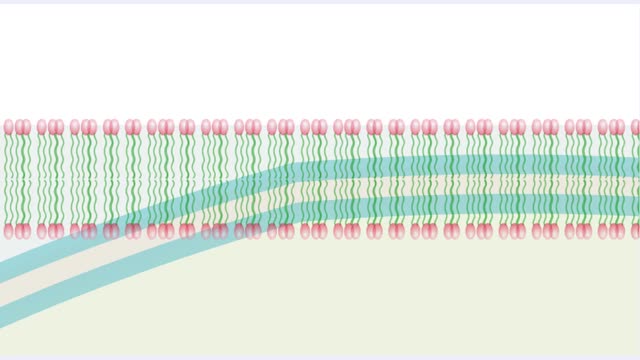
Molecules, Membrane Permeability and Structure
By: HWC, Views: 10810
Organisms are not isolated system at equilibrium and need to intake nutrients and electrolytes as remove wastes. Similarly Cells within an organism must also exchange compound by passing them through membrane. The permeability of a membrane is the rate of passive diffusion of molecules th...
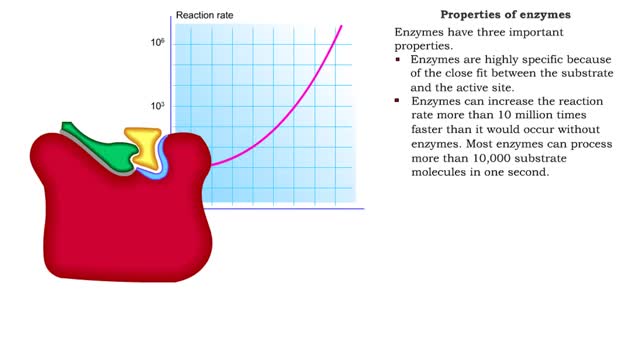
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11287
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
By: Administrator, Views: 14260
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
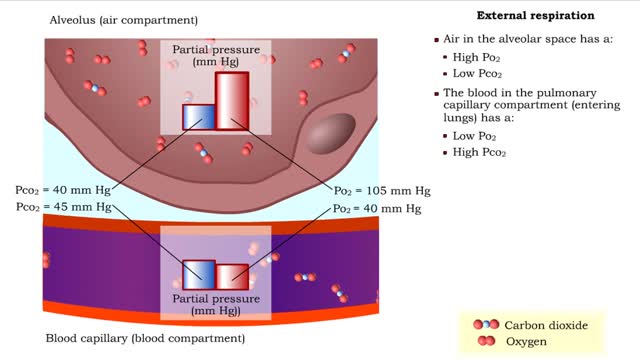
Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC, Views: 11503
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. ...
Advertisement