Search Results
Results for: 'urine%20formation'
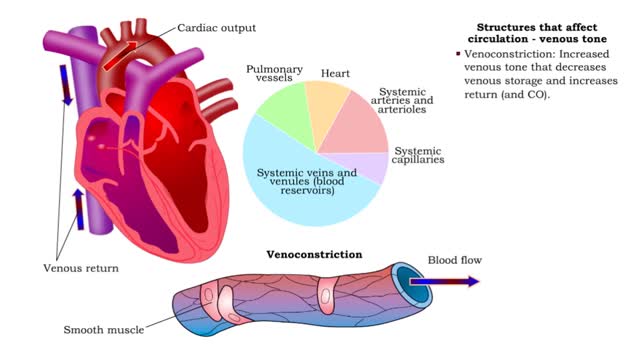
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 7215
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
By: Administrator, Views: 251
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with urination, discharge from the penis, or testicular pain. Infec...
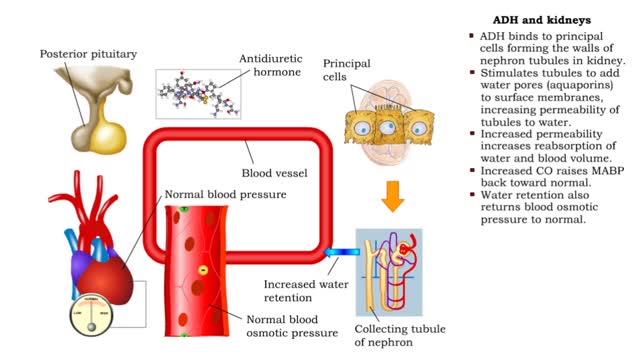
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 6781
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
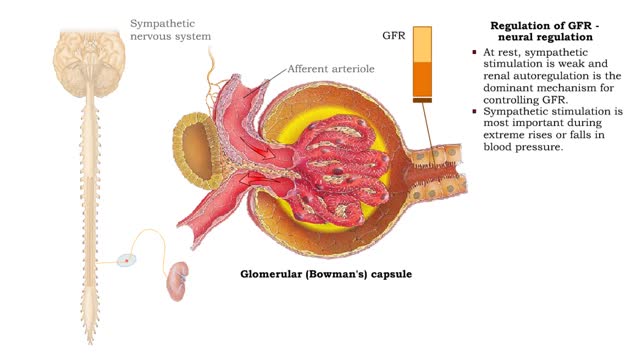
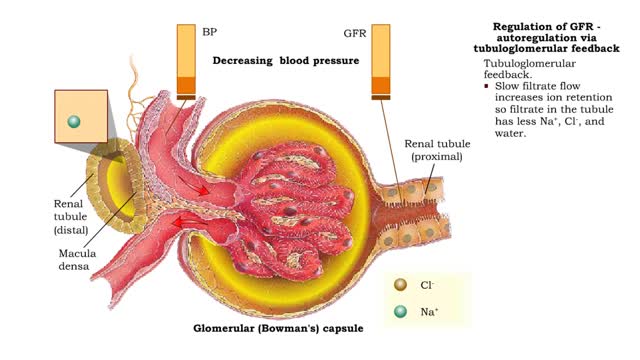
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 7808
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 8125
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
Advertisement