Search Results
Results for: 'SI'
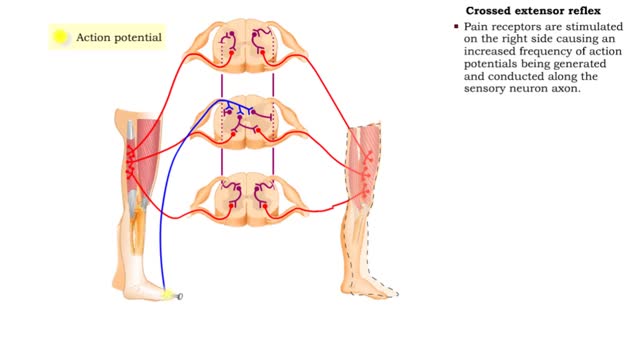
Flexor reflex & Crossed extensor reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10876
• The flexor reflex is a response to pain. This reflex is polysynaptic, ipsilateral, and intersegmental. • Pain receptors are stimulated causing increased frequency of action potentials to be generated and conducted along the sensory neuron axon. • The sensory impulses excite several ass...
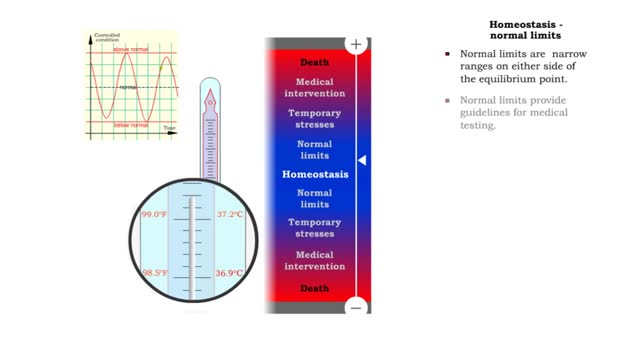
Homeostasis (range of body conditions, normal limits, mild stresses & severe stresses)
By: HWC, Views: 10792
Homeostasis: • Provides relative stability of the internal environment. • Results from constant adjustments. • Regulated by regulatory processes. • Requires system interplay. • Normal limits. • Temporary stresses. • Disruptions requiring medical intervention. • D...
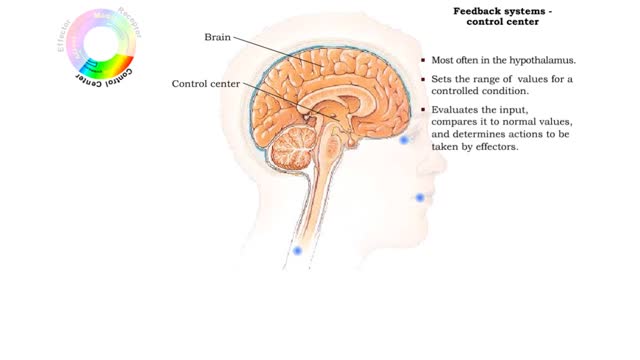
Component of feedback systems & Communication and regulation of body systems
By: HWC, Views: 11138
• Primary responsibility for communication and regulation in the body is shared by the nervous and endocrine systems. • The two systems work alone or together in specialized physiological processes called feedback systems to maintain homeostasis. • Feedback systems - or loops - are ...
By: HWC, Views: 10631
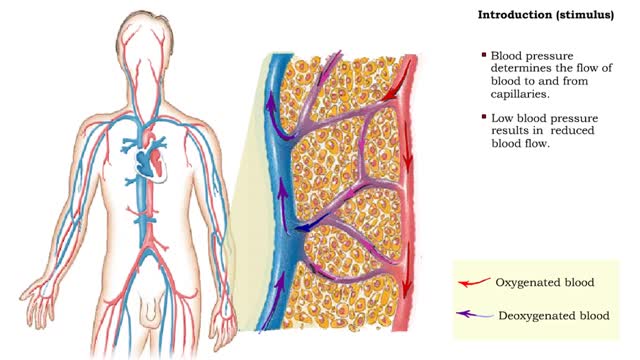
• Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. In humans, sensitivity is due to portions of the nervous system called receptors. Receptors are typicall...
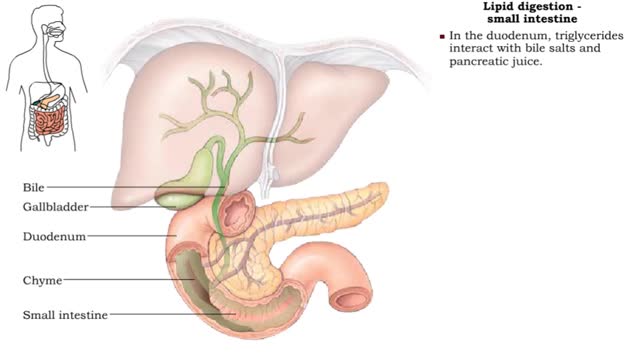
Lipid digestion - mouth, stomach and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11044
• Lipid digestion takes place primarily in the small intestine; some occurs in the mouth and stomach. • Lipases are enzymes that break down triglycerides and phospholipids. • Lingual and gastric lipases hydrolyze a small amount of triglycerides. • End products are fatty acids and...
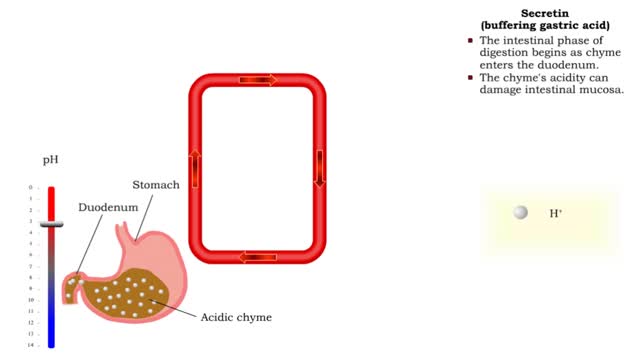
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 10507
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
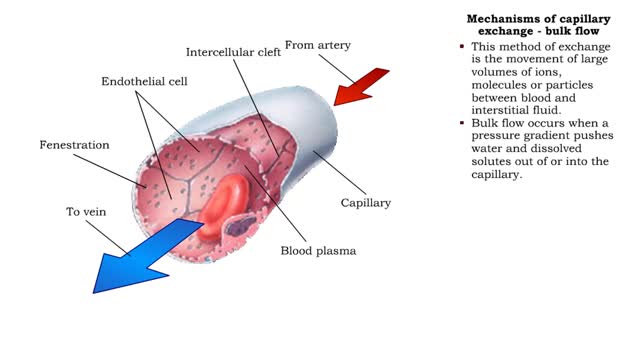
Mechanisms of capillary exchange (transcytosis & bulk flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10632
■ This method of capillary exchange is mainly used to transport small amounts of large, lipid-insoluble (water soluble) molecules, such as large proteins. ■ Substances, packaged in vesicles, move through endothelial cells via endocytosis and exocytosis. ■ This method of exchange is th...
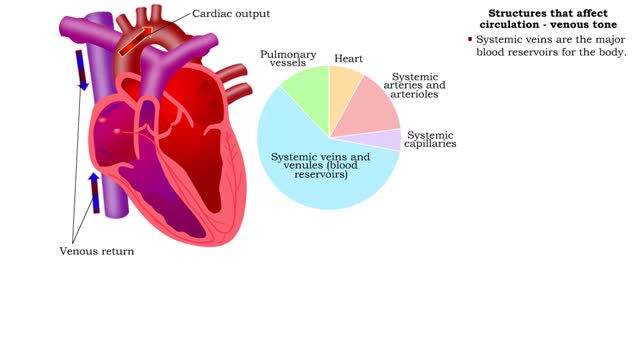
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys, blood volume and venous tone
By: HWC, Views: 10980
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
By: HWC, Views: 11074
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
Advertisement