Search Results
Results for: 'Is reverse osmosis water healthy'
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 9864
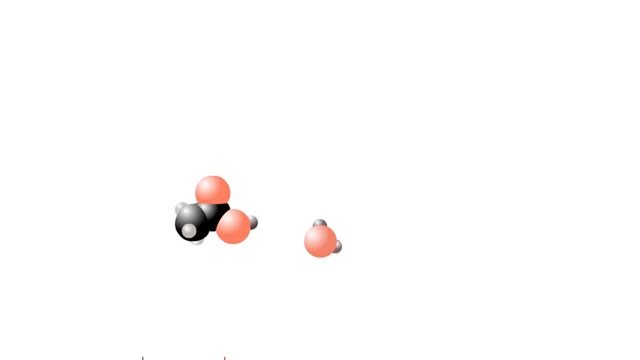
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
By: HWC, Views: 11185
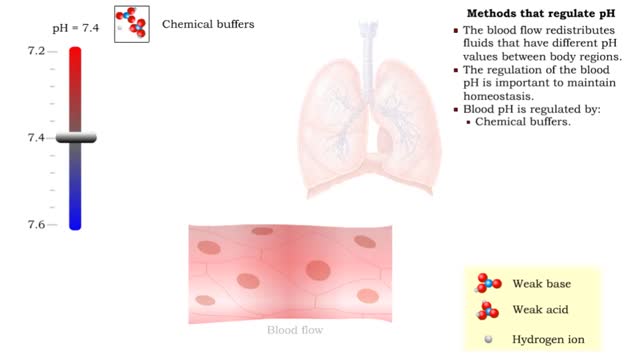
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
Brief Summary on Photosynthesis - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 10147
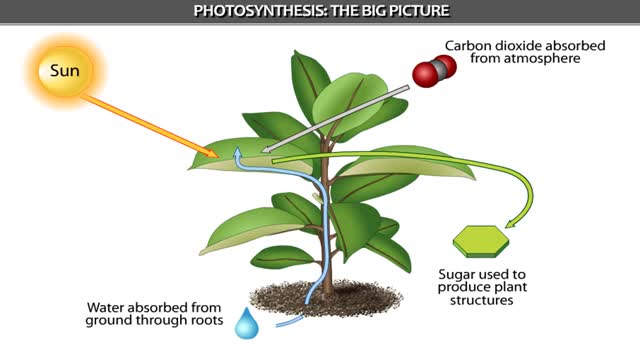
Can increase its weight by 150 pounds as it grows. Where does the new tissue come from? From the soil? From water? Or possibly from the air? The amazing truth is that new material. comes from an invisible gas in the air. In the process of photosynthesis, plants capture carbon dioxide ga...
By: HWC, Views: 11212
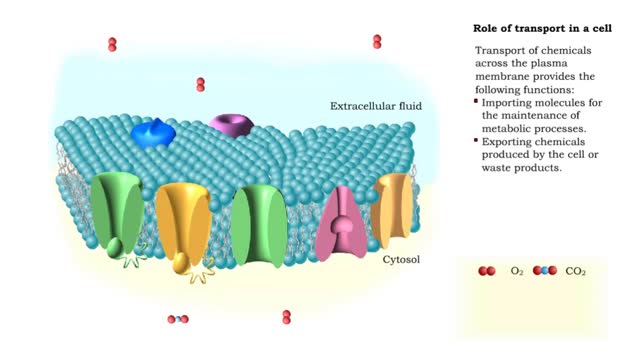
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
By: HWC, Views: 10576
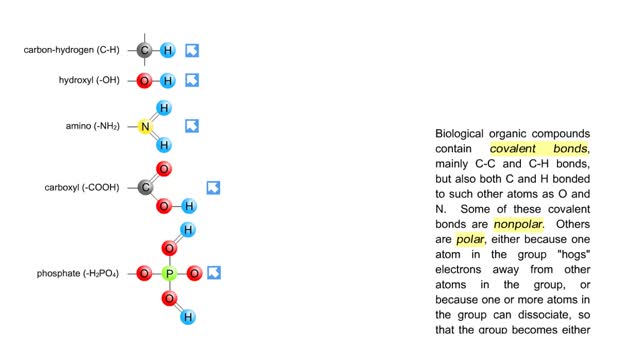
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11146
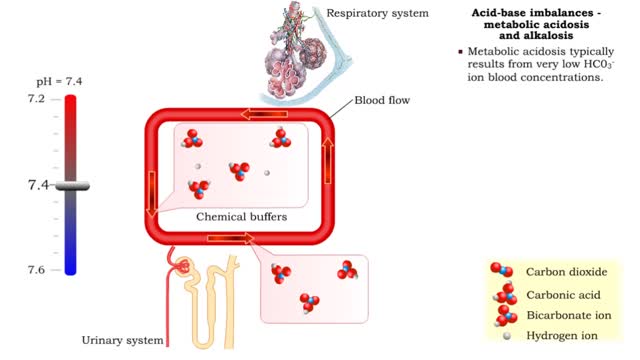
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10823
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
Mechanisms of capillary exchange (transcytosis & bulk flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10769
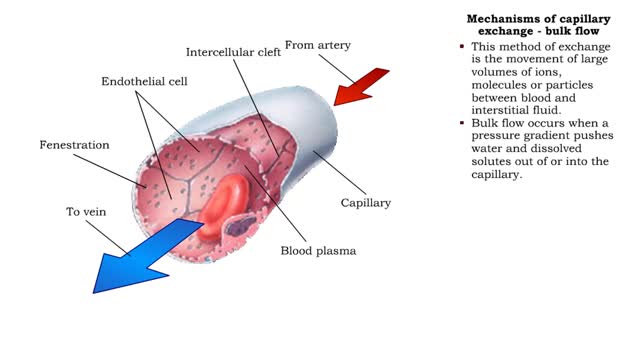
■ This method of capillary exchange is mainly used to transport small amounts of large, lipid-insoluble (water soluble) molecules, such as large proteins. ■ Substances, packaged in vesicles, move through endothelial cells via endocytosis and exocytosis. ■ This method of exchange is th...
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11404
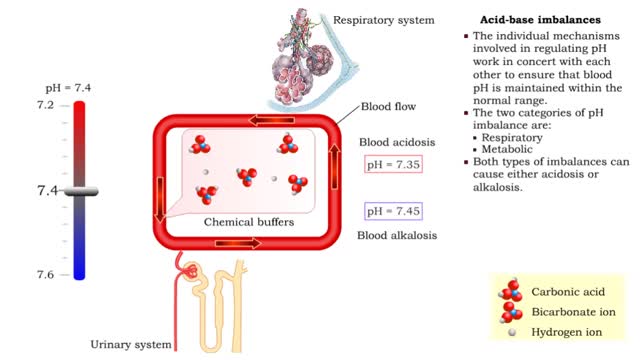
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
Advertisement