Search Results
Results for: 'metabolically active cells'
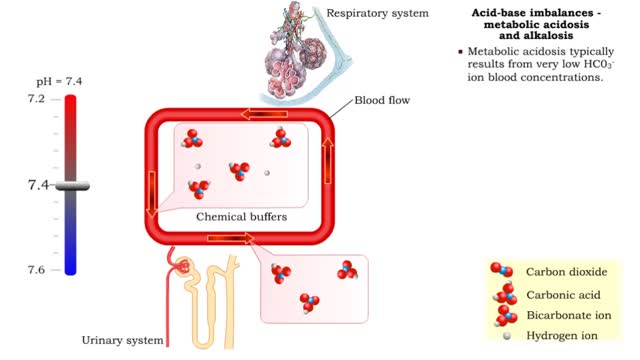
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11450
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
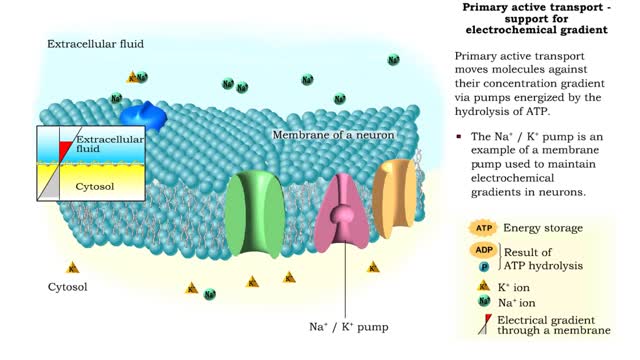
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11395
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
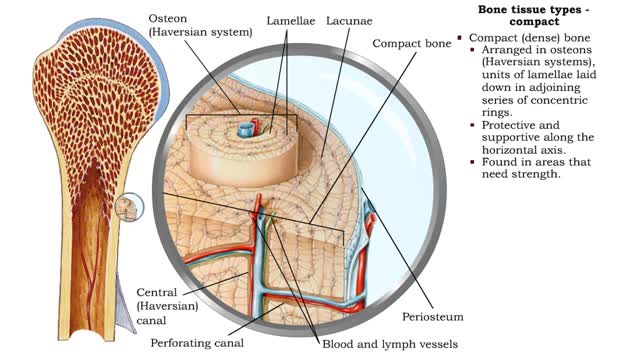
Bone tissue types - compact and spongy
By: HWC, Views: 11206
Bone tissue types • There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy. • All the bones of the skeleton have both kinds of bone tissue. • Compact (dense) bone • Arranged in osteons (Haversian systems), units of lamellae laid down in adjoining series of concentric rings. • P...
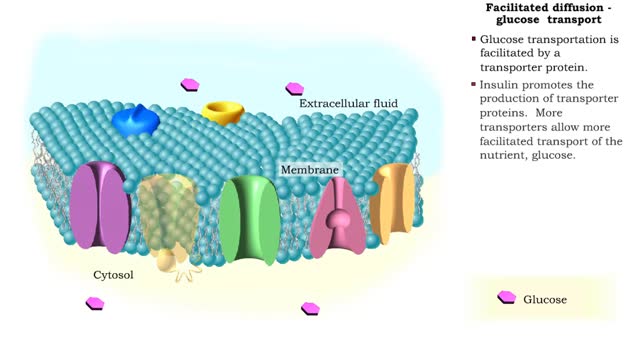
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11432
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
By: HWC, Views: 12005
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
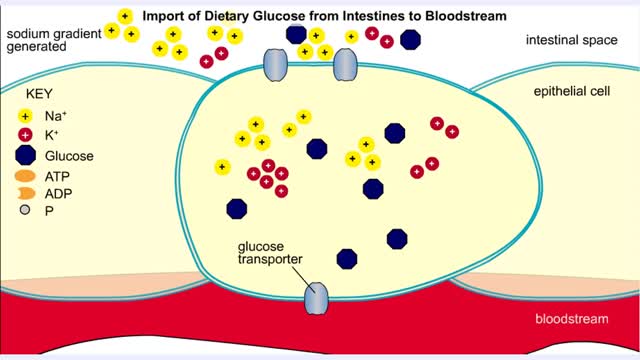
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 10628
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
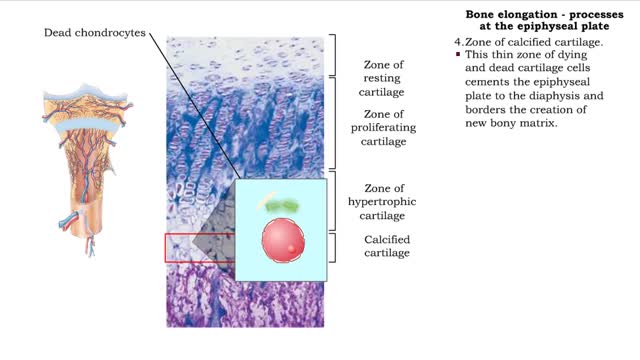
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 11364
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
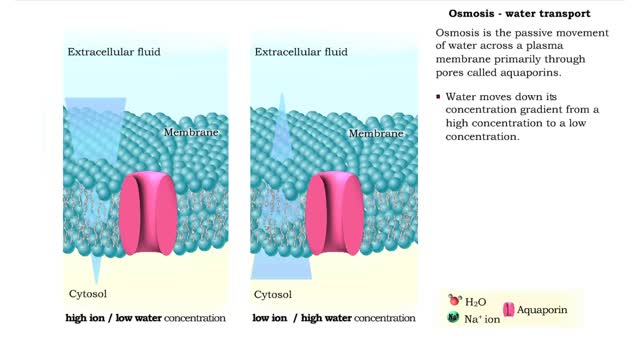
By: HWC, Views: 11366
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
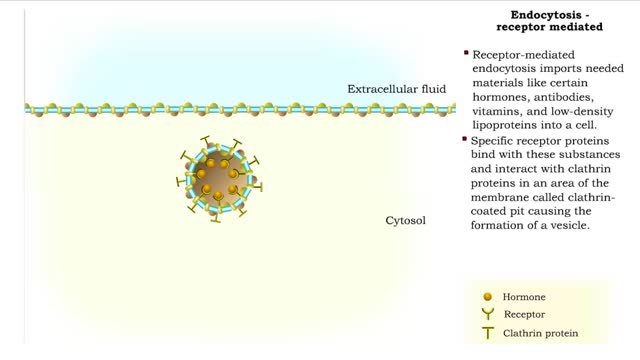
Endocytosis - pinocytosis, receptor mediated and Transcytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11109
Pinocytosis is the process in which a cell "drinks" a tiny droplet Of extracellular fluid, including its solutes. Pinocytosis (Cell Drinking) is the process by which the cell takes in fluids (as well as any small molecules dissolved in those fluids). • The plasma membrane folds inward to...
Advertisement