Search Results
Results for: 'metabolically active cells'
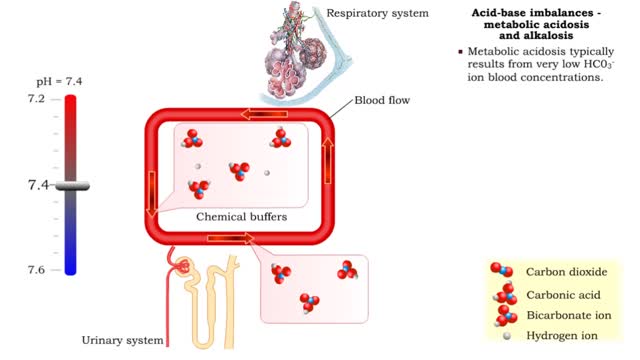
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11296
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 10841
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
By: HWC, Views: 11033
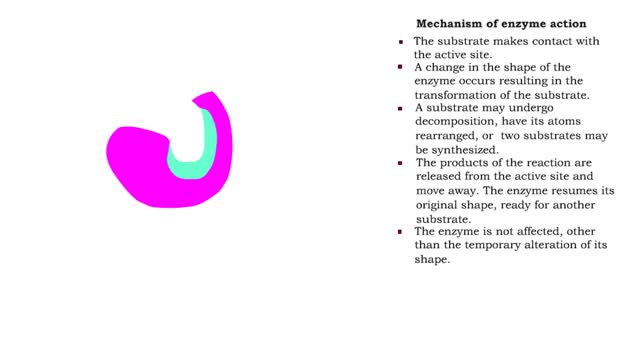
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
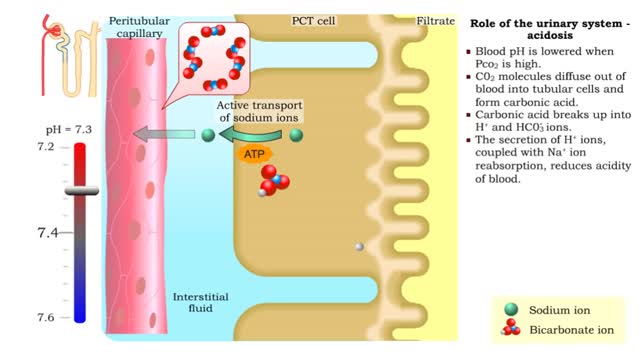
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11346
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
By: HWC, Views: 11205
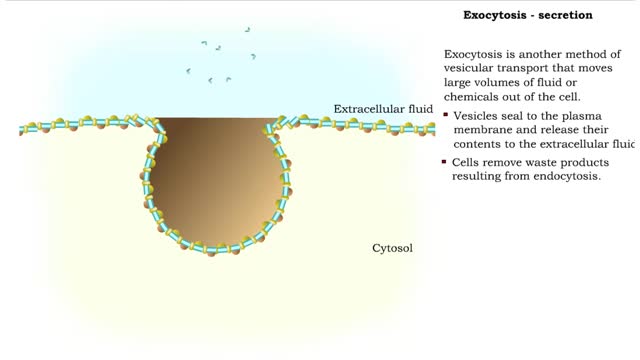
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11550
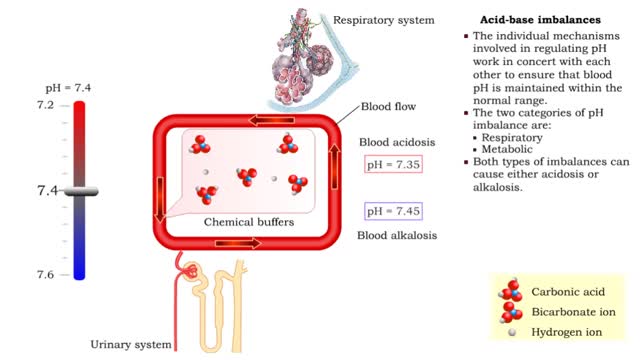
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11283
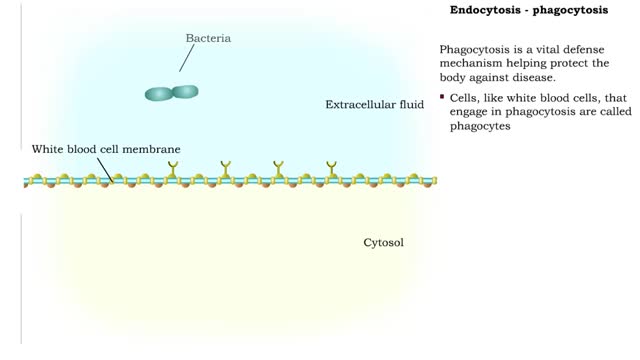
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secret...
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11308
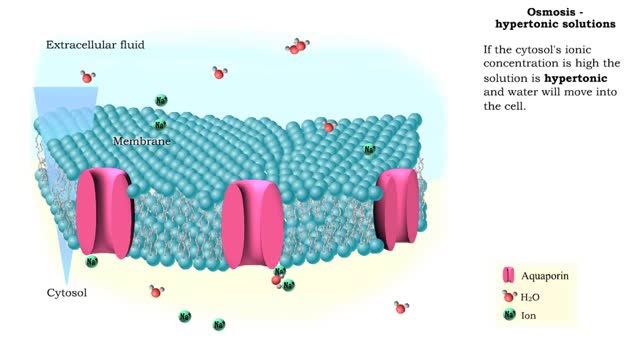
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
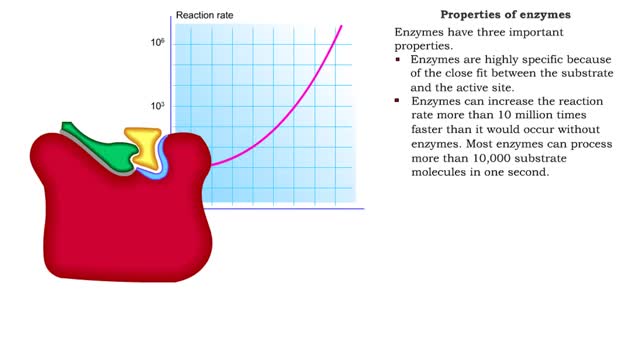
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11161
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
Advertisement