Search Results
Results for: 'Cardiac output'
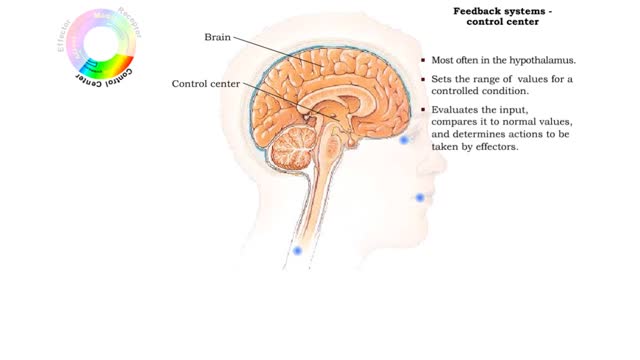
Component of feedback systems & Communication and regulation of body systems
By: HWC, Views: 11835
• Primary responsibility for communication and regulation in the body is shared by the nervous and endocrine systems. • The two systems work alone or together in specialized physiological processes called feedback systems to maintain homeostasis. • Feedback systems - or loops - are ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14468
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. Sinoat...
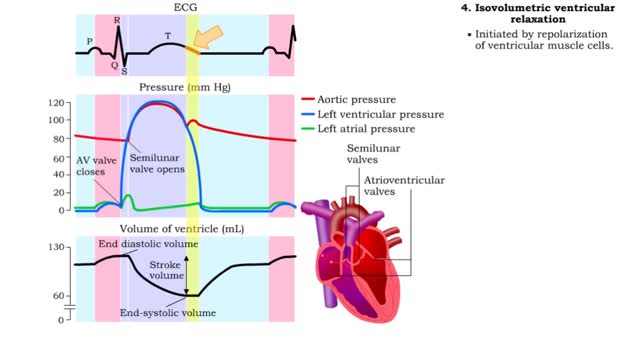
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 11578
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
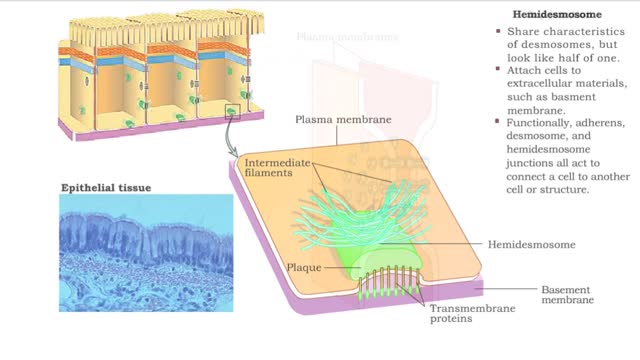
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 12012
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
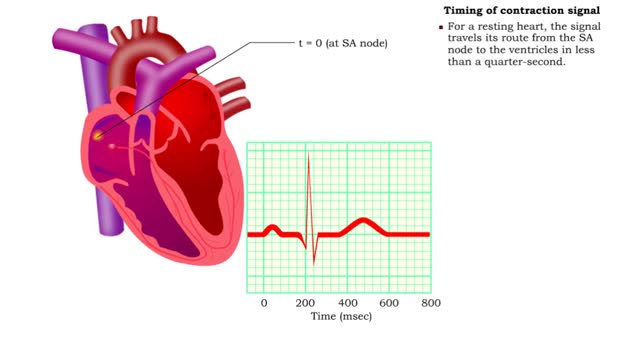
Coaductile pathway, Timing of contraction signal & Conduction system and ECG
By: HWC, Views: 11856
• When the system is healthy, the signal to contract the entire conduction system originates in the SA node - known as the heart's pacemaker. • The SA node triggers contraction because it depolarizes at a faster rate than other parts of the conduction system. • The wave of excitation fr...
Brain Anatomy Animation (Part 2 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 16042
Its nervous tissue consists of millions of nerve cells and fibers. It is the largest mass of nervous tissue in the body. The brain is enclosed by three membranes known collectively as the meninges: dura mater arachnoid pia mater The major structures are the: cerebrum cerebellum dienc...
Advertisement