Search Results
Results for: 'glucose-6-phosphate'
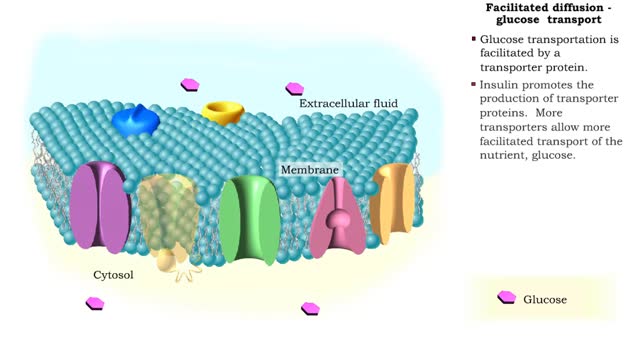
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 10917
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
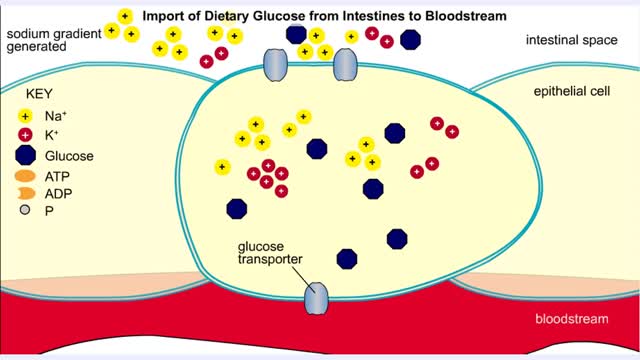
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 10075
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
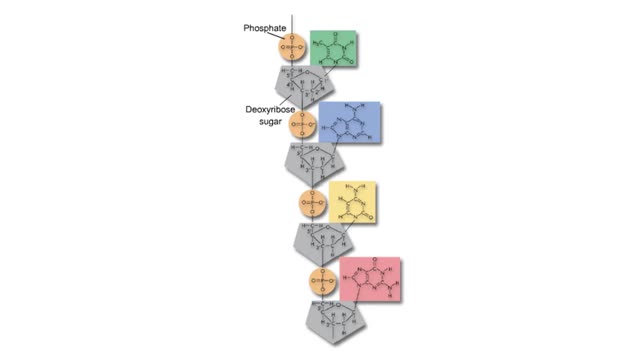
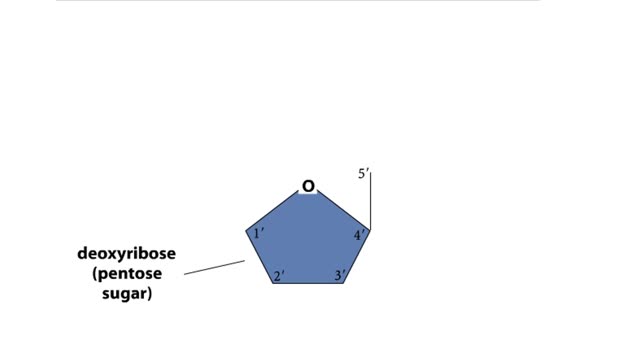
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Nucleic acids
By: HWC, Views: 10606
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids (polymers of nucleotides). Two polymers with complementary nucleotide sequences can pair with each other. This pairing endows nucleic acids with the ability to store, transmit, and retrieve genetic information. Two strands of DNA pair by hydrogen bonding. A compon...
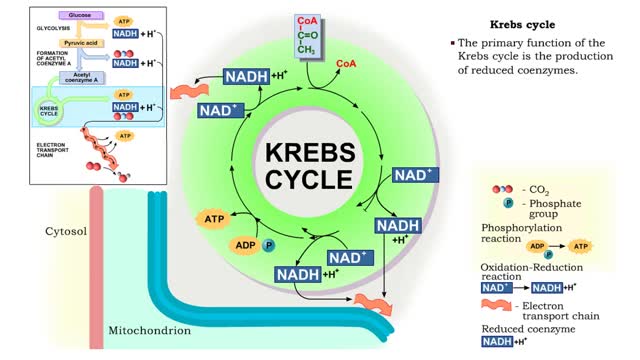
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 10857
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
By: Administrator, Views: 15290
Hyperglycemia means high (hyper) glucose (gly) in the blood (emia). Your body needs glucose to properly function. Your cells rely on glucose for energy. Hyperglycemia is a defining characteristic of diabetes—when the blood glucose level is too high because the body isn't properly using or doesn...
By: HWC, Views: 10155
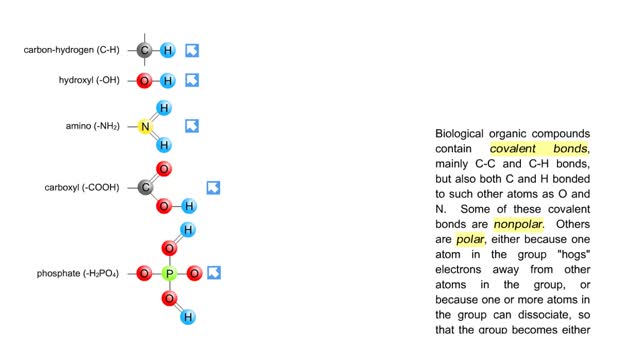
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
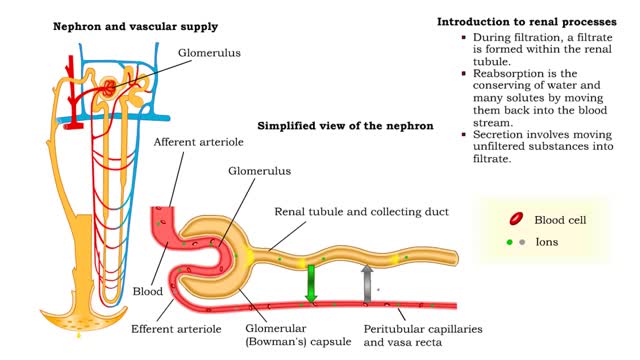
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Introduction to renal processes and filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 10827
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
By: Administrator, Views: 14770
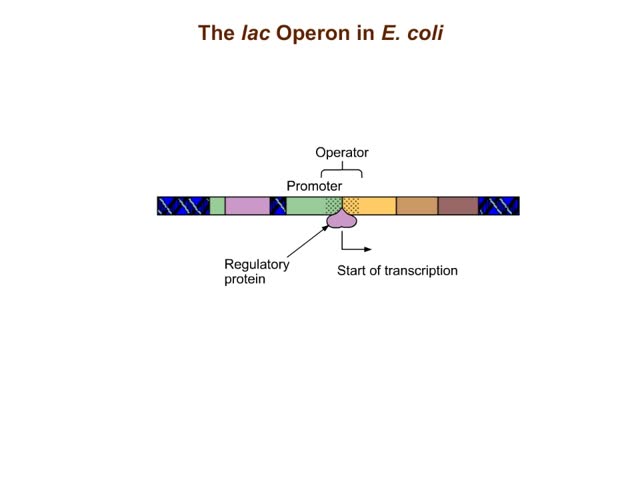
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Advertisement