Search Results
Results for: 'Factors that increase metabolic rate and heat production'
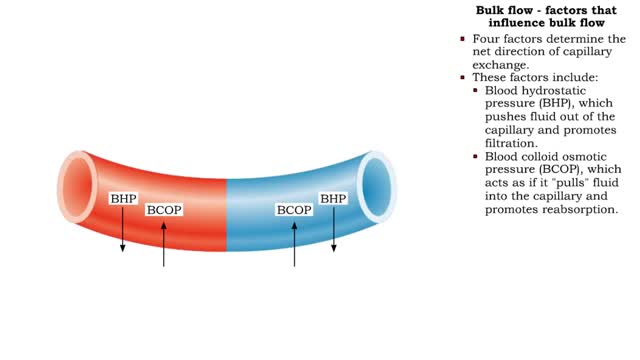
Bulk flow - factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 10878
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. • Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. • Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. • These factors in...
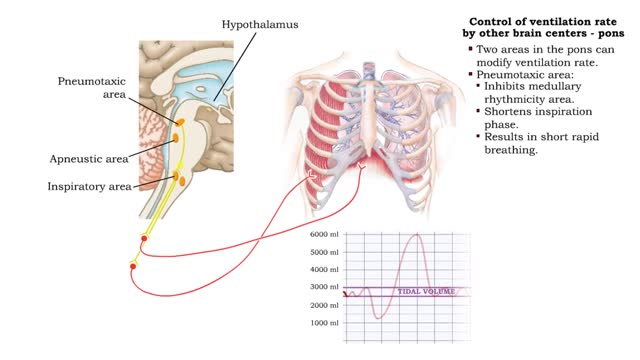
Control of ventilation rate by other brain centers (posts, hypothalamus & cerebral cortex)
By: HWC, Views: 11238
Forced ventilation: • The inspiratory area stimulates accessory inspiratory muscles. • Inspiration is more forceful. • Inspiratory area activates expiratory area, which sends impulses to the expiratory muscles (internal intercostals and abdominal muscles). • Expiration muscles c...
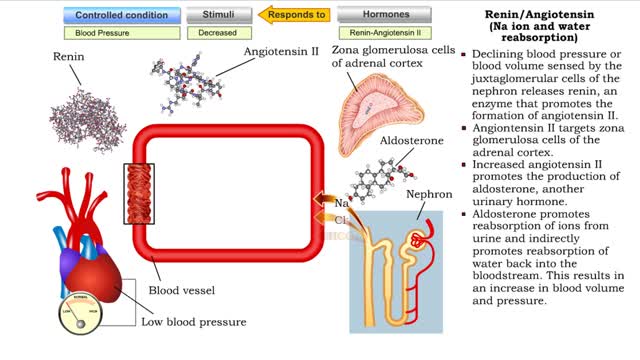
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 11279
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
By: HWC, Views: 11014
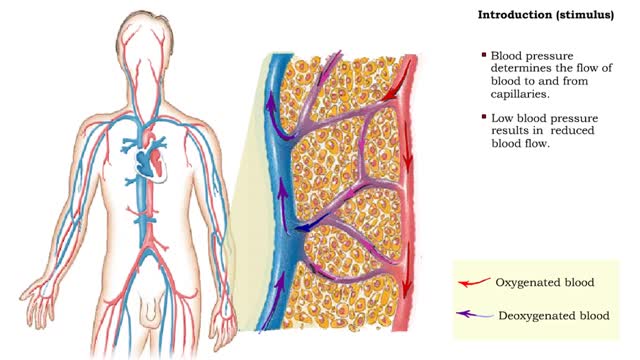
• Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. In humans, sensitivity is due to portions of the nervous system called receptors. Receptors are typicall...
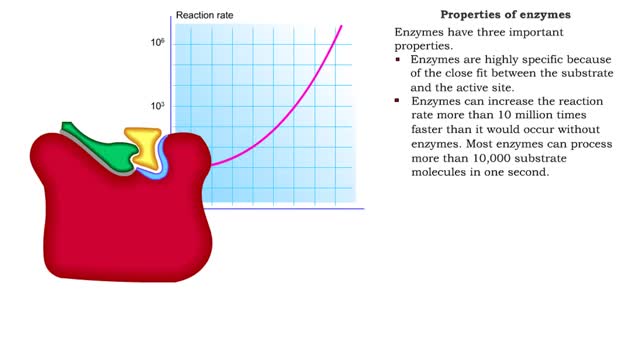
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11287
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
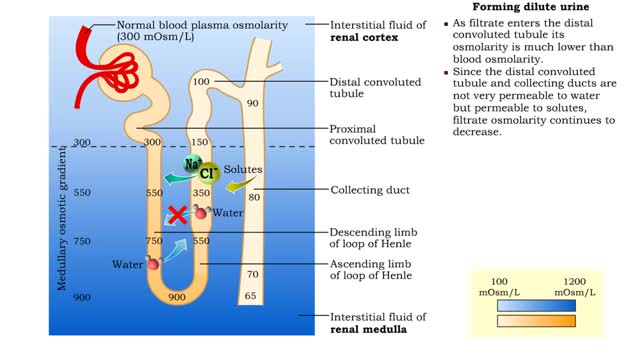
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 11804
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
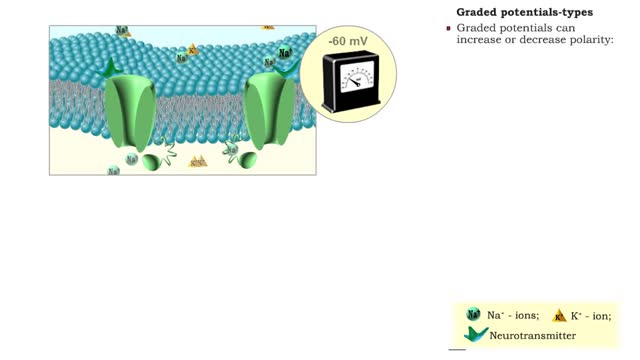
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 11541
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
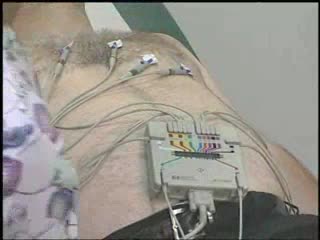
By: Administrator, Views: 14142
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. Sinoat...
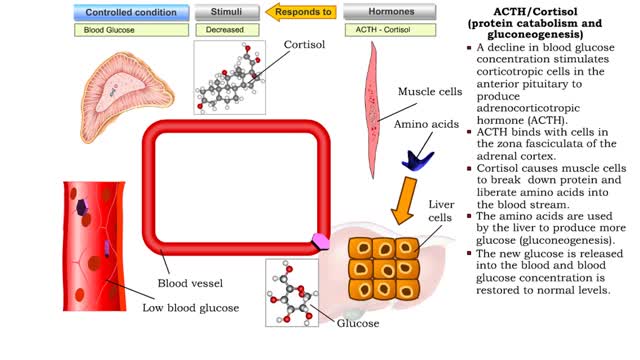
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11224
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
Advertisement