Search Results
Results for: 'Nervous control of heart rate'
By: Administrator, Views: 13698
Pericarditis refers to inflammation of the pericardium, two thin layers of a sac-like tissue that surround the heart, hold it in place and help it work. A small amount of fluid keeps the layers separate so that there's no friction between them.
By: Administrator, Views: 458
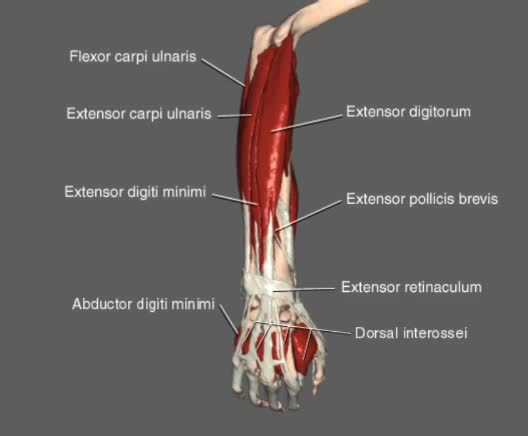
Muscles of both the upper arm and forearm control movement of the forearm. The biceps brachii flex the forearm and work with the supinator of the forearm to rotate it so the palm faces upward. The pronator teres and quadratus control pronation, or rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces do...
By: Administrator, Views: 14037
Diastole and systole are two phases of the cardiac cycle. They occur as the heart beats, pumping blood through a system of blood vessels that carry blood to every part of the body. Systole occurs when the heart contracts to pump blood out, and diastole occurs when the heart relaxes after contract...
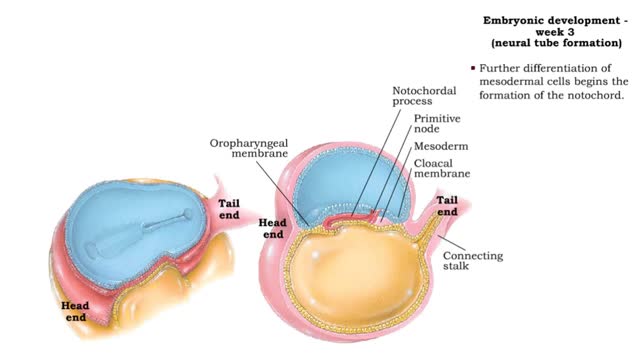
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 10957
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
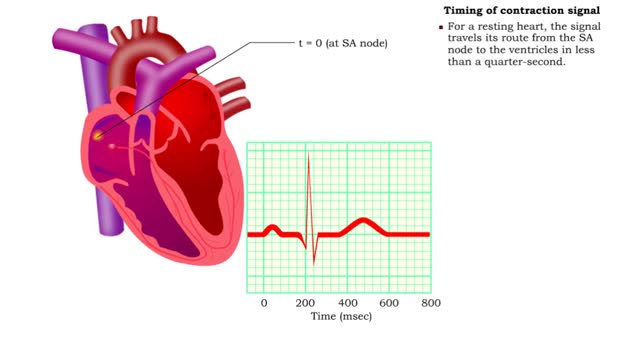
Coaductile pathway, Timing of contraction signal & Conduction system and ECG
By: HWC, Views: 11100
• When the system is healthy, the signal to contract the entire conduction system originates in the SA node - known as the heart's pacemaker. • The SA node triggers contraction because it depolarizes at a faster rate than other parts of the conduction system. • The wave of excitation fr...
By: Administrator, Views: 14318
Angina is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina, which may also be called angina pectoris, is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in your chest.
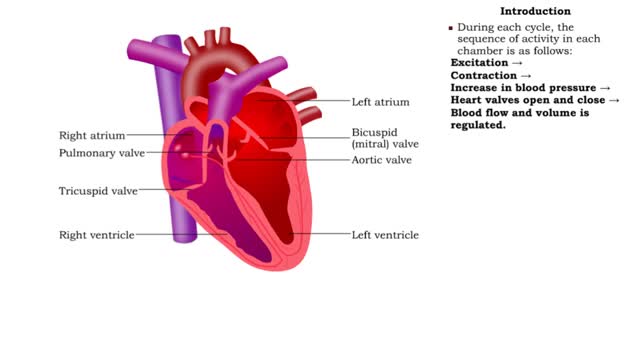
Electrical changes in the heart
By: HWC, Views: 10682
• ECG: Graph of the voltage changes that occur during the cardiac cycle. • Readings are taken by electrodes placed on the surface of the body. • Electrodes detect voltage changes caused by the electrical activity of the heart. • P wave = atrial excitation (atrial depolarization). ...
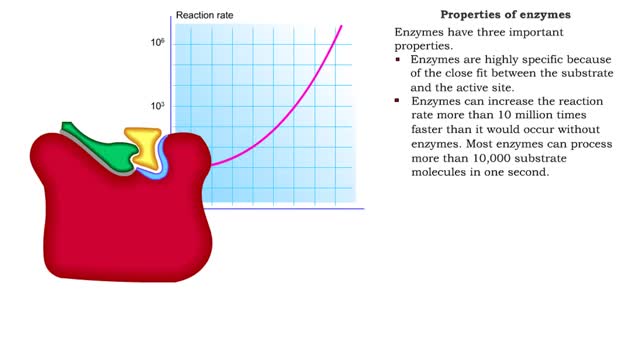
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 10842
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
Automated external defibrillator (AED)
By: Administrator, Views: 14011
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a portable electronic device that automatically diagnoses the life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias of ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia, and is able to treat them through defibrillation, the application of electricity which...
Advertisement