Search Results
Results for: 'hydrogen bond'
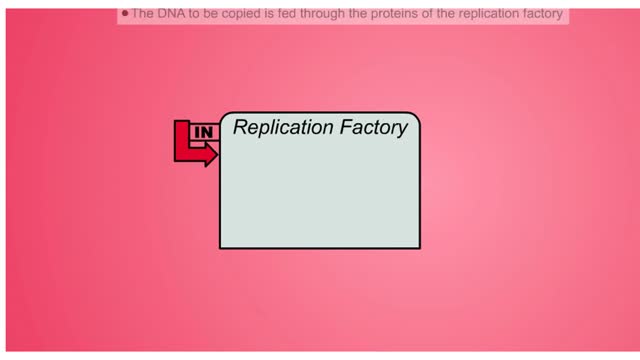
DNA Replication Factory and Protein
By: HWC, Views: 10599
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) carries all the genetic information needed to re-create itself and to pass on the characteristics of the organism. The “factory” model of DNA replication hypothesizes a specific nuclear structure in which the molecular machinery for replication forks are brou...
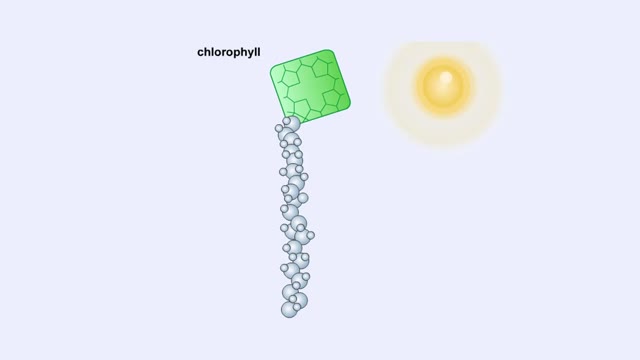
Electromagnetic Spectrum, Chlorophyll and Pigment & Light
By: HWC, Views: 10781
The sun gives off radiation that is called the electromagnetic spectrum. This is energy that travels as wavelengths and includes radio waves, X-rays and ultraviolet light. A portion of this radiation is known as visible light, and is the type of radiation that plants use to manufacture sugars. ...
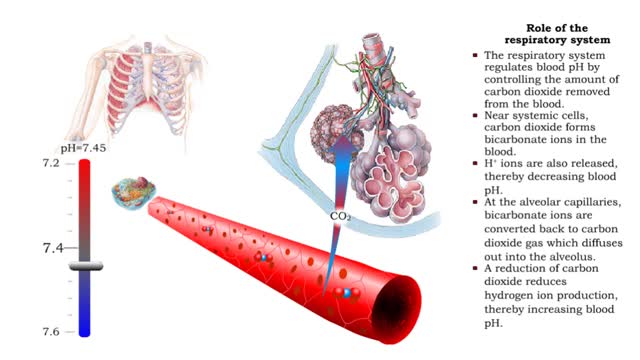
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 11582
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
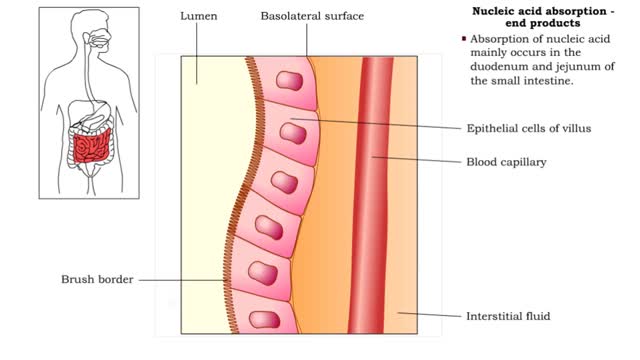
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10815
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
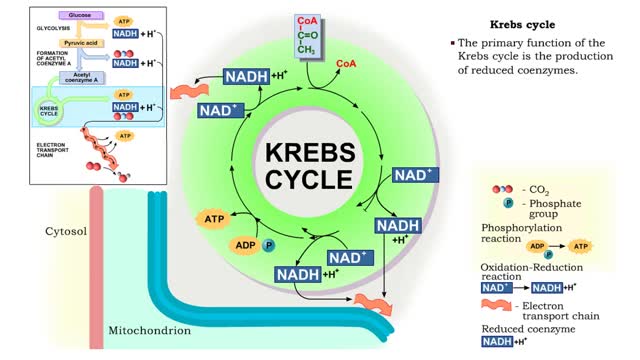
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11198
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
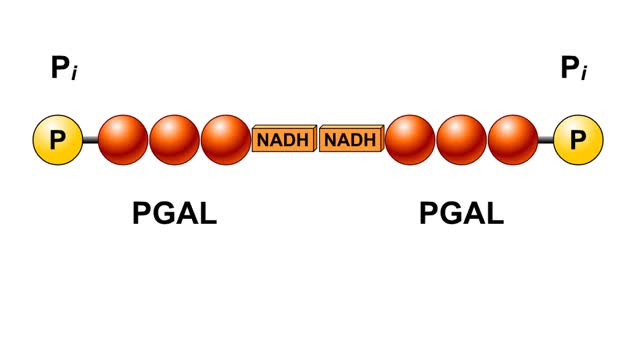
By: HWC, Views: 5005
In glycolysis, a six-carbon glucose molecule is split into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules. In this animation, each carbon molecule is represented by a red ball. The end products of glycolysis are two molecules of pyruvate. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of ...
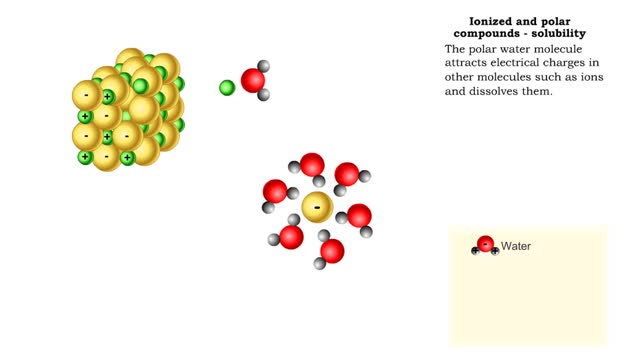
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11123
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
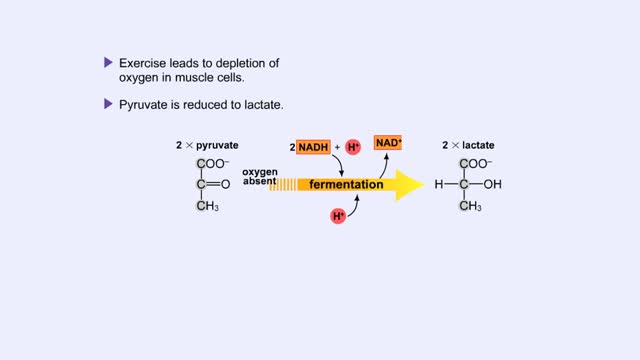
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 10471
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10752
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
Advertisement