Search Results
Results for: 'partial pressure'
By: Administrator, Views: 14643
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
By: Administrator, Views: 14832
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet c...
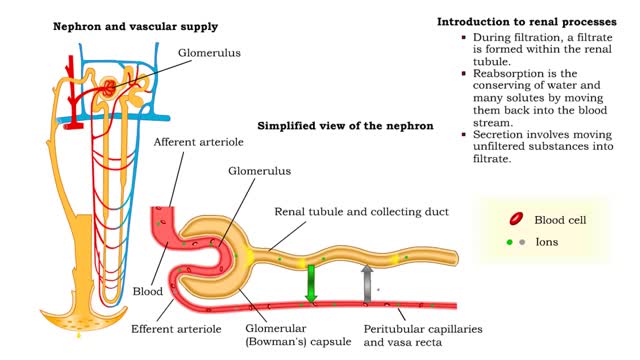
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Introduction to renal processes and filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 11893
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
By: HWC, Views: 11320
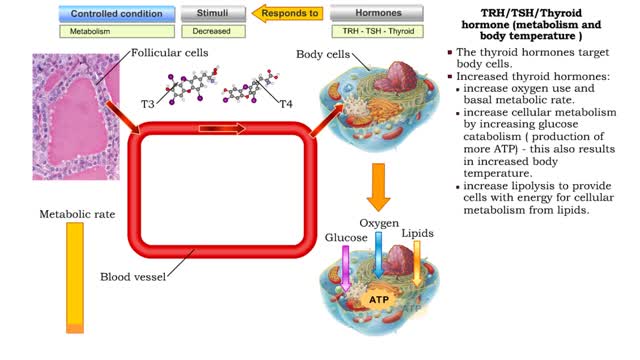
Thyroid hormone production • A decline in metabolic rate caused by increased metabolic need or physical exertion stimulates the production of thyrotropin hormone releasing (TRH) hormone from the cells of the hypothalamus. • Thyrotropin hormone releasing hormone targets the thyrotrophic ce...
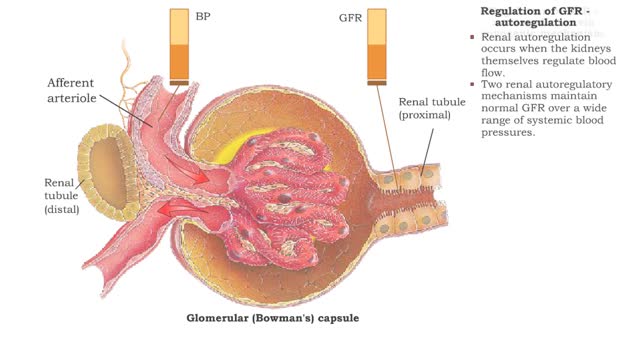
Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12189
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Ren...
By: HWC, Views: 11884
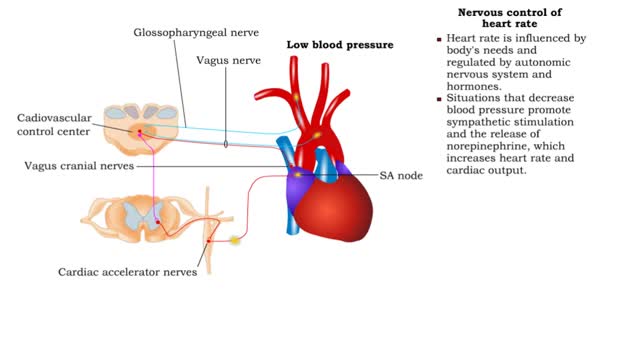
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous ...
By: Administrator, Views: 15140
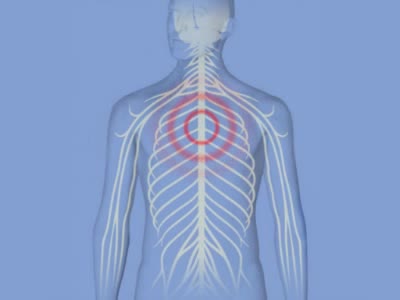
Angina is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina, which may also be called angina pectoris, is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in your chest.
By: Administrator, Views: 14838
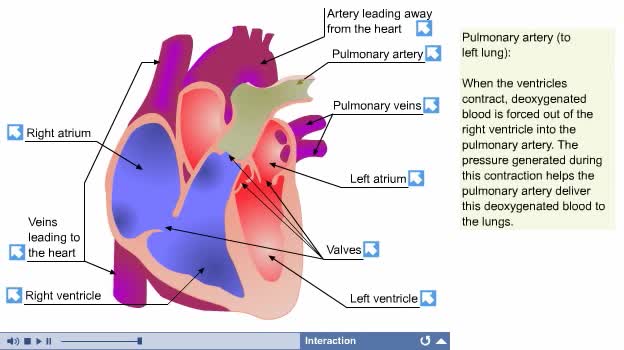
Circulation of blood through the chambers of the heart Septum divides heart into the right and left heart. Each side contains an upper and lower chamber: Atria, or upper chambers, receive blood. Ventricles, or lower chambers, pump blood. Valves control intake and outflow of blood in chamber...
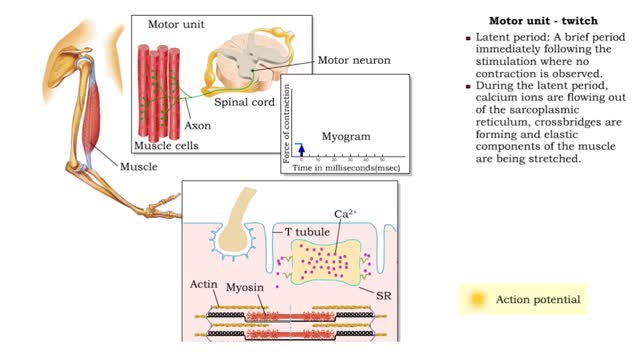
Muscle Twitch and Muscle Tension - Motor unit size and force
By: HWC, Views: 11991
• A motor unit is a group of muscle cells controlled by a single neuron. • A stimulus of sufficient intensity will cause all the cells in the motor unit to contract. • A single contraction, caused by a single action potential, is called a muscle twitch. • Latent period: A brief per...
Advertisement