Search Results
Results for: 'Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions'
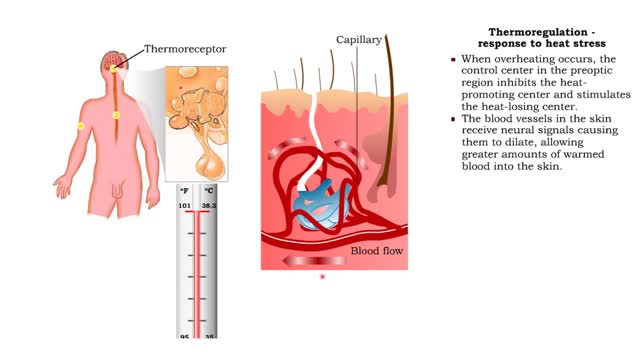
Metabolic Rate, Heat and Thermoregulation - response to heat and cold stresses
By: HWC, Views: 11945
• A neuron group in the anterior portion of the hypothalamus controls heat balance. • Neurons in the preoptic region of the hypothalamus integrate signals that come from thermoreceptors. • The temperature control center in the preoptic region propagates control signals to two other part...
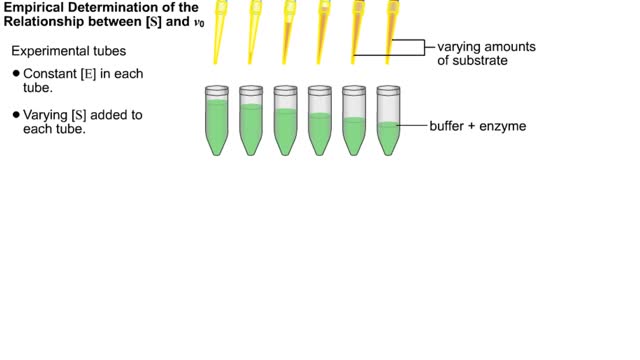
Kinetic parameters & Kinetic experiment
By: HWC, Views: 11562
Kinetics is a measure of the speed or rate of a chemical reaction. A study of kinetics allows us to determine which variables to control (temperature, reactants, catalysts) and how to vary them in order to maximize the amount of products formed and minimize the time involved. Vmax = maximum ve...
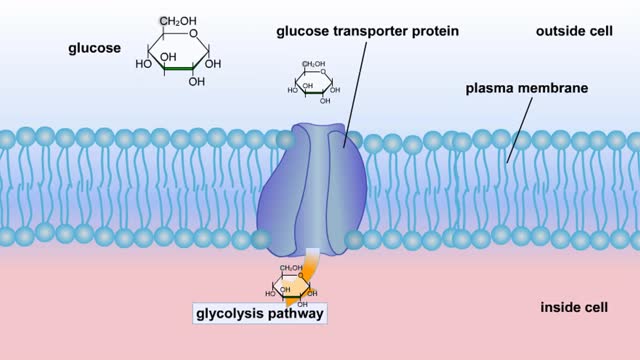
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11444
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
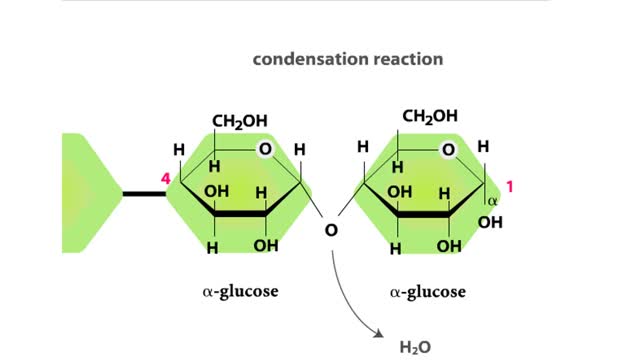
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 11262
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
By: HWC, Views: 5730
In glycolysis, a six-carbon glucose molecule is split into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules. In this animation, each carbon molecule is represented by a red ball. The end products of glycolysis are two molecules of pyruvate. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of ...
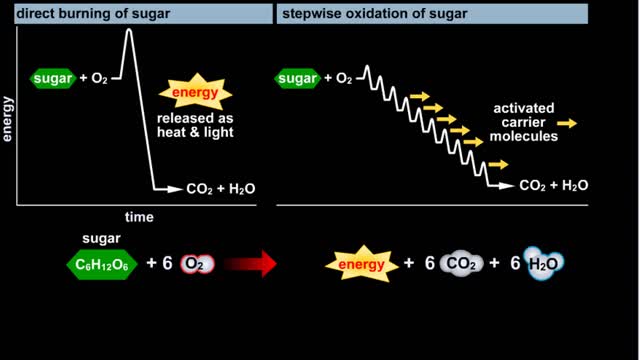
Glycolysis - Introduction to ATP and the burning of sugar
By: HWC, Views: 11960
Do you use sugar with your coffee or tea? Or do you occasionally drink a sport or soft drink? As millions of people do each day, they obtain energy from the sugar added or contained in these drinks. How can we understand this concept of energy within a sugar molecule? Let's take a tablespoon ...
Transferring genes into plants Animation
By: HWC, Views: 9175
Researchers extract DNA from an organism that has a trait they want to introduce into a plant. The genetic donor can be a bacterial cell, a plant cell. or even an animal cell. The desired gene will be transferred into a plasmid, a small circle of bacterial DNA. The gene is cut out of th...
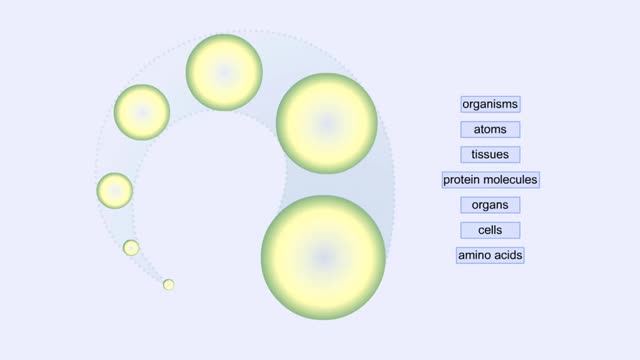
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 11278
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
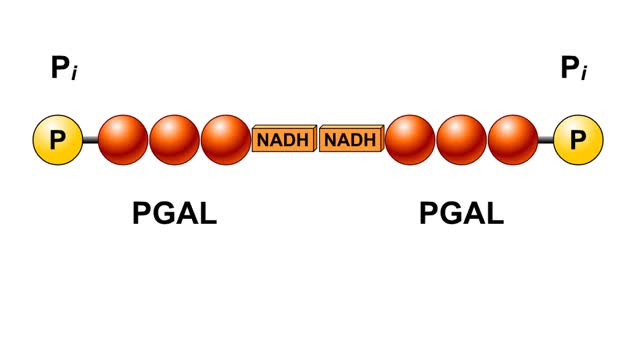
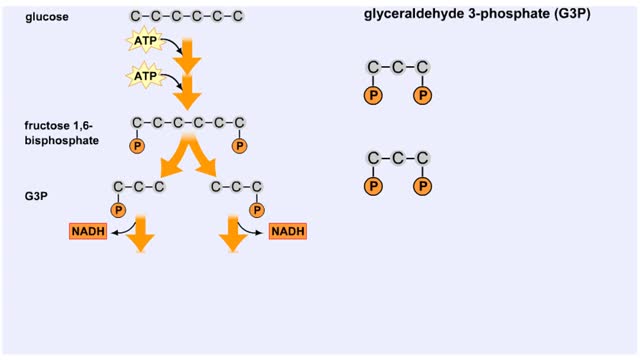
Splitting of Sugar, Oxidation/ Reduction & ATP Generation
By: HWC, Views: 11422
The next reaction shows us the meaning of "glycolysis" or the splitting of glucose. The fructose bisphosphate molecule is split into two molecules each containing 3 carbons as the backbone. FBP is split into two 3-carbon molecules called G3P, or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Notice that the phos...
Advertisement