Search Results
Results for: 'inhibiting gastric acid secretion'
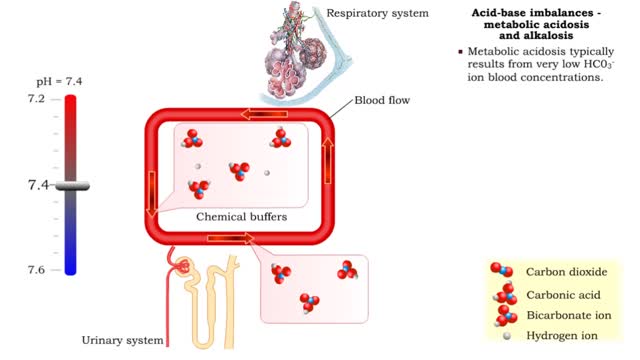
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11460
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
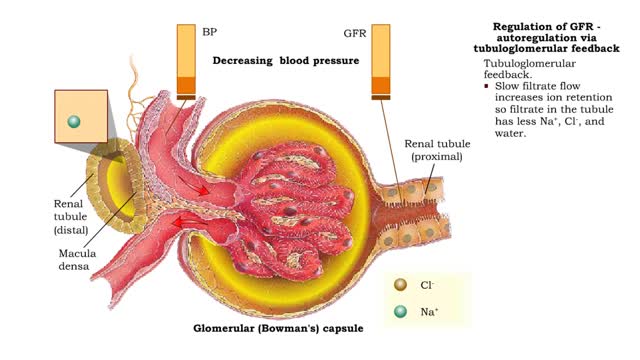
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12908
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
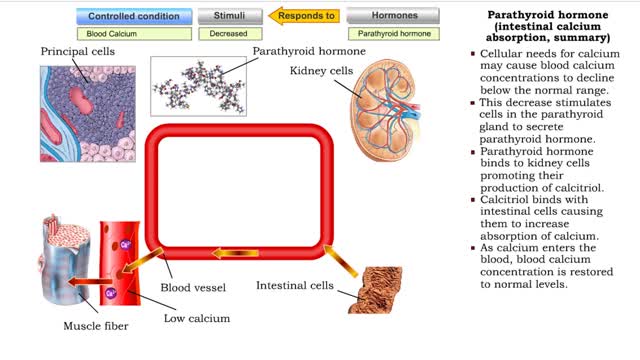
Parathyroid hormone (bone resorption) & Calcitonin (bone deposition)
By: HWC, Views: 11224
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range. • This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone. • Binding of parathyroid hormone to osteoclasts in bone tissue promotes bone resorption and th...
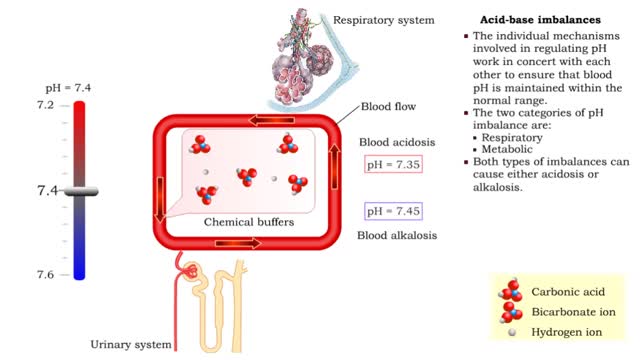
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11685
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
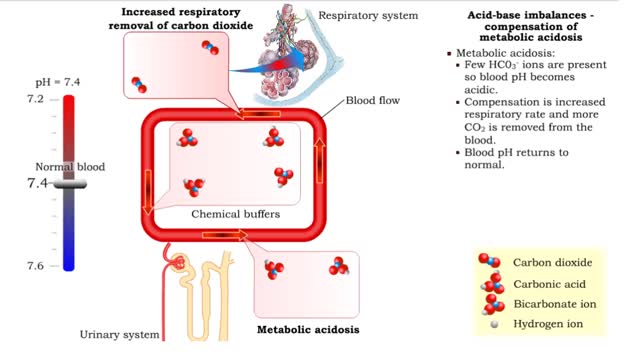
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11509
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
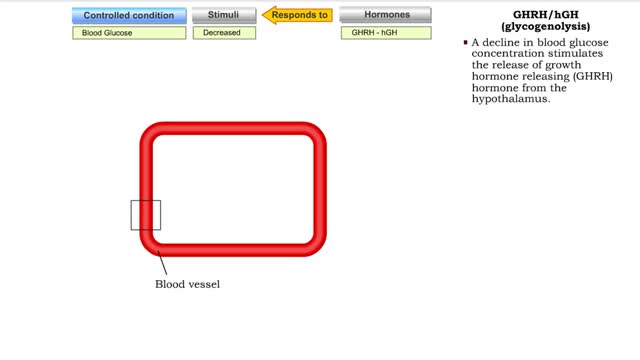
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11119
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
By: HWC, Views: 7891
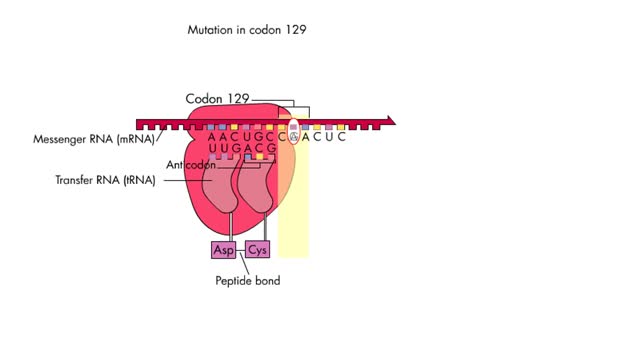
A mutation, which may arise during replication and/or recombination, is a permanent change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. Damaged DNA can be mutated either by substitution, deletion or insertion of base pairs. Mutations, for the most part, are harmless except when they lead to cell death or t...
Protein Secondary and Tertiary Structures - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7546
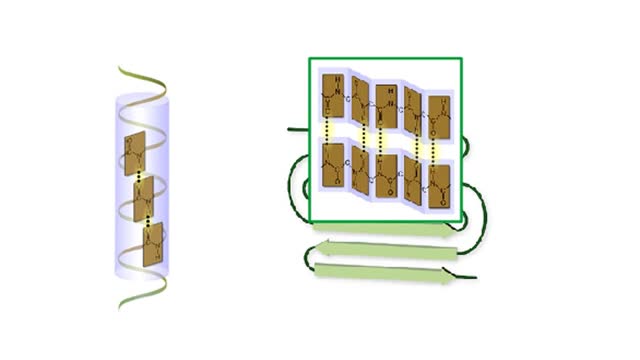
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like r...
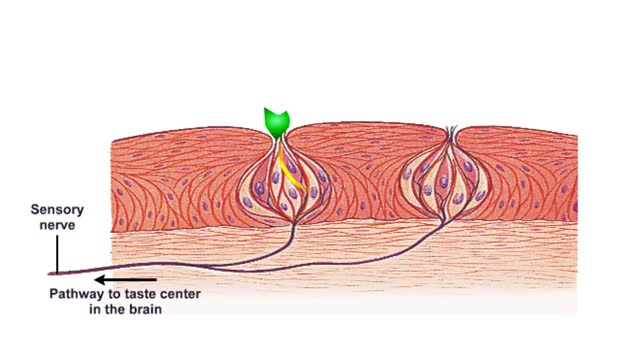
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8223
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
Advertisement