Search Results
Results for: 'inhibiting gastric acid secretion'
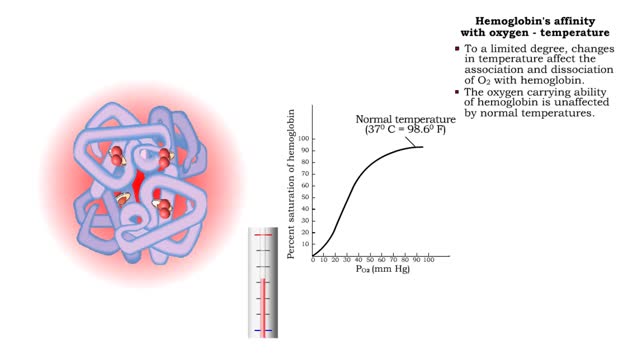
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 11327
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
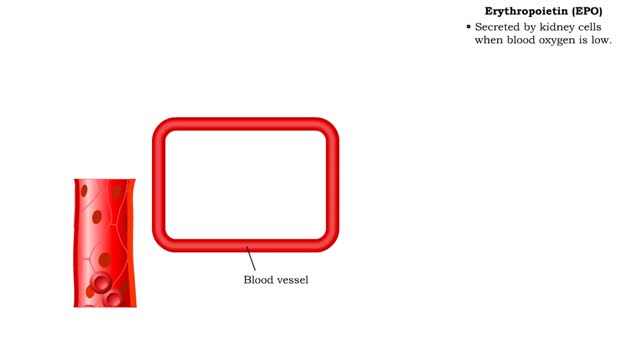
Red Blood Cells - Erythropoietin (EPO)
By: HWC, Views: 11257
• The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone aft...
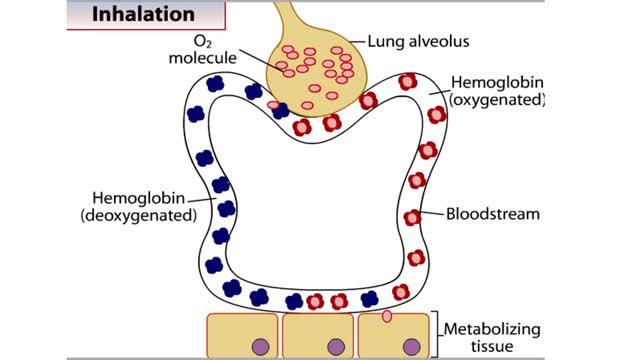
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 10754
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
By: Administrator, Views: 14683
Autism is a developmental disorder characterized by difficulties with social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. Parents usually notice signs during the first three years of their child's life. These signs often develop gradually, though some children with au...
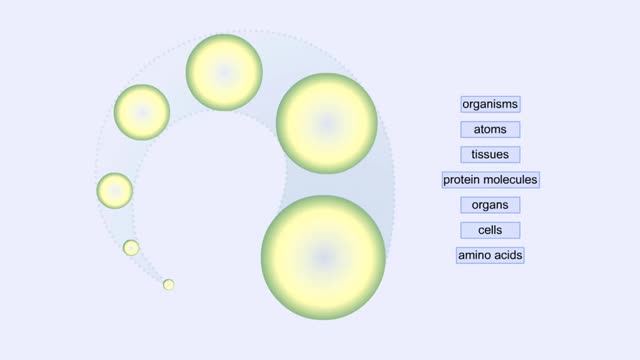
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 10859
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
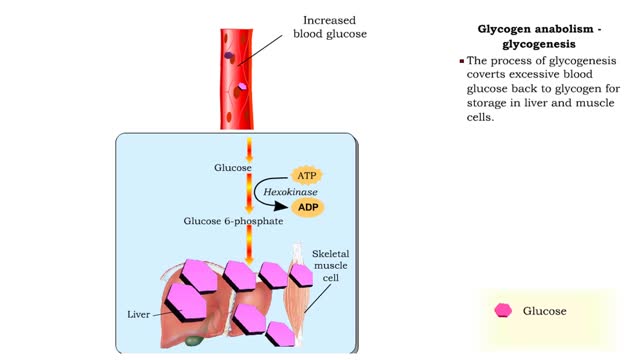
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11708
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
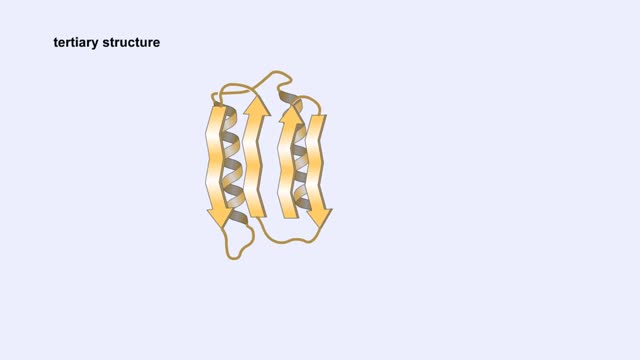
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 11218
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
By: Administrator, Views: 15496
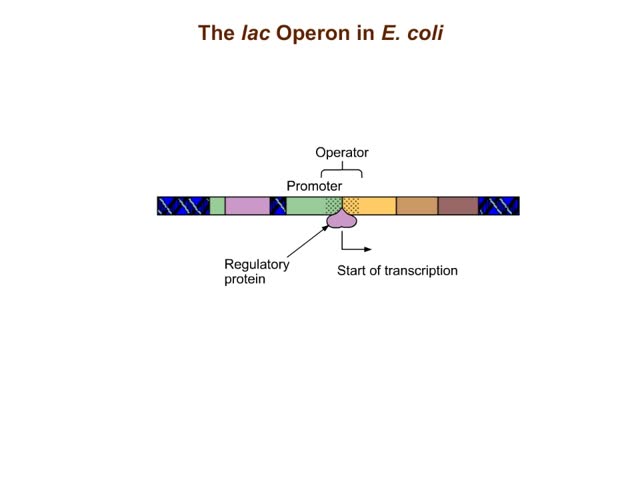
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Advertisement