Search Results
Results for: 'glucose molecule'
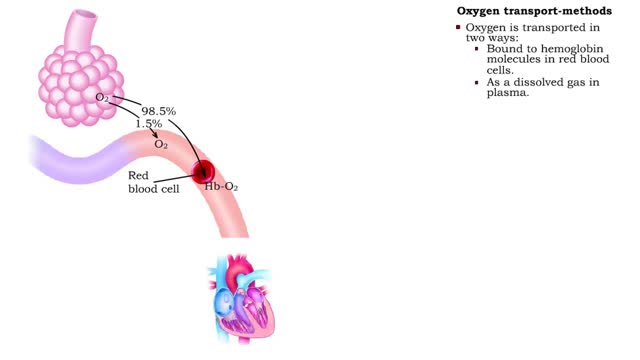
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 10753
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
By: HWC, Views: 5089
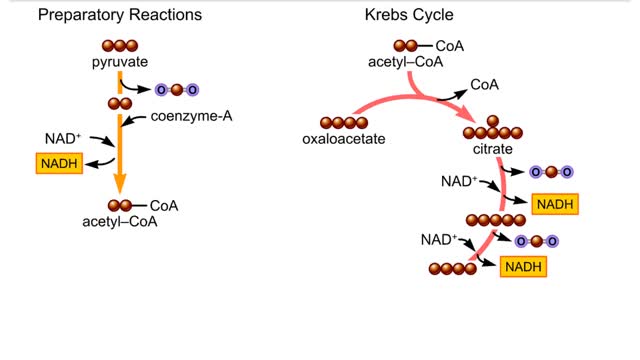
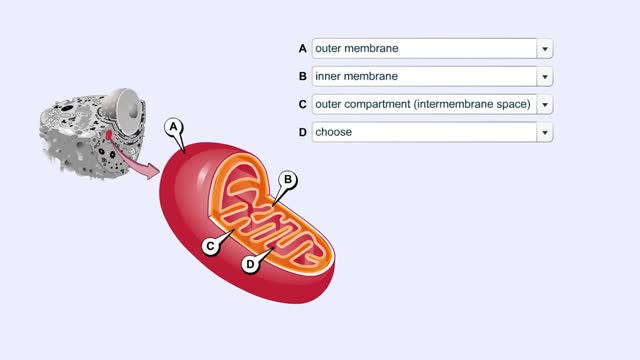
The second-stage reactions of aerobic respiration. The second-stage reactions occur in a mitochondrion's inner compartment. In the first preparatory reaction, a carbon atom is stripped from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide. The remaining carbons combine with coenzyme A and give ...
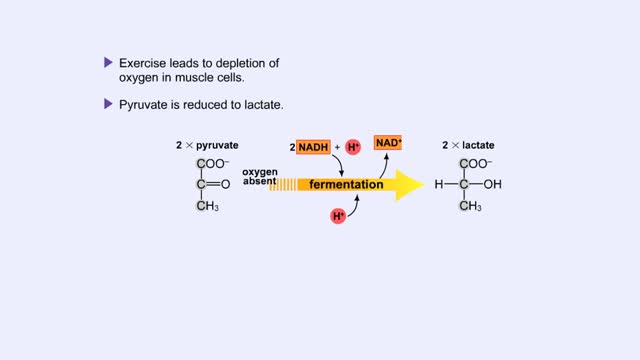
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 10348
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
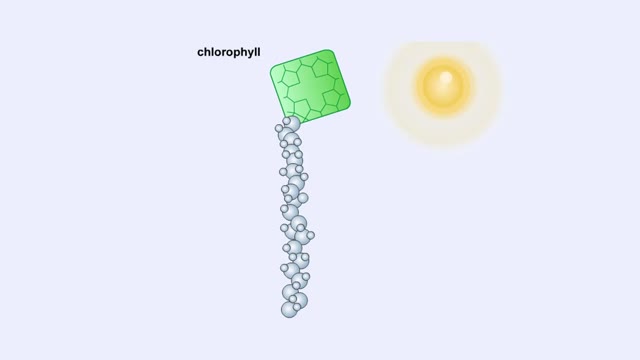
Electromagnetic Spectrum, Chlorophyll and Pigment & Light
By: HWC, Views: 10669
The sun gives off radiation that is called the electromagnetic spectrum. This is energy that travels as wavelengths and includes radio waves, X-rays and ultraviolet light. A portion of this radiation is known as visible light, and is the type of radiation that plants use to manufacture sugars. ...
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10478
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10629
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
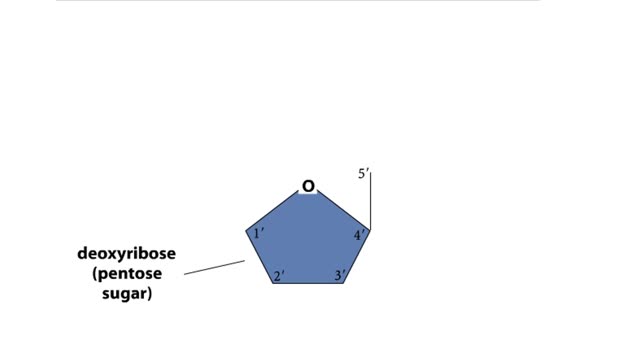
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Nucleic acids
By: HWC, Views: 10847
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids (polymers of nucleotides). Two polymers with complementary nucleotide sequences can pair with each other. This pairing endows nucleic acids with the ability to store, transmit, and retrieve genetic information. Two strands of DNA pair by hydrogen bonding. A compon...
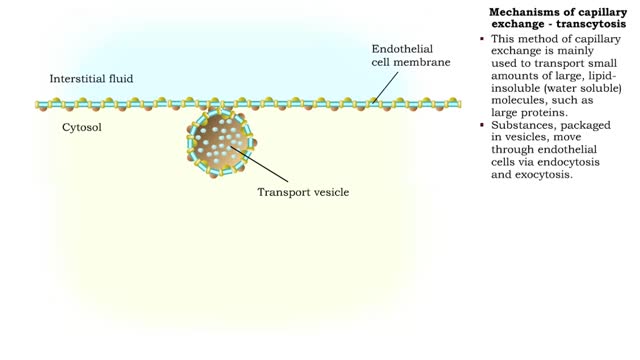
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11083
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
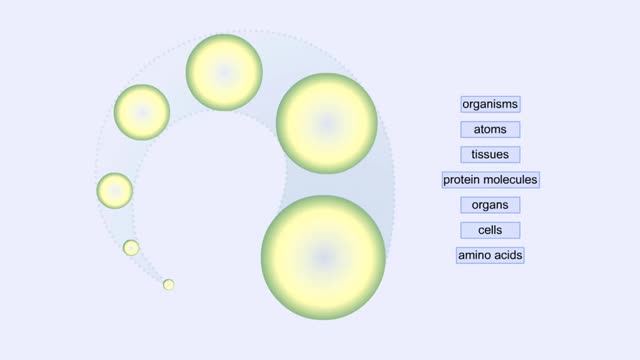
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 10360
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
Advertisement