Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 10/29/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Gas exchange partial pressure alveolar and blood compartments external respiration systemic tissue cells internal respiration blood and systemic cell compartments alveolar spaces pulmonary capillaries Low Pco2 High PO2 Diffusion of gases Internal respiration
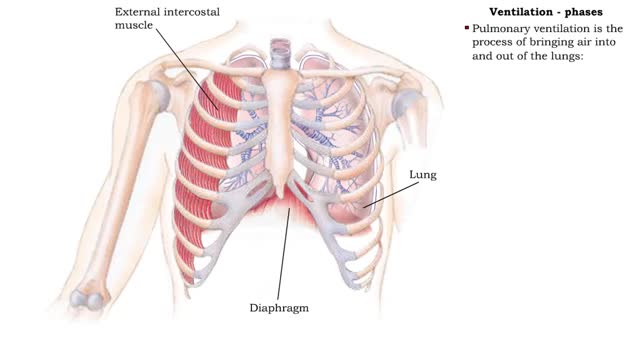
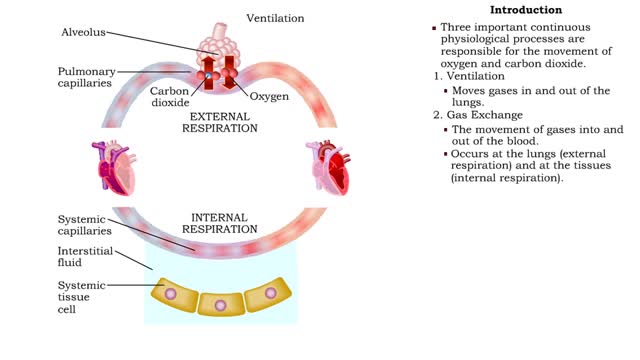
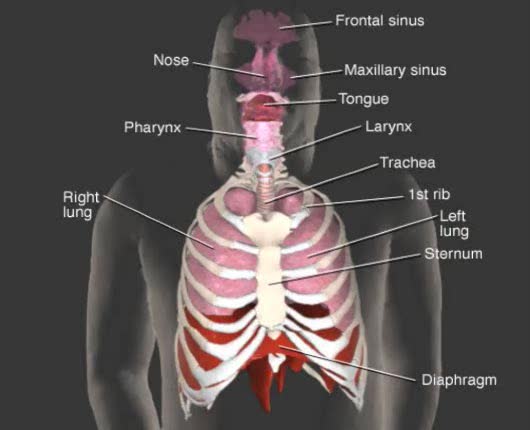
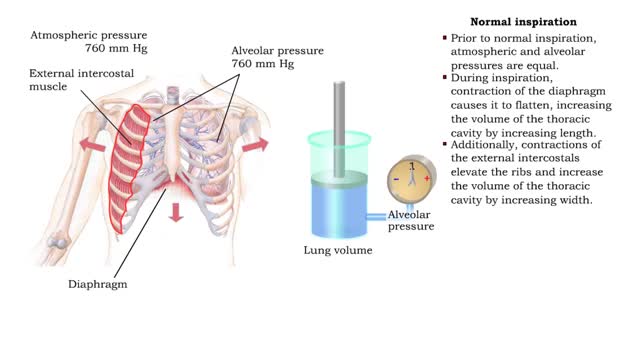
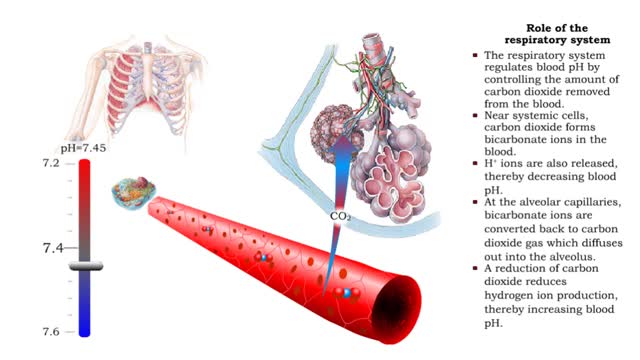
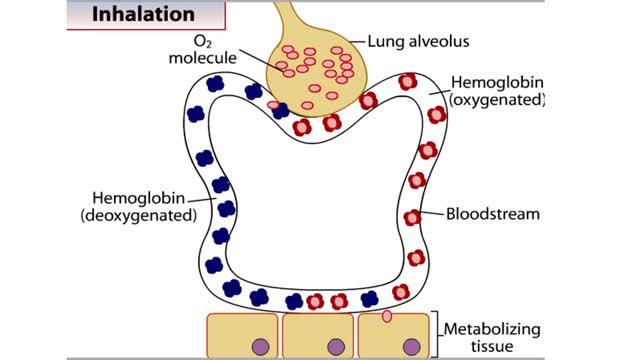
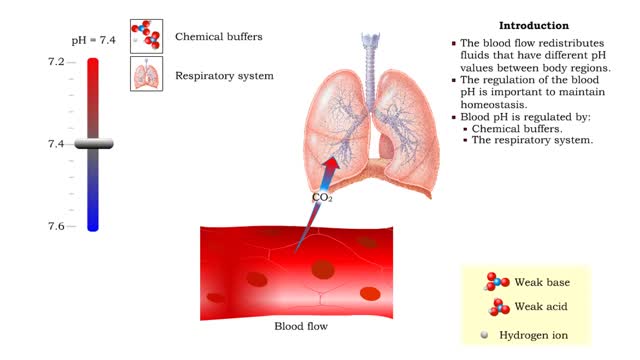
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. • Gas molecules diffuse from regions of higher pressure (higher concentration) to regions of lower pressure (lower concentration). • At the lungs, gas exchange occurs between the alveolar and blood compartments. This is external respiration. • At the systemic tissue cells, gas exchange occurs between the blood and systemic cell compartments. This is internal respiration. • The gas exchange between the alveolar spaces in the lungs and the blood in pulmonary capillaries is called external respiration. • Ventilation brings air, rich in oxygen, into the alveolar spaces in the lung. • Air in the alveolar space has a: • High PO2 • Low PCO2 • The blood in the pulmonary capillary compartment (entering lungs) has a: • Low PO2 • High PCO2 • Diffusion of gases is dependent on the partial pressure of the gases. • O2 moves from the alveolar compartment to the capillary compartment. • CO2 moves from the capillary compartment to the alveolar compartment. • The gas exchange between the systemic blood capillaries and tissue cells is called internal respiration. • Blood, high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide, circulates past tissue cells. • The blood near the tissues has a: • High PO2 • Low PCO2 • Each cell in the tissue compartment has a: •Low PO2 ▪ High PCO2 • Diffusion of gases is dependent on the partial pressure of the gases. • O2 moves from the capillary blood compartment to the cell compartment. ▪ CO2 moves from the cell compartment to the blood in the capillary compartment. ▪ During external respiration, oxygen will diffuse from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillaries ▪ CO2 moves in the opposite direction ▪ During internal respiration, oxygen will diffuse from the systemic capillaries into the tissue ▪ CO2 moves in the opposite direction
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.