Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/03/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Effect of blood chemistry Blood pH Blood Pco2 Blood P02 Chemoreceptors peripheral nervous systems hyperventilation response inspiratory area medullary rhythmicity area hypoventilation response
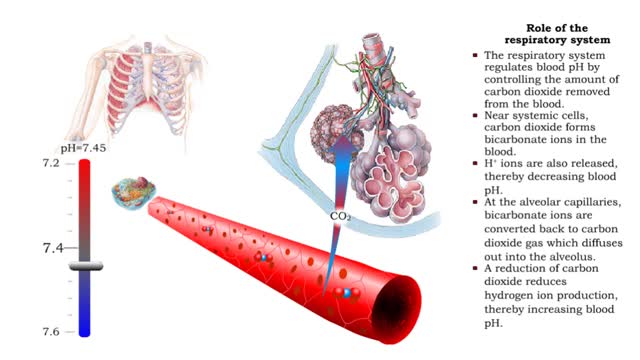
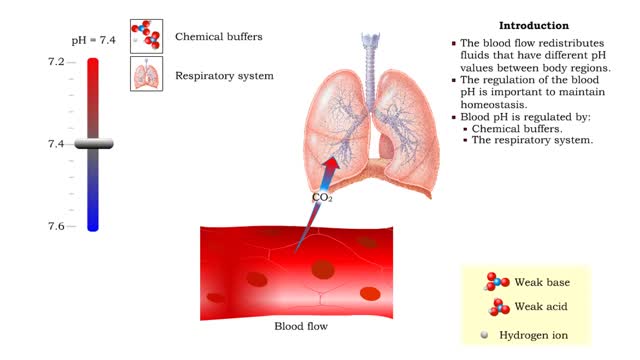
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory rate. • When CO2 and H+ levels increase, or O2 level drops, increased impulses from the chemoreceptors stimulate the inspiratory area in the medullary rhythmicity area. • Excitation of the inspiratory area increases respiratory rate. • Hyperventilation is a greater intensity of rate and depth of breathing. • Increased respiratory rate: • Removes CO2. • Increases pH. • Increases oxygen inflow, returning values to normal. • When CO2 and H+ levels decrease or O2 level rises, decreased impulses from the chemoreceptors inhibit the inspiratory area in the medullary rhythmicity area. • Inhibition of the inspiratory area decreases respiratory rate. • Hypoventilation is a decreased intensity of rate and depth of breathing. • Decreased respiratory rate: • Allows CO2 to accumulate. • Decreases pH. • Decreases oxygen inflow, promoting a return to normal values.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



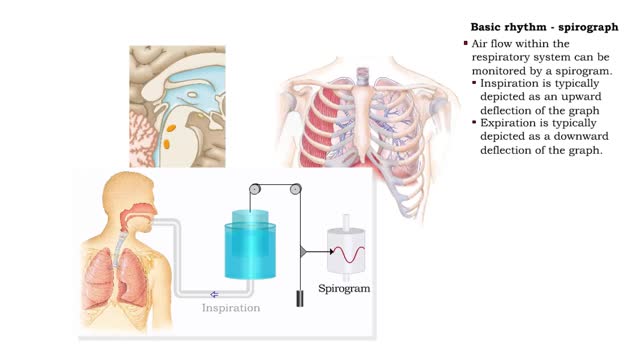
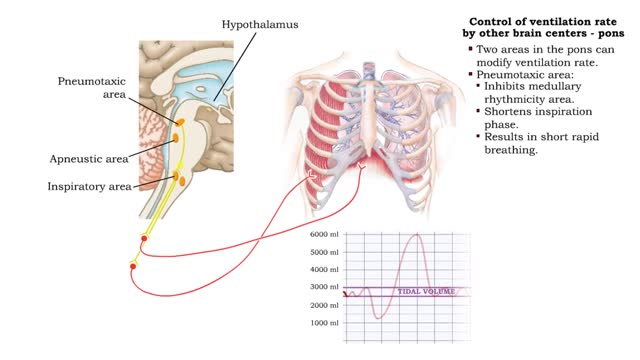
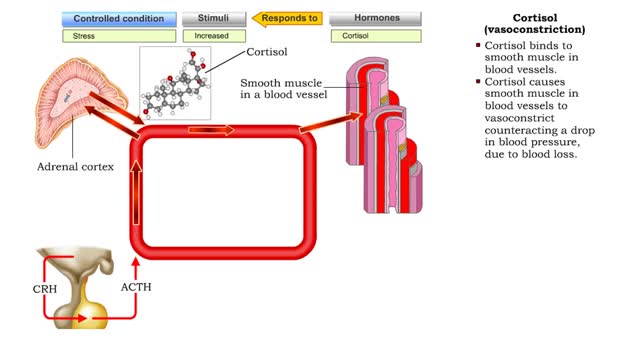

Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.