Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/19/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Insulin pancreatic islets glycogen Insulin Production
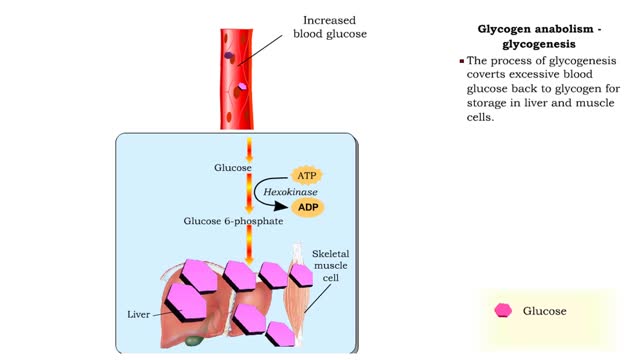
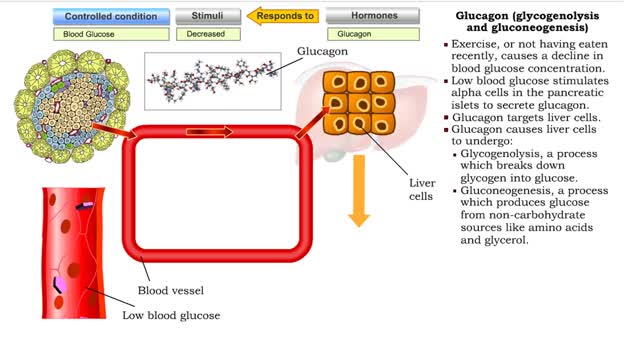
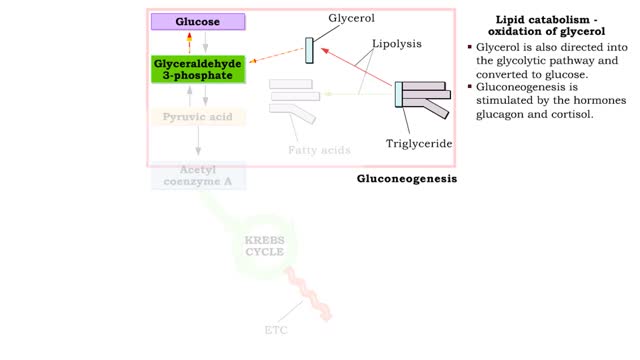
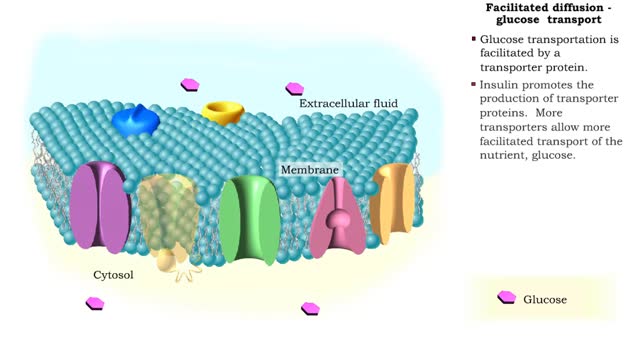
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentioned, insulin is released when needed to keep the body regulated and help keep the blood-sugar balance in check. • The absorption of a meal in the digestive tract will cause blood glucose levels to rise. • A rise in blood glucose levels stimulates beta cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete insulin. • Insulin can bind to many cells in the body. • Under the influence of insulin, the body cells - especially skeletal muscle cells - increase uptake of glucose and amino acids. • As glucose is removed from the blood, blood glucose concentration is restored to normal levels. • The absorption of a meal in the digestive tract will cause blood glucose levels to rise. • A rise in blood glucose levels stimulates beta cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete insulin. • Insulin can bind to liver cells. • Under the influence of insulin, liver cells convert glucose to glycogen, a process known as glycogenesis. Glycogen is stored in the liver. • As glucose is removed from the blood, blood glucose concentration is restored to normal levels. • The absorption of a meal in the digestive tract will cause blood glucose levels to rise. • A rise in blood glucose levels stimulates beta cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete insulin. • Insulin can bind to adipose cells. • Under the influence of insulin, adipose cells convert glucose into triglyceride fats, a process known as lipogenesis. • As glucose is removed from the blood, blood glucose concentration is restored to normal levels. • Increased insulin causes: • Increased transport of glucose out of the blood into body cells, especially skeletal muscle cells. • Formation and storage of glycogen in liver cells. • Formation and storage of triglyceride lipid in adipose cells. • The total response of all of the actions of insulin is to decrease blood glucose levels.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement





Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.