Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/20/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Cortisol protein catabolism gluconeogenesis hypothalamic corticotropin releasing hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone zona fasciculata cells vasoconstriction vasoconstrict macrophages lymphocytes
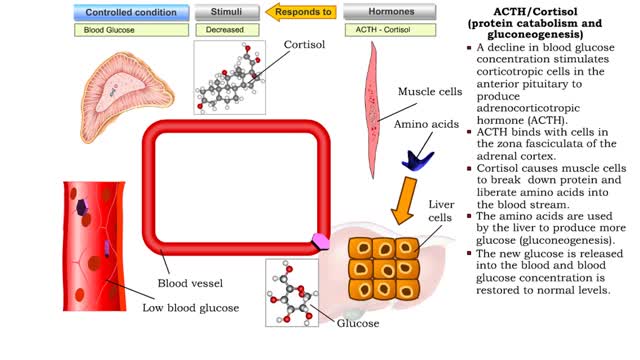
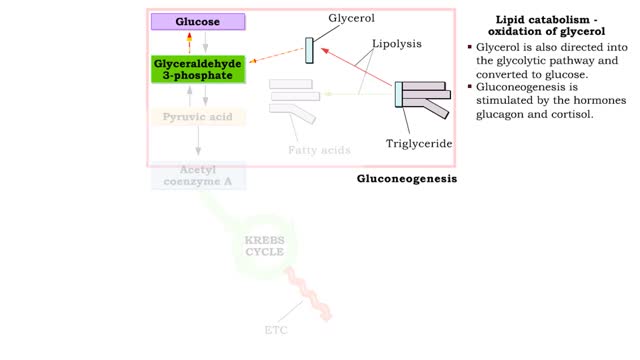
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cortisol binds to muscle and liver cells. • Cortisol causes muscle cells to break down protein and liberate amino adds into the blood stream. The 1 amino acids are used by the % liver to produce more glucose (gluconeogenesis). • Increased glucose is delivered to cells and organs so stress can be resisted. • Cortisol binds to smooth muscle in blood vessels. • Cortisol causes smooth muscle in blood vessels to vasoconstrict counteracting a drop in blood pressure, due to blood loss. • Blood flow is maintained during stress. • Cortisol binds to macrophages and lymphocytes. • Increased cortisol inhibits macrophages production of inflammatory producing chemicals. • This effect reduces swelling in tissues. • Increased cortisol inhibits proliferation of lymphocytes reducing the immune response. • This response of cortisol prevents immune responses from becoming dangerous. • Cortisol promotes: • The breakdown of proteins for increased gluconeogenesis; • Vasoconstriction to raise blood pressure and blood flow; • And suppression of immune responses. This response of cortisol prevents immune responses from becoming dangerous. • The overall response of cortisol is to reduce stress.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



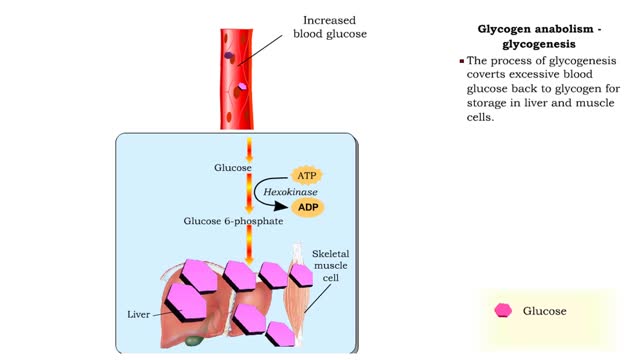
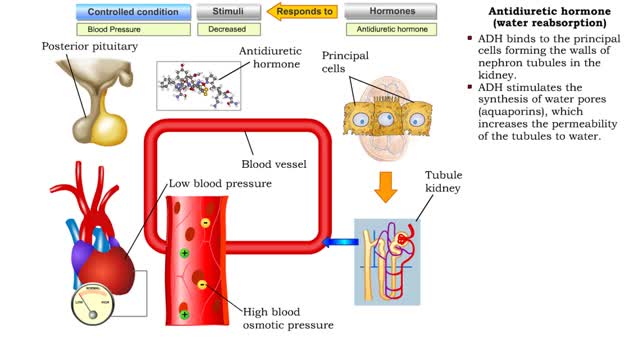
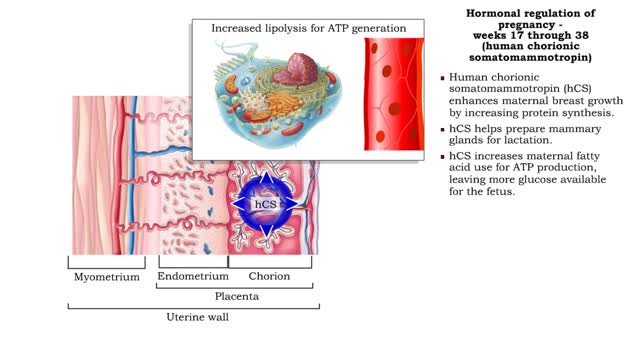
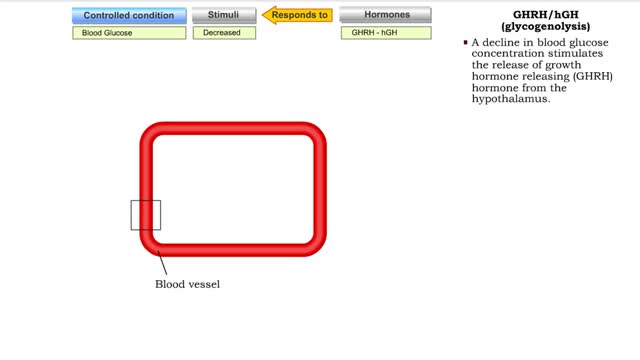
Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.