Cytotoxic T cell receptors, activation, proliferation, differentiation & action
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/27/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Cytotoxic T cell receptors MHC-I molecules thymus gland Cytotoxic T cell activation viruses antigen cytokines Cytotoxic T cell proliferation and differentiation Cytotoxic T cell action
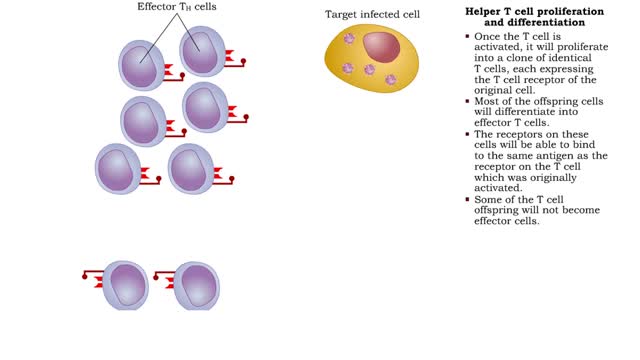
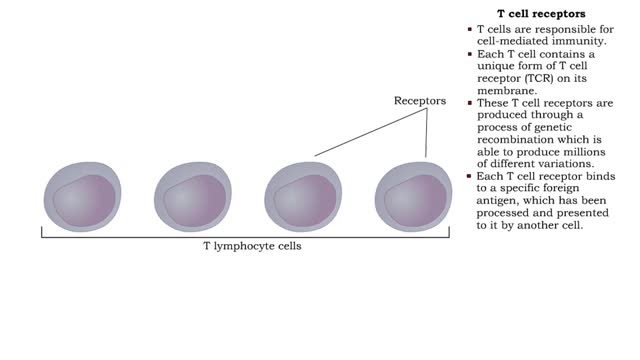
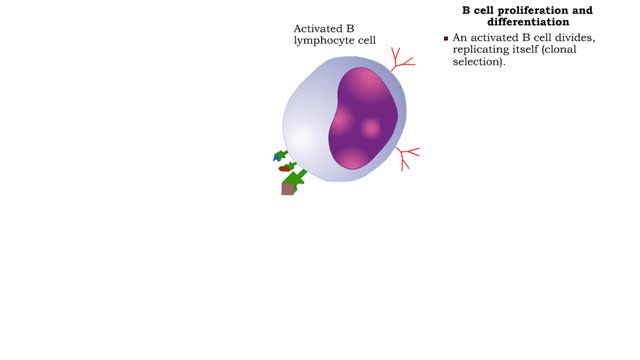
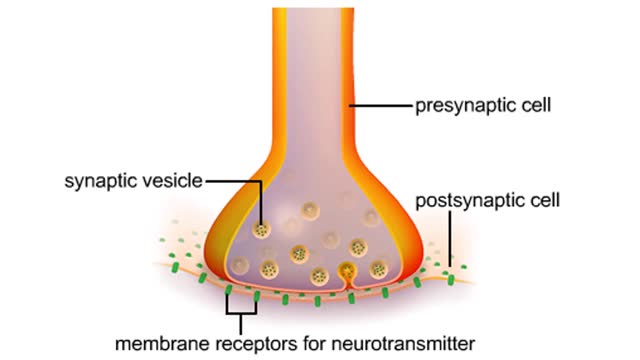
• Most cells which have CD8 on their surface become cytotoxic T cells (Tc cells). • CD8 T cells recognize a foreign antigen when it is presented in conjunction with the protein, MHC-I. • Nearly all nucleated cells in the body express MHC-I molecules. • T cells that recognize self-peptides expressed by MHC-I on the surface of healthy cells don't survive in the thymus gland. • The surviving T cells can therefore recognize: • Certain tumor cells expressing abnormal proteins that are seen as foreign. • Transplanted cells that express foreign MHC-I with their specific proteins. • Body cells infected by viruses which have viral antigen on their surface. • Binding to antigen presented to it by a foreign, tumor or viral infected cell is not enough for activation. • Costimulation needed for activation of a cytotoxic T cell is provided by the close association of molecules on the two cell membranes and cytokines released by a Th cell. • Once the Tc cell is activated, it will proliferate into a clone of identical Tc cells, each expressing the Tc cell receptor of the original cell. • Most of the offspring cells will differentiate into effector Tc cells. • The receptors on these cells will bind to the same antigen as the receptor on the original Tc cell. • Some Tc clones will not become effector cells but will differentiate into memory cells. • Memory Tc cells will respond rapidly to future exposure to the same antigen. • Tc cells can therefore eliminate cells which are infected or have become cancerous. They can also act against foreign cells. • Tc cells kill target cells using two major mechanisms: • Perforin induced cytolysis • Tc cells release perforin which creates holes in target cell membranes, causing a target cell to burst. • Lymphotoxin induced cell death - Tc cells can also secrete lymphotoxin which starts a cascade of events in the target cell, leading to degradation of its DNA and cell death.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.