Exercise and cardiac output & Definition of stroke volume
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 12/03/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Cardiac output stroke volume Exercise and cardiac output diastole systole Factors influencing stroke volume ventricular muscle
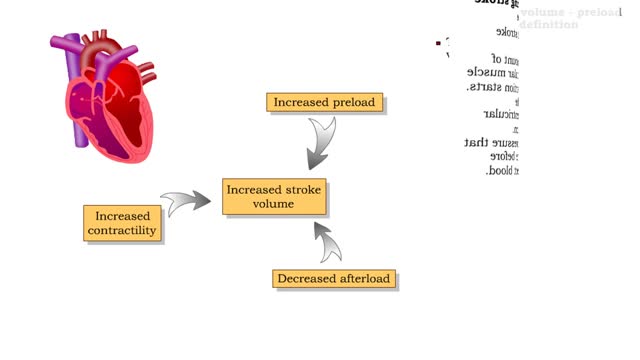
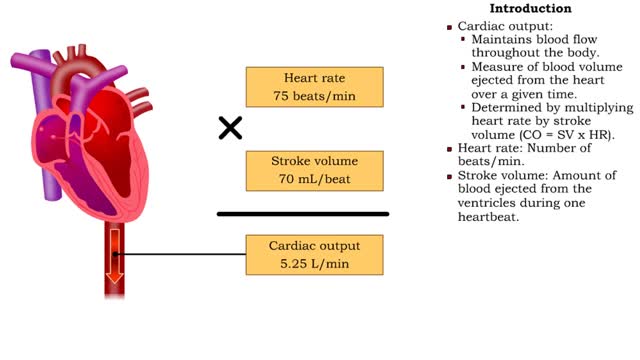
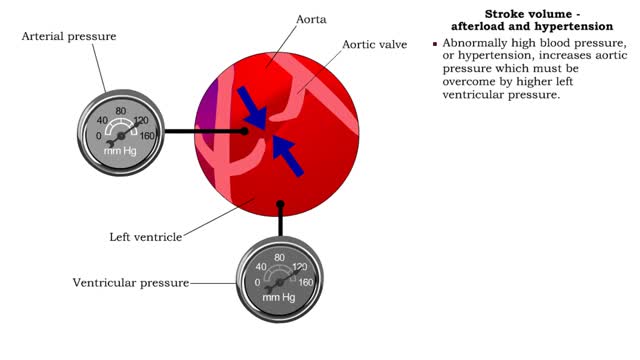
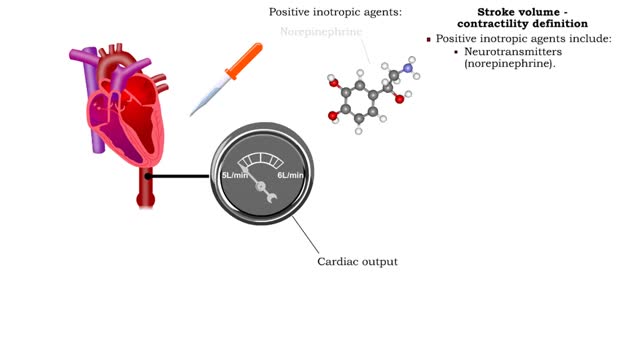
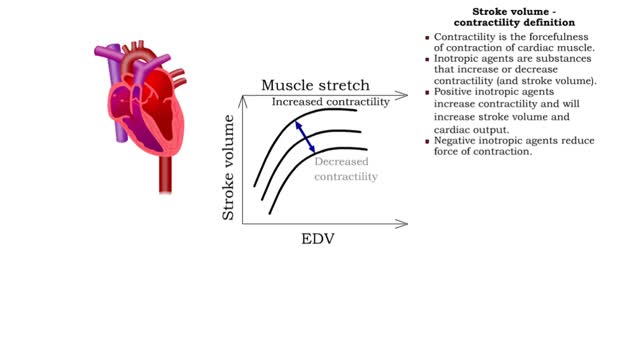
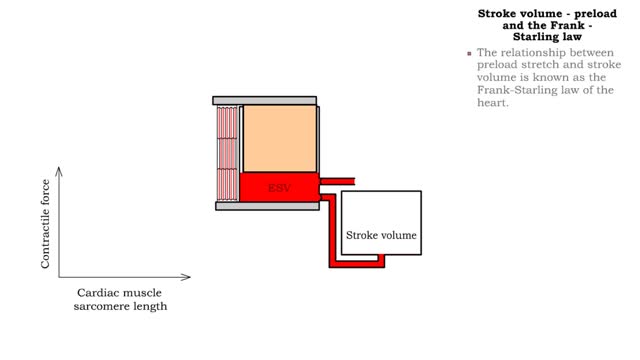
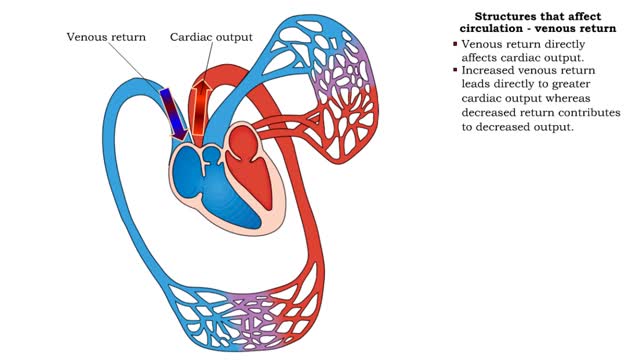
▪ Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood ejected from the ventricles during one heartbeat. • Cardiac output: • Varies according to body's metabolic demands. • Increases dramatically during exercise. • Cardiac output during vigorous exercise can be as much as 20 L/min. • Stroke volume is directly correlated with cardiac output-the greater the stroke volume the greater the cardiac output. ▪ Stroke volume represents the difference in the amount of blood between: • the volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume EDV); • the volume after systole (end-systolic volume ESV). ▪ Normal resting stroke volume is 70 ml. Factors influencing stroke volume • Three factors affect stroke volume: • Preload is the amount of stretch of ventricular muscle before the contraction starts. • Contractility is the forcefulness of ventricular muscle contraction. • Afterload is the pressure that must be overcome before ventricles can eject blood.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.