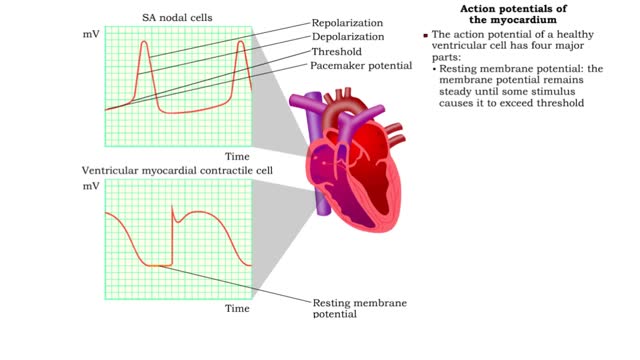
Definition of heart rate
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 12/03/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC sinoatrial Cardiac output Nervous control of heart rate norepinephrine acetylcholine Chemical control of heart rate epinephrine thyroxine
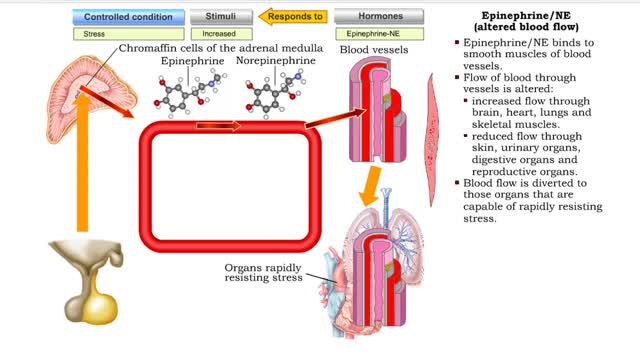
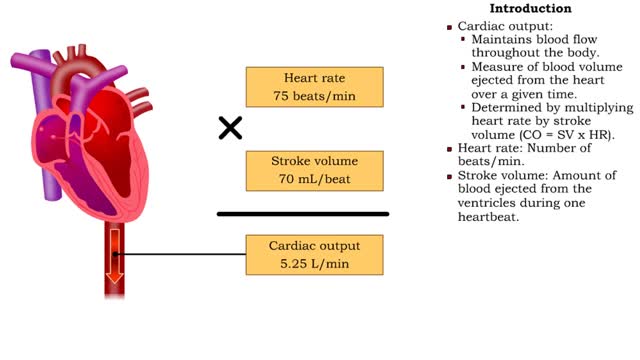
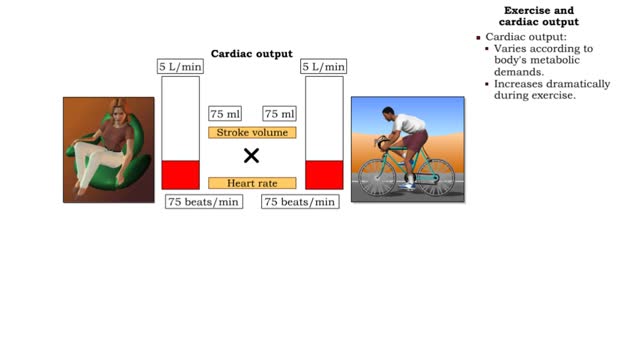
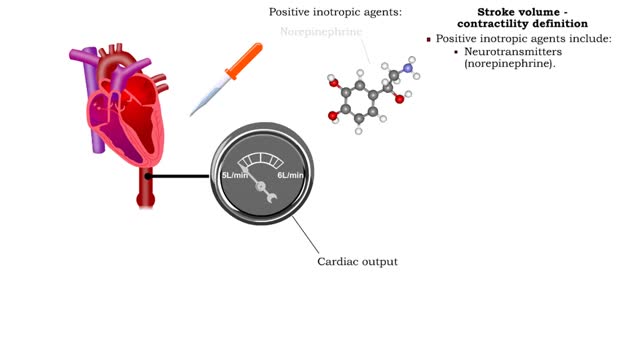
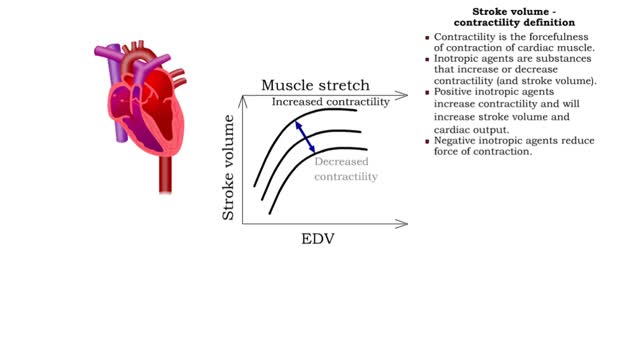
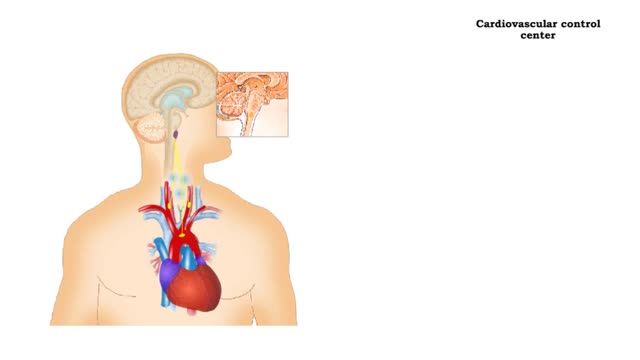
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous control of heart rate ▪ Heart rate is influenced by body's needs and regulated by autonomic nervous system and hormones. ▪ Situations that decrease blood pressure promote sympathetic stimulation and the release of norepinephrine, which increases heart rate and cardiac output. ▪ Situations that increase blood pressure promote parasympathetic stimulation and the release of acetylcholine, which decreases heart rate and cardiac output. Chemical control of heart rate • Heart rate is influenced by body's needs and regulated by autonomic nervous system and hormones. • The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine as well as thyroxine, accelerate heart rate. • Low blood O2 and pH as well as high blood CO2 trigger an increased heart rate. • Moderate increases in cytosolic levels of ionic Ca+ also increase heart rate.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.