Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 01/27/2020
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Secretin inhibiting gastric acid secretion Cholecystokinin chyme gastric mucosa pancreatic lipas duodenum
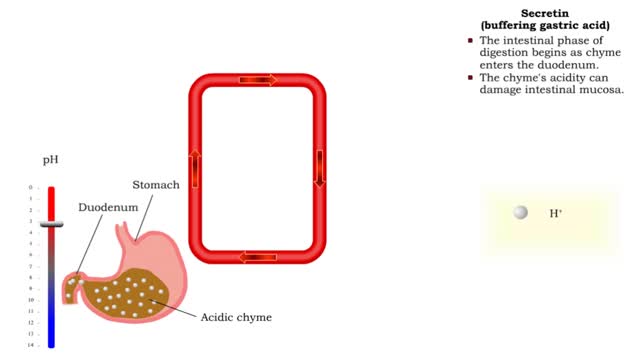
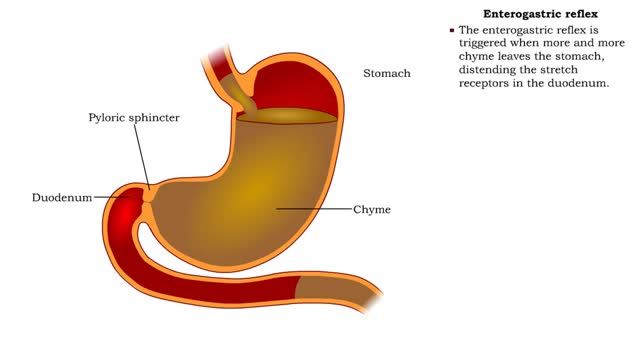
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also regulates the intestinal phase of digestion. • If fatty chyme enters the duodenum, enteroendocrine cells of the intestinal mucosa are stimulated to produce cholecystokinin (CCK). • CCK targets pancreatic acinar cells and the biliary system. • Delivery of pancreatic lipase and bile is increased to the small intestine. • CCK promotes the digestion of fats in the chyme. Cholecystokinin (gastric emptying) • CCK also regulates gastric emptying. • Distended duodenum and fatty acids or undigested proteins in the chyme promote the secretion of CCK. • CCK triggers the closing of the pyloric sphincter, thereby inhibiting gastric emptying. • High-protein and high-fat meals stimulate the secretion of CCK and consequently take longer to digest and empty.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.