What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 02/27/2020
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Carbohydrates High Carb Food low-carb diet diet sports drinks pasta cellulose complex carbohydrate macromolecule hydrates of carbon glucose simple sugar double bond monosaccharides saccharum
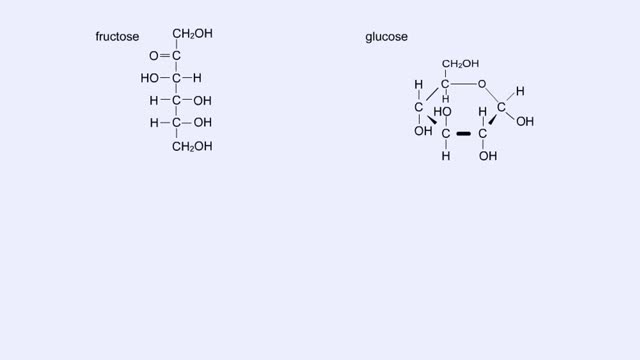
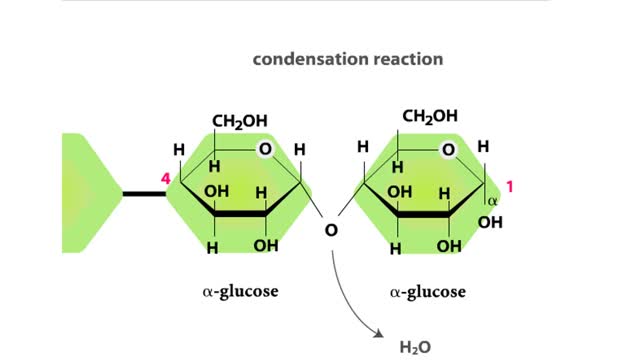
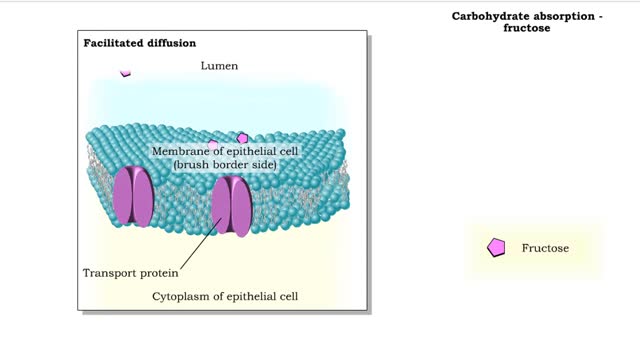
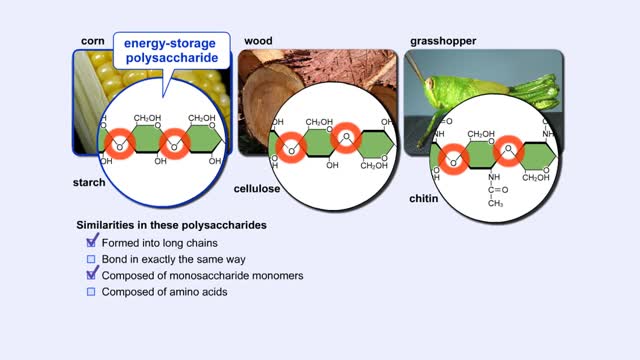
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carbohydrates are molecules which contain much of the energy that we utilize to build new cells and tissues. Without carbohydrates in our diet, our bodies would have to obtain the required energy from proteins and fats, a proposition whose health benefits are still being debated. Carbohydrates are the sugars found in sports drinks and the starches of our favorite pasta. Did you know that each year Americans consume an average of 140 pounds of sugar per person? Or that cellulose, a complex carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, is the most abundant organic compound on Earth? Foods are often high in one macromolecule. Some are high in protein, and others are high in fat. All of these foods are high in carbohydrates. As you can see, these are foods that are either plants or produced from plants. Now that you know where you can find a carbohydrate, let's look at what a carbohydrate really is. Carbohydrates are simply defined as "hydrates of carbon," which means that they contain carbon and water in the ratio C(H20). For every carbon atom, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Carbon forms the backbone of the molecule with various functional groups attached. Let's construct a simple sugar, glucose, and then examine some other simple sugars which are similar to glucose. Glucose is a 6-carbon molecule, so our first job is to make the carbon backbone from 6 carbon atoms. Once these atoms are in place, add H's and OH's so that each carbon atom has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom on average. However, you may notice something special about the first and sixth carbon atoms. Glucose is a 6-carbon carbohydrate with the molecular formula C6H1206. The carbon atoms in the middle of the glucose molecule each have one hydrogen atom and one OH group attached to them. The first carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and the sixth carbon atom has an extra hydrogen atom. Glucose belongs to a group of carbohydrates called simple sugars or monosaccharides (from "mono" meaning "one" and "saccharum" meaning "sugar"). The number of carbon atoms and the arrangements of hydrogen atoms, OH groups, and double-bonded oxygen atoms differentiate between different simple sugars.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



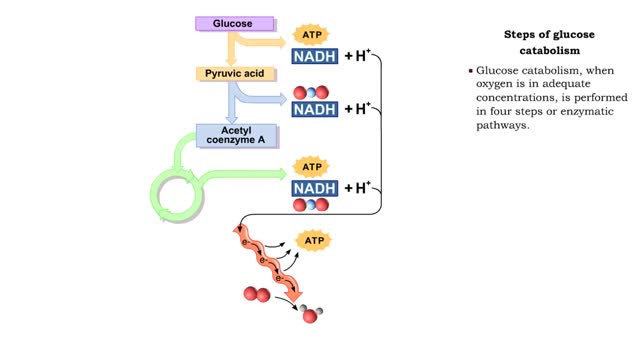
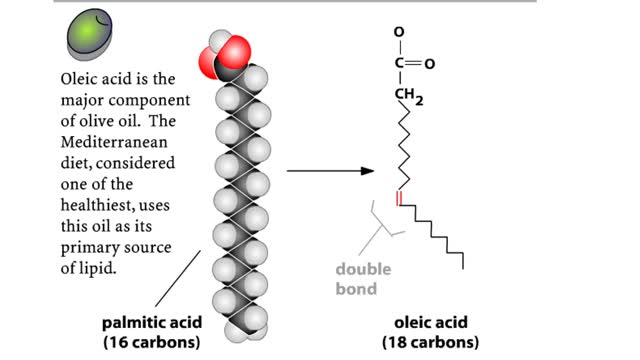

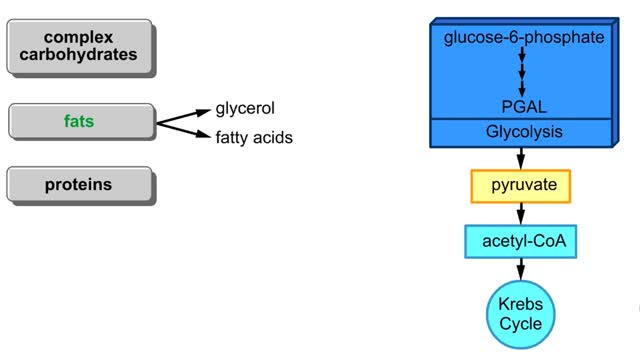
Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.