Search Results
Results for: 'Normal inspiration'
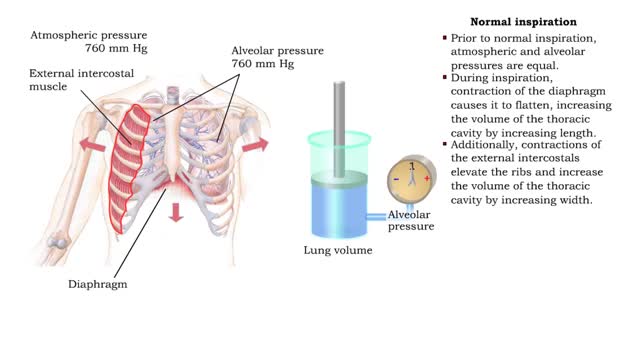
Pressure volume relationships - Normal inspiration and expiration
By: HWC, Views: 11518
• Changing the relative pressure in the compartments can control the direction of airflow between compartments. • In a closed compartment, pressure and volume are inversely related. • Reducing the volume will increase the pressure. • Increasing the volume will decrease the pressure. ...
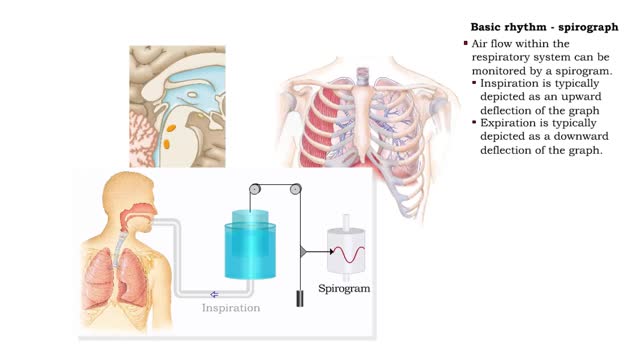
Basic rhythm - control centers in medulla oblongata, spirograph and normal tidal cycle
By: HWC, Views: 11575
• Normal ventilation is rhythmic and involves continuous cycles of inspiration and expiration. • Various regions of the brain closely regulate this rhythmic pattern of ventilation. • The rhythmicity area in the medulla regulates the basic rhythm of ventilation. • The medullary rhy...
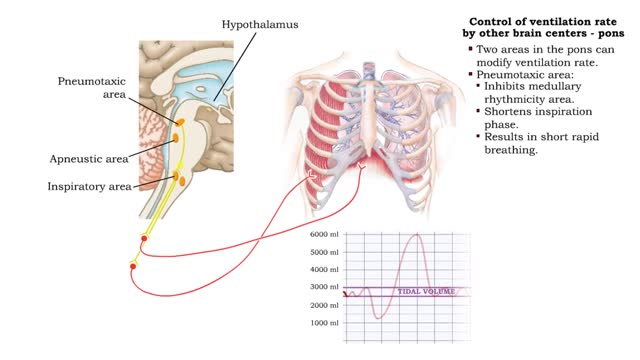
Control of ventilation rate by other brain centers (posts, hypothalamus & cerebral cortex)
By: HWC, Views: 11670
Forced ventilation: • The inspiratory area stimulates accessory inspiratory muscles. • Inspiration is more forceful. • Inspiratory area activates expiratory area, which sends impulses to the expiratory muscles (internal intercostals and abdominal muscles). • Expiration muscles c...
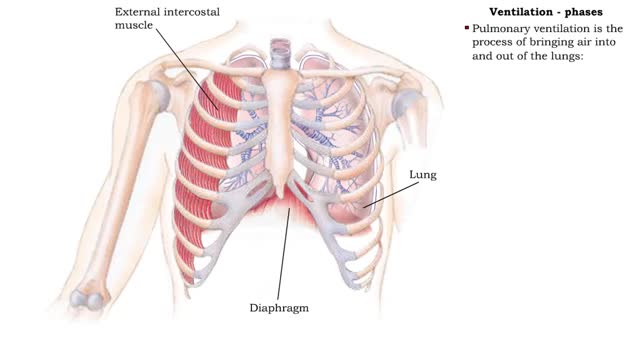
Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC, Views: 11818
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system b...
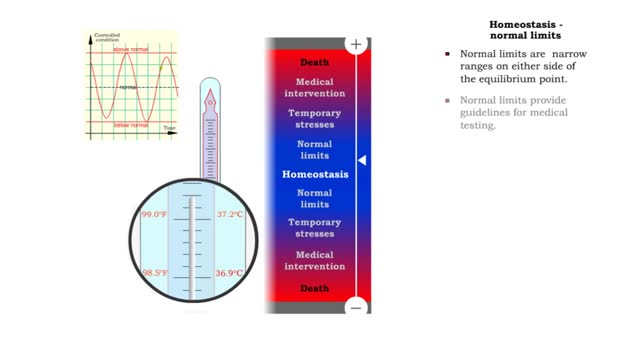
Homeostasis (range of body conditions, normal limits, mild stresses & severe stresses)
By: HWC, Views: 11519
Homeostasis: • Provides relative stability of the internal environment. • Results from constant adjustments. • Regulated by regulatory processes. • Requires system interplay. • Normal limits. • Temporary stresses. • Disruptions requiring medical intervention. • D...
Introduction to Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
By: Administrator, Views: 14624
Human immunodeficiency virus gains entry into helper T cells, uses the cell DNA to replicate, interferes with normal function of the T cells, and destroys the normal cells. 1 in 10 persons with AIDS: age 50 or older. 4% of all AIDS cases: age 65 or older. AIDS’ main form of treatment: an...
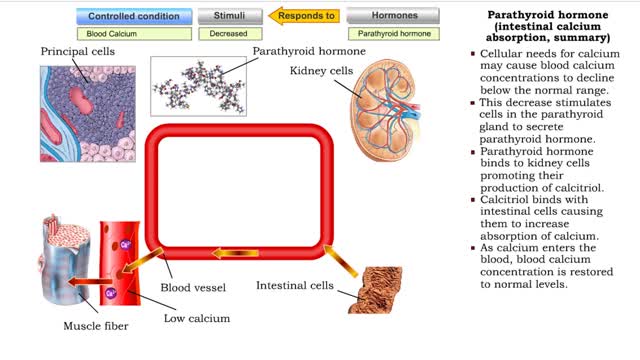
Parathyroid hormone (bone resorption) & Calcitonin (bone deposition)
By: HWC, Views: 11577
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range. • This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone. • Binding of parathyroid hormone to osteoclasts in bone tissue promotes bone resorption and th...
By: HWC, Views: 11793
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
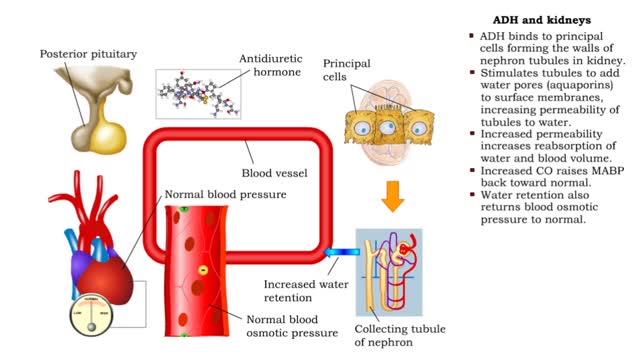
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11800
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
Advertisement