Search Results
Results for: 'arteriole radius'
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses
By: HWC, Views: 10636
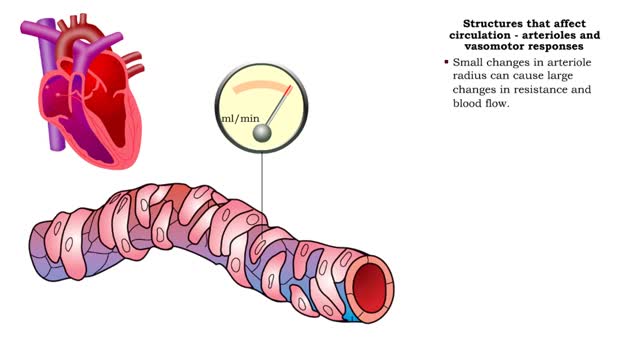
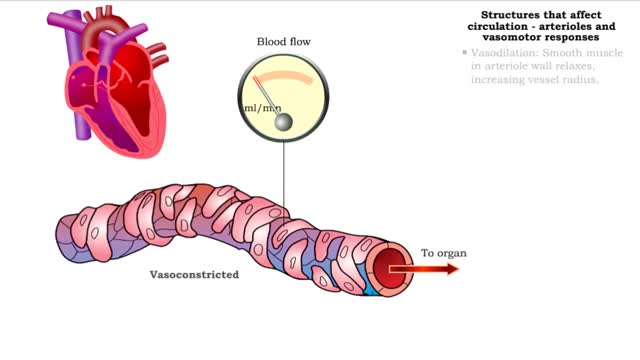
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. ■ Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. ■ Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 11042
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11514
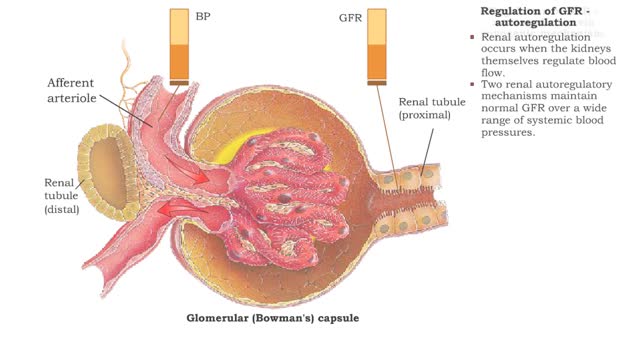
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Ren...
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12555
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
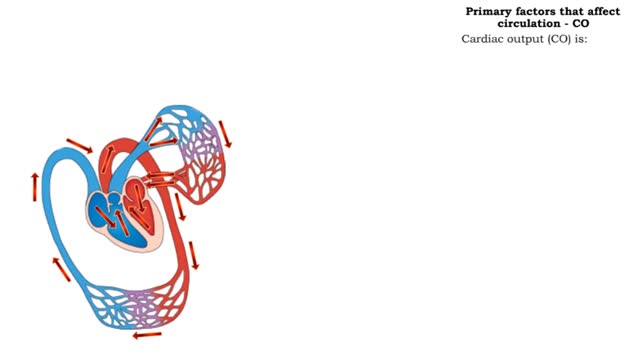
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 11394
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
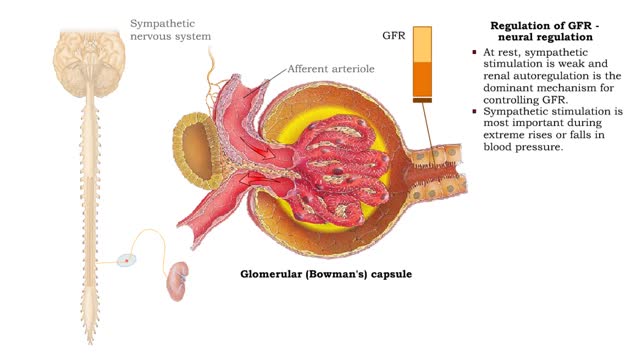
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12065
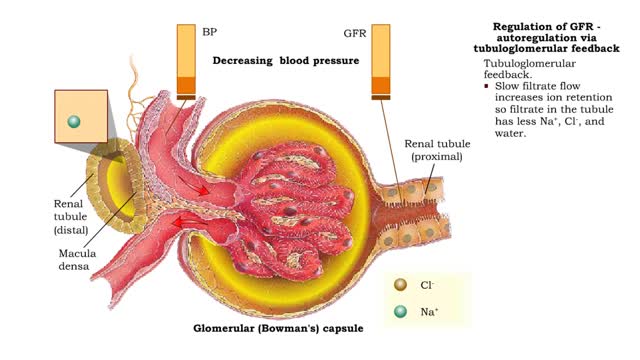
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
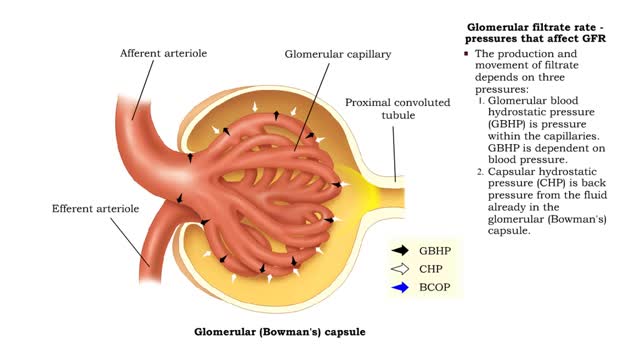
Glomerubular filtrate rate -pressures that affect GFR and net filtration pressure
By: HWC, Views: 11405
• The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed per minute within the renal corpuscle. • Once the filtrate is formed it moves down the tubule. • The production and movement of filtrate depends on three pressures: I. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) is pre...
By: Administrator, Views: 714
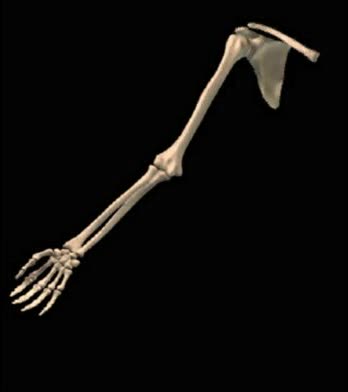
The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercle...
By: Administrator, Views: 13983
Types of fractures: - Colles' - Pott's - Compression - Vertebral compression - Epiphyseal - Stress - Hip Closed, or simple–A completely internal break that does not involve a break in the skin (x-ray of the tibia and fibula). Note the break in the fibula (smaller bone). Open, or co...
Advertisement