Search Results
Results for: 'vascular tissues animation'
By: Administrator, Views: 14521
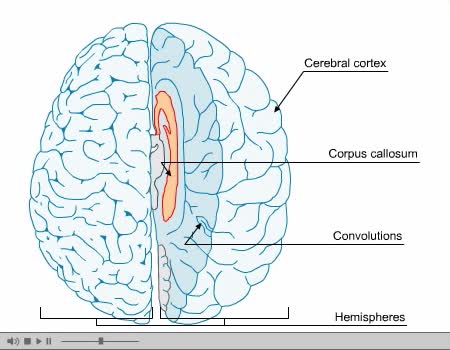
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick, nerve tract consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, con...
Cavernous Sinus Larynx Middle Ear Orbit: Granulesm Animation
By: HWC, Views: 10905
The cavernous sinuses are located within the middle cranial fossa, on either side of the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone (which contains the pituitary gland). The cavernous sinuses, a rich plexuses of veins that surround the internal carotid arteries, lie lateral to the pituitary fossa. Ant...
Chromosome structural organization/ Mechanisms for chromosome movement Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7813
How the chromosome is organized. At metaphase, the chromosomes are duplicated and are at their most condensed. In each chromosome, two identical sister chromatids are held together at a constricted region called the centromere. When a chromosome is condensed, interactions among chromosomal ...
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 15048
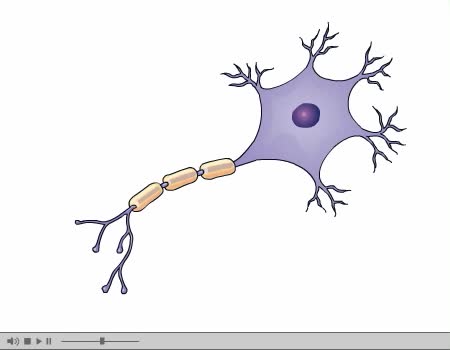
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
Sister chromatids of a metaphase chromosome animation
By: HWC, Views: 9789
At metaphase, the chromosomes are duplicated and are at their most condensed. In each chromosome. two identical sister chromatids are held together at a constricted region called the centromere. When a chromosome is condensed, interactions among chromosomal proteins keep loops of DNA tightly ...
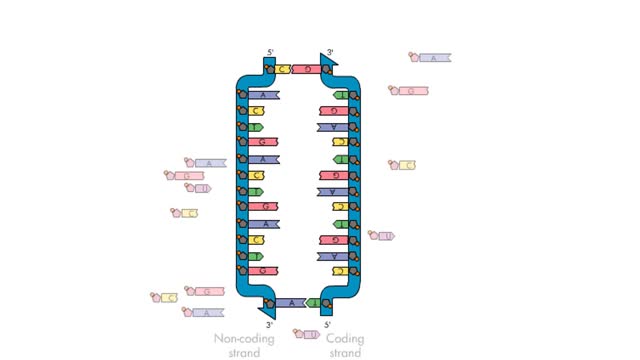
Transcription—A molecular view
By: HWC, Views: 7287
Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene's protein information encoded in DNA. During transcription, a DNA molecule is copied into RNA molecules that are then used to translate...
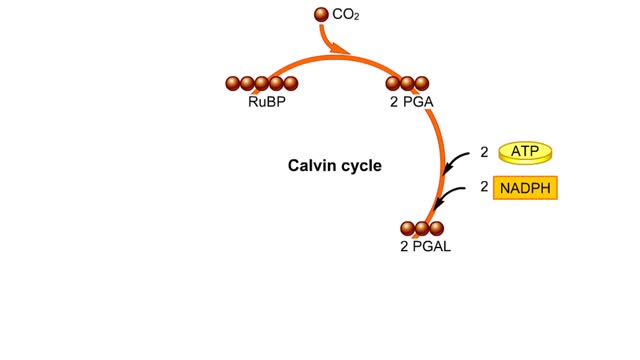
By: HWC, Views: 11405
he light-independent reactions make sugars by way of a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. The cycle begins when rubisco attaches a carbon from carbon dioxide to ribulose bisphosphate. The molecule that forms splits into two molecules of PGA. Each PGA gets a phosphate group from ATP a...
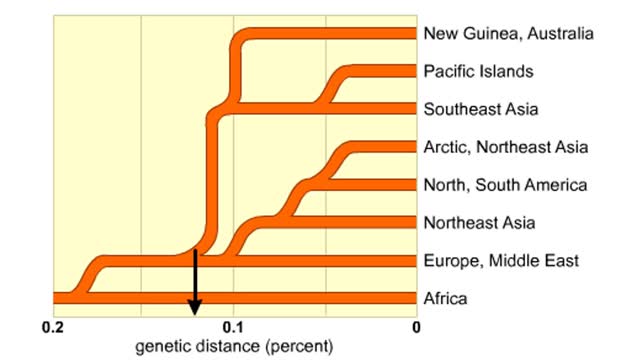
Genetic distance between human groups
By: HWC, Views: 8464
One proposed family tree for modern humans. This family tree is based on nucleic-add hybridization studies of many genes and immuno-logical comparisons. Branch points show presumed genetic divergences. This data indicates that the greatest genetic distance separates humans native to Afri...
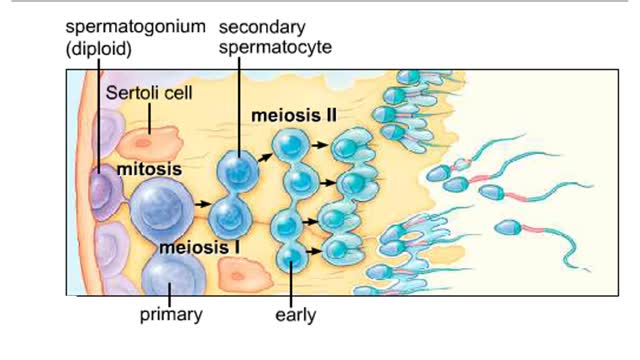
By: HWC, Views: 9747
Spermatogenesis takes place inside the seminiferous tubules. Diploid spermatogonia located near the outer edge of the tubule divide mitotically to form primary spermatocytes. The first meiotic division produces secondary spermatocytes with a haploid number of duplicated chromosomes. T...
Advertisement