Search Results
Results for: 'pH'
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 10799
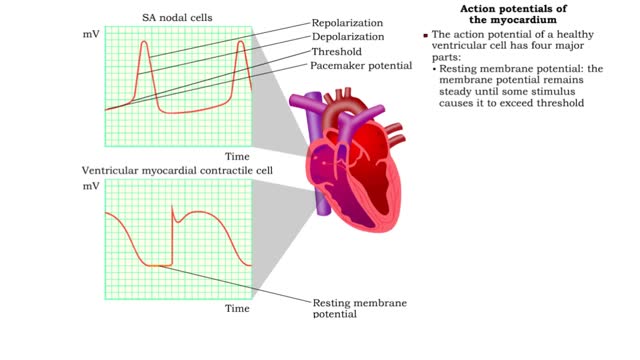
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 10995
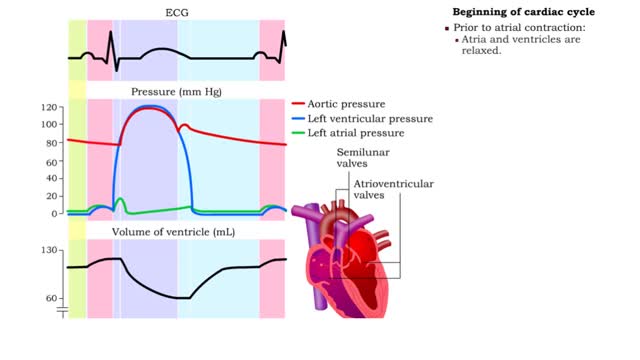
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
Electrical changes in the heart
By: HWC, Views: 10711
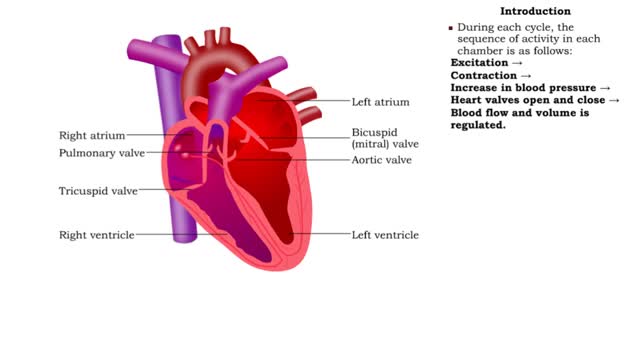
• ECG: Graph of the voltage changes that occur during the cardiac cycle. • Readings are taken by electrodes placed on the surface of the body. • Electrodes detect voltage changes caused by the electrical activity of the heart. • P wave = atrial excitation (atrial depolarization). ...
By: HWC, Views: 10875
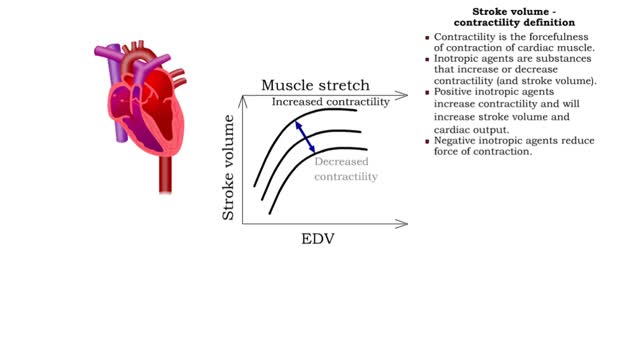
Preload definition • Preload is the degree of stretch of cardiac muscles cells prior to contraction. • The amount of stretch is related to the end-diastolic volume[EDV]. • Increased return blood flow from the veins increases end-diastolic volume. Cardiac muscle sarcomeres stretch and ...
By: HWC, Views: 11051
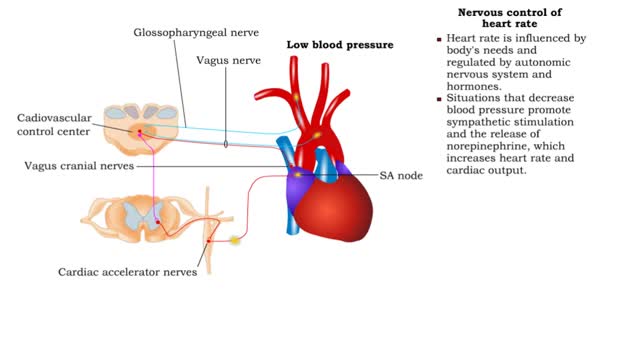
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous ...
Component of feedback systems & Communication and regulation of body systems
By: HWC, Views: 11110
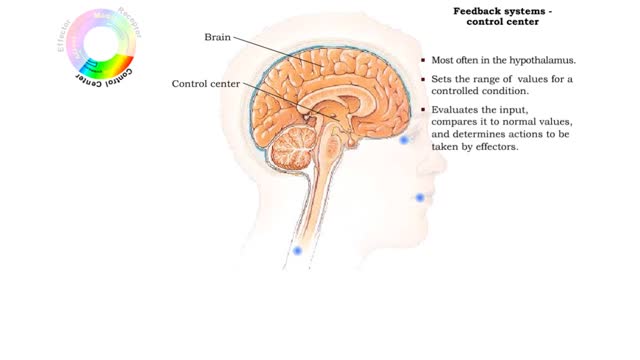
• Primary responsibility for communication and regulation in the body is shared by the nervous and endocrine systems. • The two systems work alone or together in specialized physiological processes called feedback systems to maintain homeostasis. • Feedback systems - or loops - are ...
By: HWC, Views: 10602
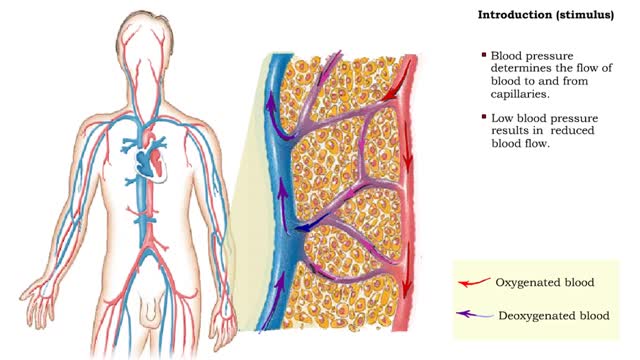
• Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. In humans, sensitivity is due to portions of the nervous system called receptors. Receptors are typicall...
Lipid digestion - mouth, stomach and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11022
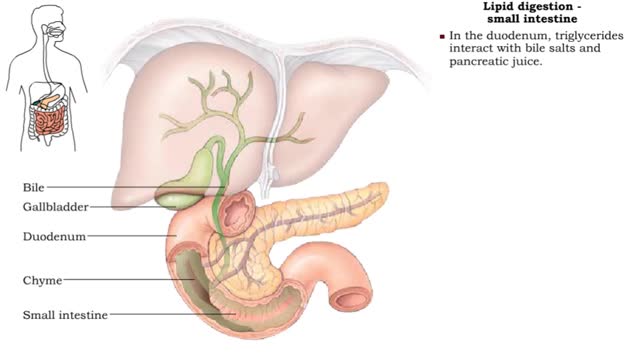
• Lipid digestion takes place primarily in the small intestine; some occurs in the mouth and stomach. • Lipases are enzymes that break down triglycerides and phospholipids. • Lingual and gastric lipases hydrolyze a small amount of triglycerides. • End products are fatty acids and...
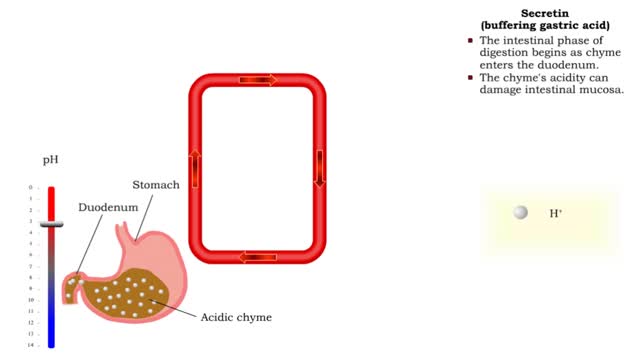
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 10490
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
Advertisement