Search Results
Results for: 'pH'
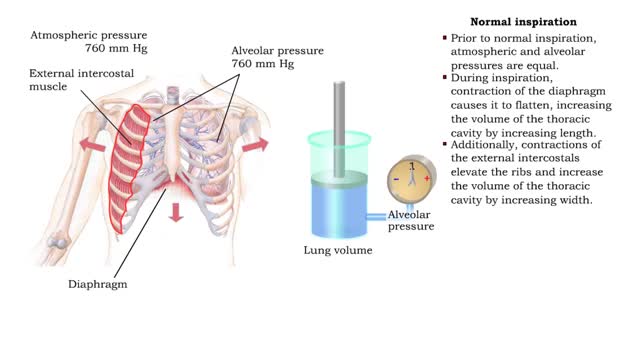
Pressure volume relationships - Normal inspiration and expiration
By: HWC, Views: 10817
• Changing the relative pressure in the compartments can control the direction of airflow between compartments. • In a closed compartment, pressure and volume are inversely related. • Reducing the volume will increase the pressure. • Increasing the volume will decrease the pressure. ...
By: HWC, Views: 10944
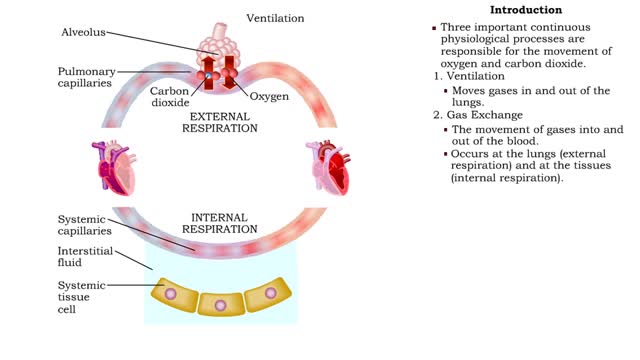
• The respiratory system is responsible for the movement of gases involved in cellular metabolism. • Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is generated during the aerobic breakdown of glucose and other fuel molecules in order to produce ATP. • Three important continuous physiological pro...
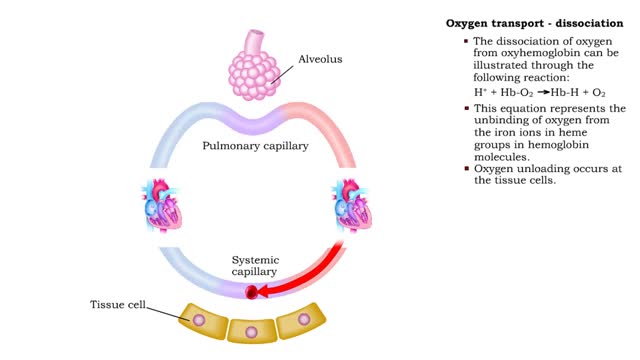
Oxygen transport: association and dissociation & Factors that affect hemoglobin's saturation with O2
By: HWC, Views: 10846
• The production of oxyhemoglobin can be illustrated through the following reaction: 02 + Hb-H --) Hb-02 + H+ • This equation represents the binding of oxygen to the iron ions in heme groups in hemoglobin molecules. • Oxygen binding or loading occurs at the lungs • The dissociatio...
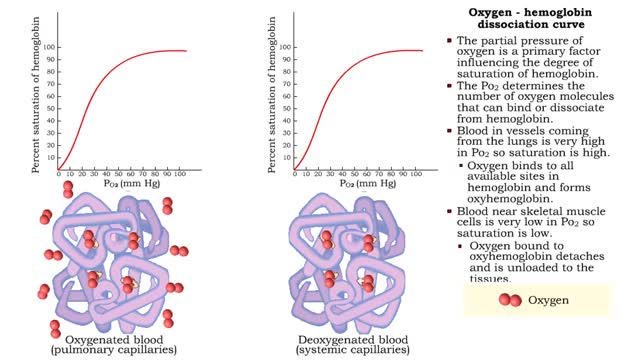
Oxygen - hemoglobin dissociation curve & Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - acidity
By: HWC, Views: 11539
• The partial pressure of oxygen is a primary factor influencing the degree of saturation of hemoglobin. • The Po2 determines the number of oxygen molecules that can bind or dissociate from hemoglobin. • Blood in vessels coming from the lungs is very high in Po2 so saturation is high. ...
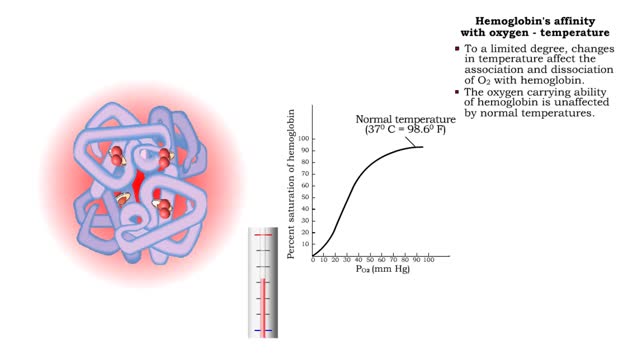
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 10926
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
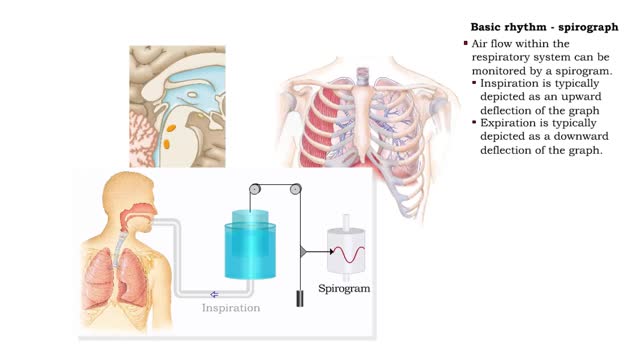
Basic rhythm - control centers in medulla oblongata, spirograph and normal tidal cycle
By: HWC, Views: 10786
• Normal ventilation is rhythmic and involves continuous cycles of inspiration and expiration. • Various regions of the brain closely regulate this rhythmic pattern of ventilation. • The rhythmicity area in the medulla regulates the basic rhythm of ventilation. • The medullary rhy...
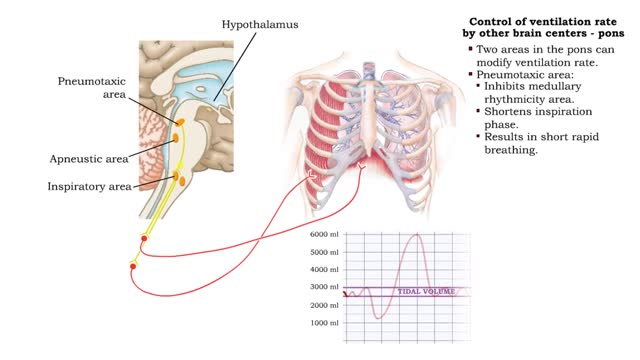
Control of ventilation rate by other brain centers (posts, hypothalamus & cerebral cortex)
By: HWC, Views: 10864
Forced ventilation: • The inspiratory area stimulates accessory inspiratory muscles. • Inspiration is more forceful. • Inspiratory area activates expiratory area, which sends impulses to the expiratory muscles (internal intercostals and abdominal muscles). • Expiration muscles c...
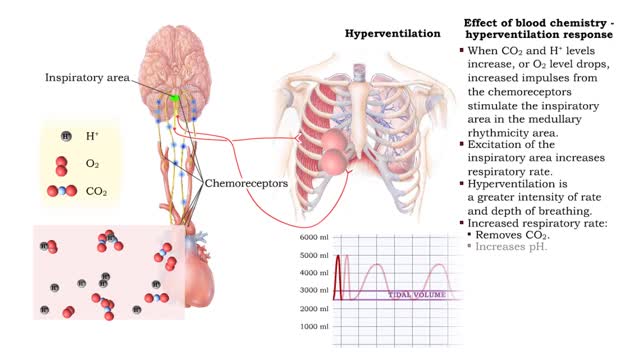
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 10588
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
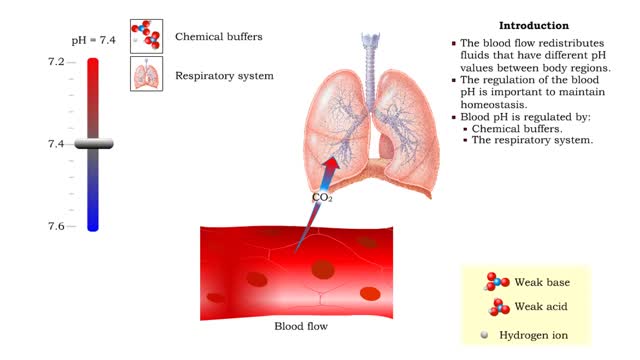
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 10810
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
Advertisement