Search Results
Results for: 'pH'
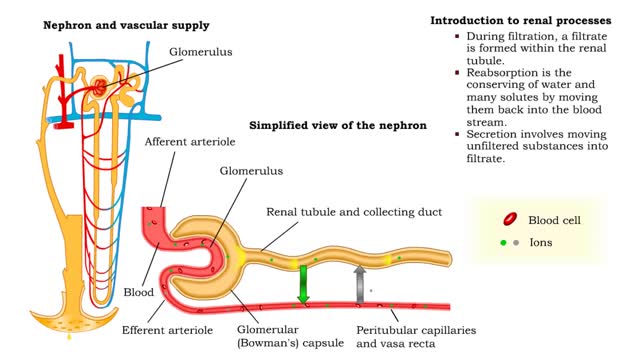
Introduction to filtration - filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 11063
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
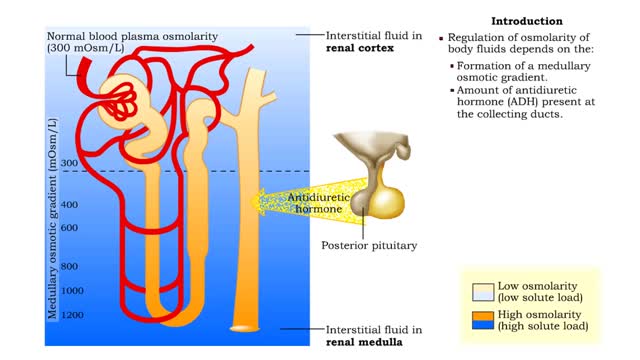
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 11347
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
By: HWC, Views: 11676
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
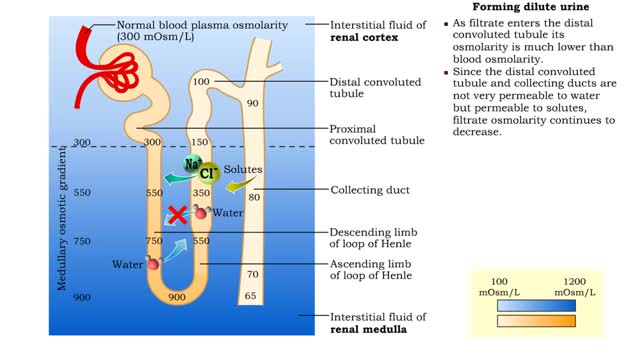
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 11375
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
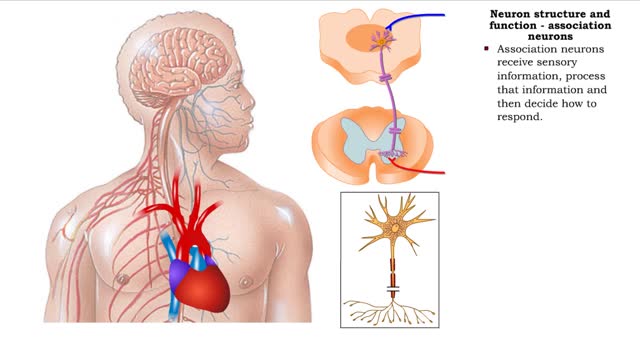
Neuron structure and function - sensory neurons, association neurons & motor neurons
By: HWC, Views: 10882
• The primary function of the nervous system is to provide rapid communication within the body to maintain homeostasis. • This function underlies behaviors, thinking and control of organ functions. • The basic functions of the nervous system are provided by: • Sensory neurons • ...
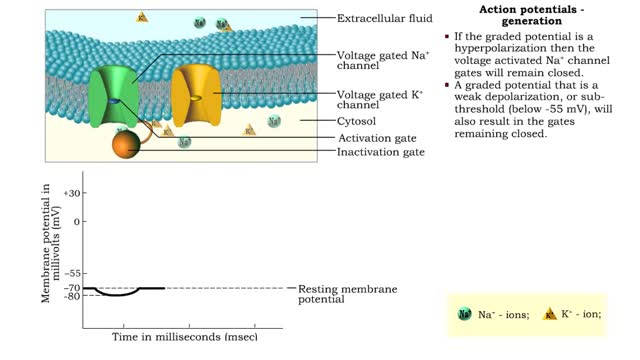
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 10737
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
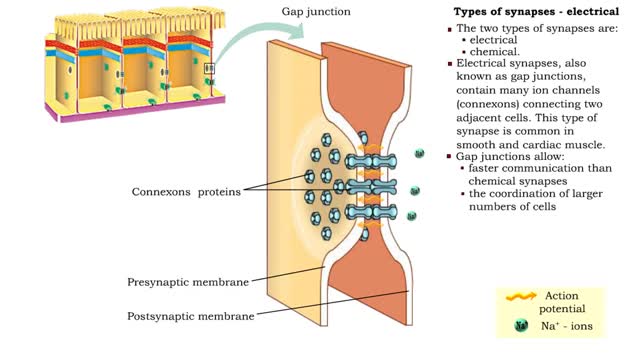
Types of synapses - electrical & chemical
By: HWC, Views: 10981
• Neurons communicate with one another or effector cells via synapses that allow information to be filtered and integrated. • The two types of synapses are: • electrical • chemical. • Electrical synapses, also known as gap junctions, contain many ion channels (connexons) conne...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 10836
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
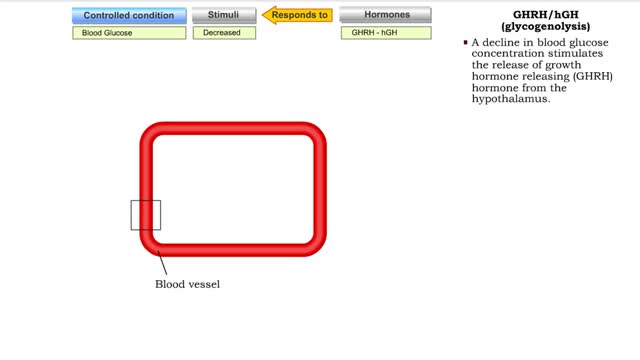
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10716
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
Advertisement