Search Results
Results for: 'Partial positive charge'
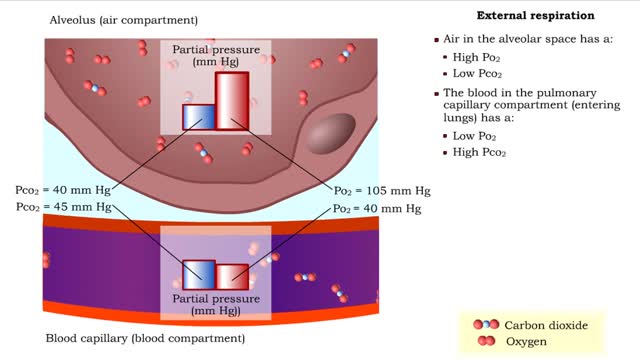
Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC, Views: 11197
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. ...
Double Vacuum Process (Illustration No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 10078
In this so-called low-pressure process, the wood is first subjected to a short and relatively weak initial vacuum, after which the treatment vessel is flooded with preservative solution and reduced to normal pressure The double vacuum container is loaded with timber. A partial vacuum is draw...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 10968
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
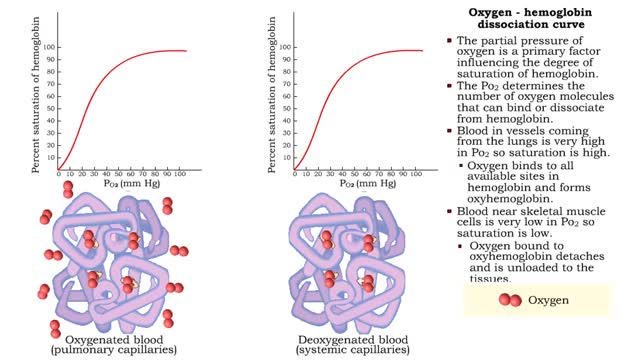
Oxygen - hemoglobin dissociation curve & Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - acidity
By: HWC, Views: 11617
• The partial pressure of oxygen is a primary factor influencing the degree of saturation of hemoglobin. • The Po2 determines the number of oxygen molecules that can bind or dissociate from hemoglobin. • Blood in vessels coming from the lungs is very high in Po2 so saturation is high. ...
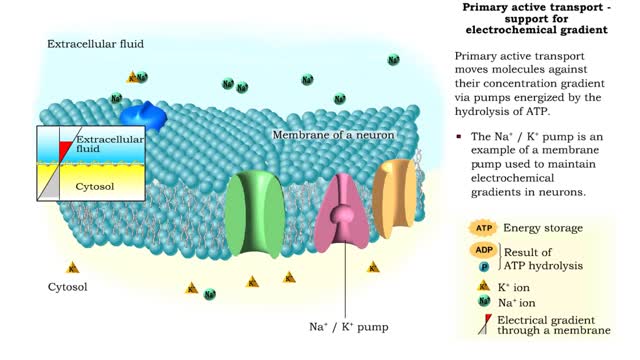
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11206
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
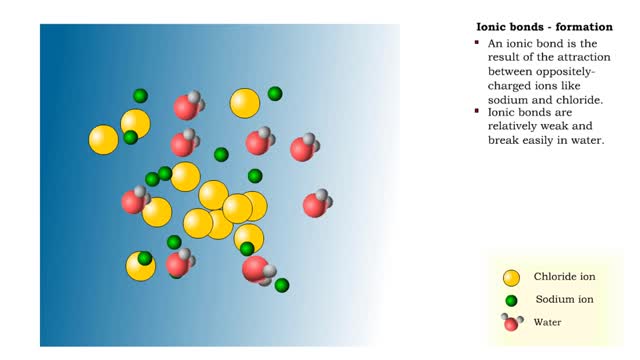
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11292
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
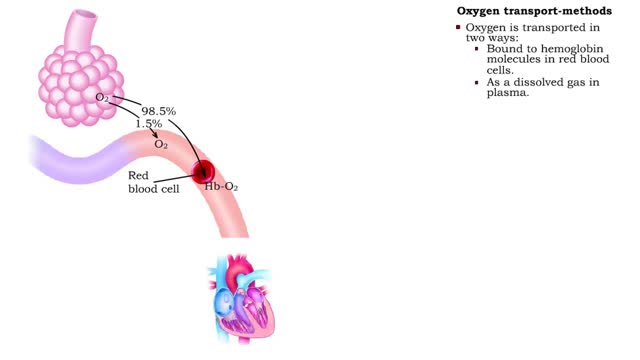
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 10871
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
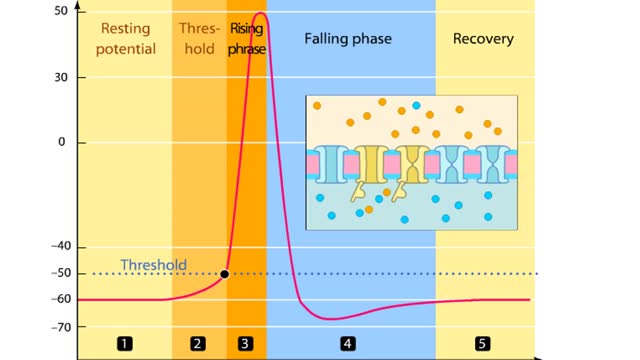
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 10438
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
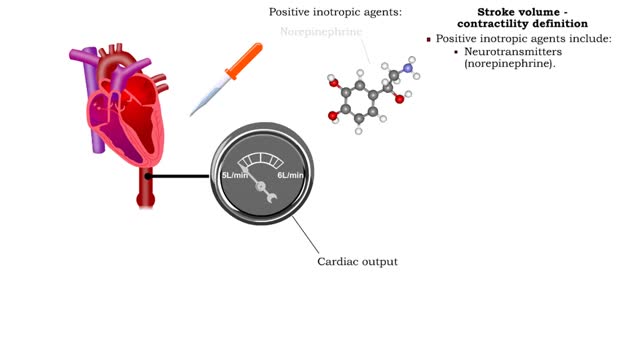
Stroke volume - contractility definition
By: HWC, Views: 10707
Contractility is the forcefulness of contraction of cardiac muscle. • Inotropic agents are substances that increase or decrease contractility (and stroke volume). • Positive inotropic agents increase contractility and will increase stroke volume and cardiac output. • Negative inotropi...
Advertisement