Search Results
Results for: 'Sympathetic impulses'
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14772
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
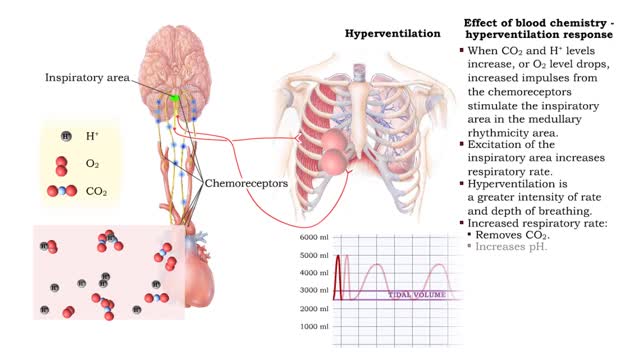
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 10994
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
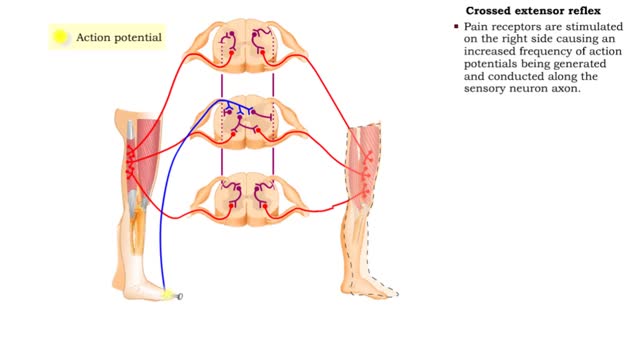
Flexor reflex & Crossed extensor reflex
By: HWC, Views: 11262
• The flexor reflex is a response to pain. This reflex is polysynaptic, ipsilateral, and intersegmental. • Pain receptors are stimulated causing increased frequency of action potentials to be generated and conducted along the sensory neuron axon. • The sensory impulses excite several ass...
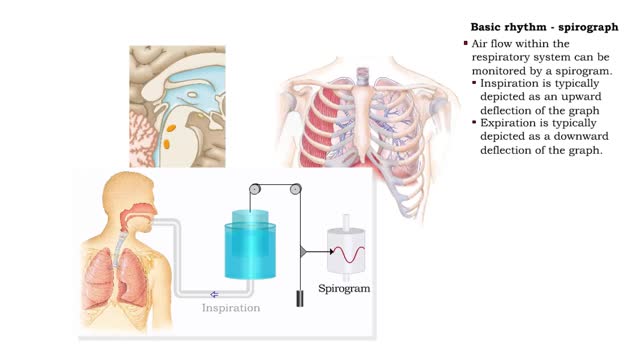
Basic rhythm - control centers in medulla oblongata, spirograph and normal tidal cycle
By: HWC, Views: 11202
• Normal ventilation is rhythmic and involves continuous cycles of inspiration and expiration. • Various regions of the brain closely regulate this rhythmic pattern of ventilation. • The rhythmicity area in the medulla regulates the basic rhythm of ventilation. • The medullary rhy...
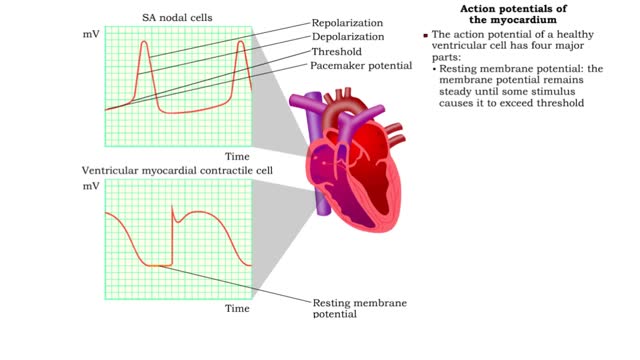
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 11243
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14491
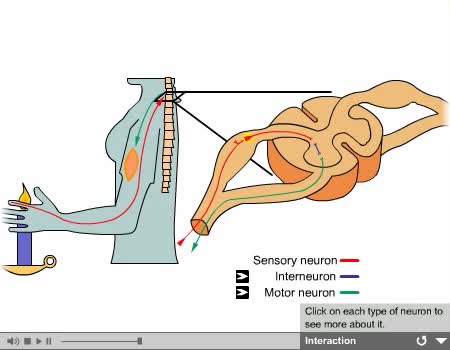
Interneurons: - Are called central or associative neurons. - Located entirely within the central nervous system. - They function to mediate impulses between sensory and motor neurons.
By: Administrator, Views: 14624
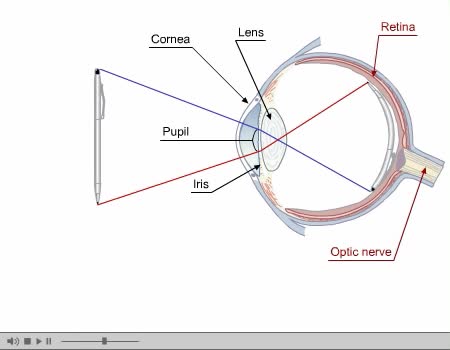
Eye Composed of special anatomical structures that work together to facilitate sight: Cornea Pupil Lens Vitreous body Light stimulates sensory receptors (rods and cones) in the retina or innermost layer of the eye. Vision is made possible through the coordinated actions of nerves that co...
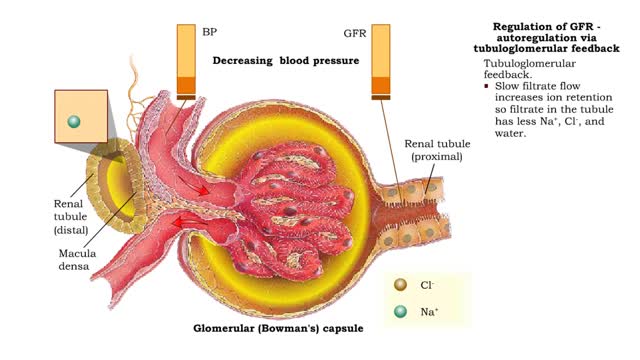
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12901
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
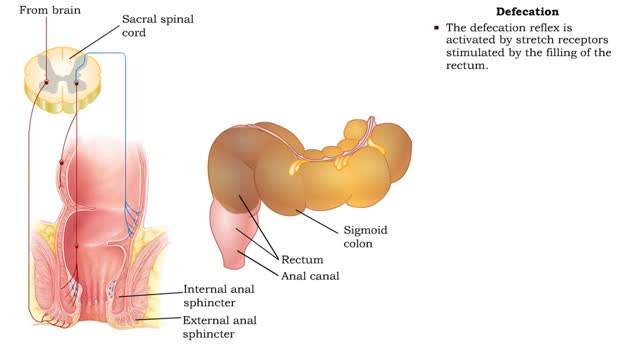
Haustral churning, Gastrocolic reflex and mass peristalsis & Defecation
By: HWC, Views: 11704
• As the cecum becomes filled and distends, a local reflex causes: • Closure of the ileocecal valve. • Activation of haustral churning. • Haustral churning mixes the chyme, which helps absorption of water, salts, and vitamins. • Haustral churning propels the contents of the colo...
Advertisement