Search Results
Results for: 'disulfide bonds'
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 8343
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
Activation Energy - Valence Electrons
By: HWC, Views: 10457
■ Shared electrons in the outermost orbital form bonds. These electrons are called valence electrons. ■ Valence electrons are disrupted and can be rearranged into a new bond. ■ The energy necessary to start a reaction and break bonds is called the activation energy. ■ Reactants have...
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11293
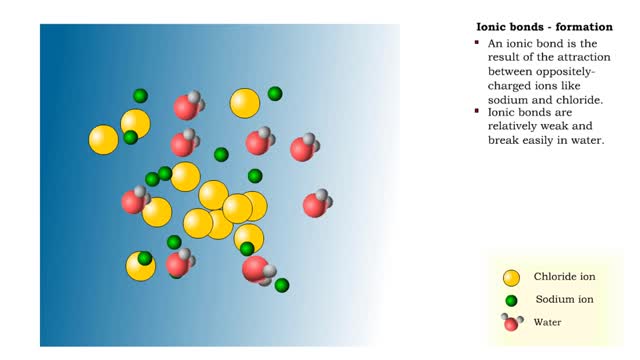
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Lipids
By: HWC, Views: 10417
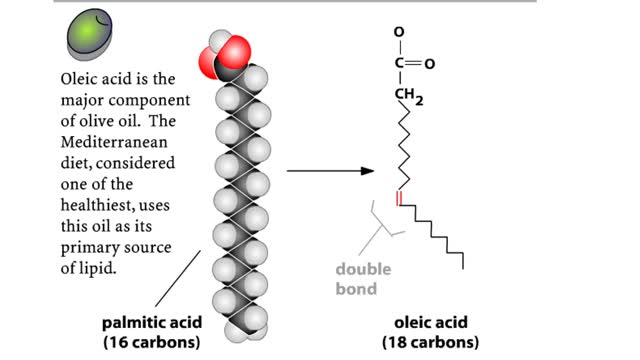
A triglyceride (also called triacylglycerol) is composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. The fatty acids attach to the glycerol molecule by a covalent ester bond. The long hydrocarbon chain of each fatty acid makes the triglyceride molecule nonpolar and hydrophobic. Pa...
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 10633
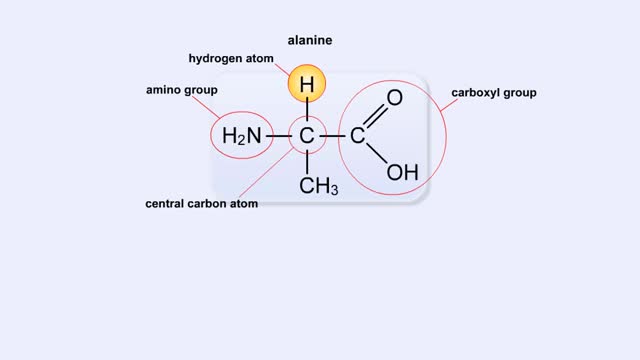
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
By: HWC, Views: 10798
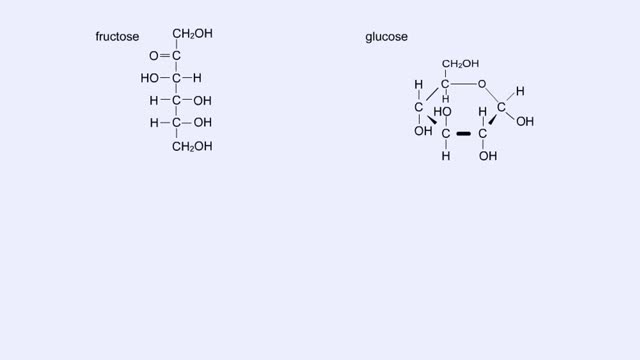
Here are the molecular structures of three simple sugars: glucose, ribose, and fructose. Look at these simple sugars and identify what characteristics they all share. As you can see, all of the carbohydrates have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 and there is always a double bo...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Nucleic acids
By: HWC, Views: 10970
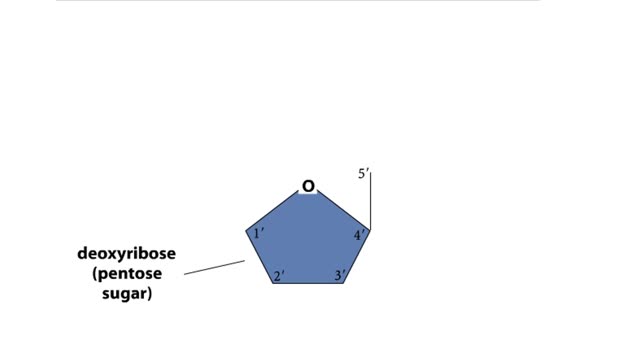
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids (polymers of nucleotides). Two polymers with complementary nucleotide sequences can pair with each other. This pairing endows nucleic acids with the ability to store, transmit, and retrieve genetic information. Two strands of DNA pair by hydrogen bonding. A compon...
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 10520
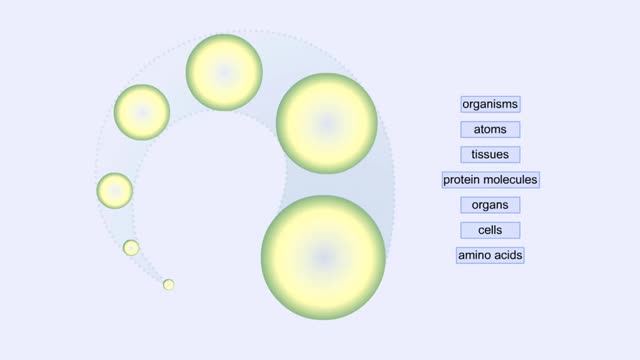
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Proteins
By: HWC, Views: 10542
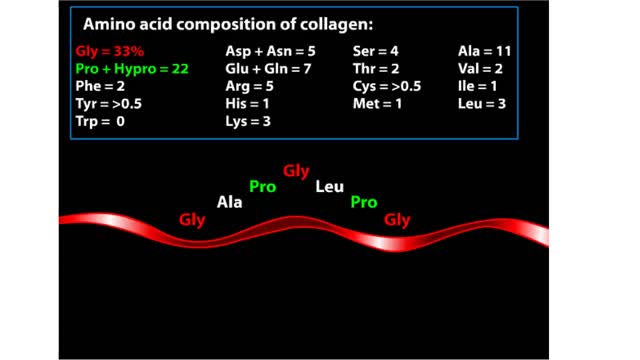
Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The 20 different amino acids used to make all proteins differ only in their side chains, and the properties of these side chains account for the great diversity of protein structure and function. Collagen is an example of how a prote...
Advertisement