Search Results
Results for: 'hydrolytic digestive reactions'
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14442
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
By: HWC, Views: 5399
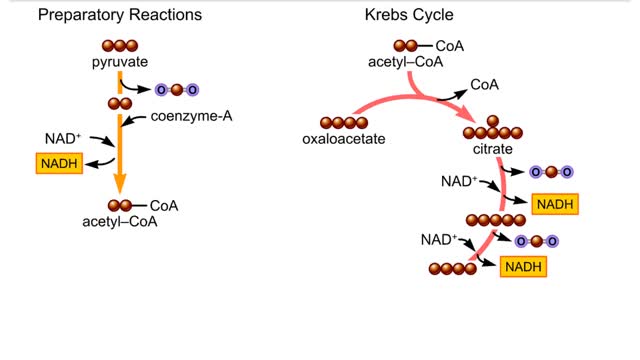
The second-stage reactions of aerobic respiration. The second-stage reactions occur in a mitochondrion's inner compartment. In the first preparatory reaction, a carbon atom is stripped from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide. The remaining carbons combine with coenzyme A and give ...
By: HWC, Views: 10982
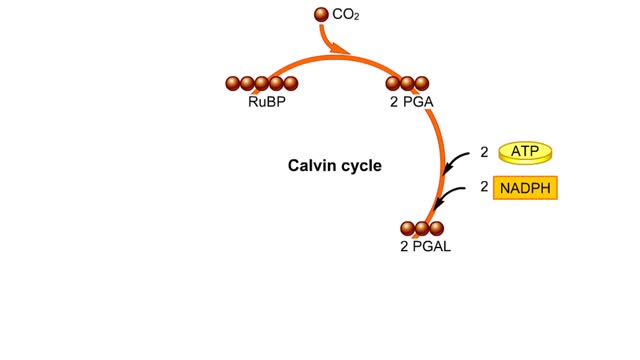
he light-independent reactions make sugars by way of a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. The cycle begins when rubisco attaches a carbon from carbon dioxide to ribulose bisphosphate. The molecule that forms splits into two molecules of PGA. Each PGA gets a phosphate group from ATP a...
By: HWC, Views: 10528
Observe the burning logs of wood. The logs burn to emit heat, light and carbon dioxide. What is left behind is ash. This residue is a new substance with a different molecular structure than the original wood. Similarly when baking the dough into bread, it becomes fluffy and light. There is a ch...
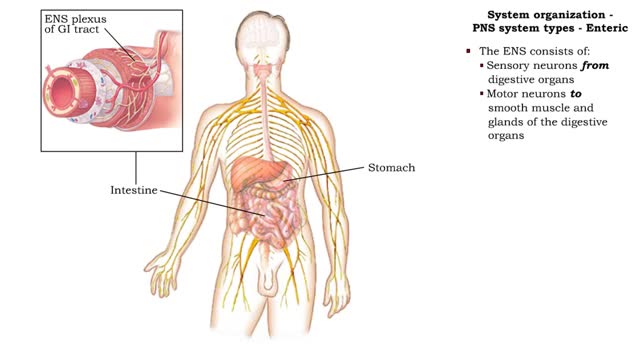
System organization - PPM system types (Somatic, Autonomic & Enteric) and Reflex arc types
By: HWC, Views: 11386
• The PNS consists of all nervous tissue outside of the CNS. • It is divided into three functional components: • Somatic nervous system (SNS) • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Enteric nervous system (ENS) • The SNS consists of: • Sensory neurons from skeletal muscles ...
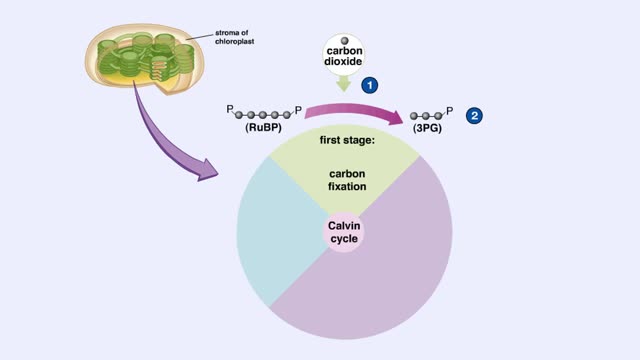
Calvin cycle (The light-independent reactions )
By: HWC, Views: 10968
The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the stroma of the chloroplast. Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through tiny pores or stomata and diffuses into the chloroplast. The first stage of the Calvin cycle is the attachment of a carbon dioxide molecule to a 5-carbon ribulose bi...
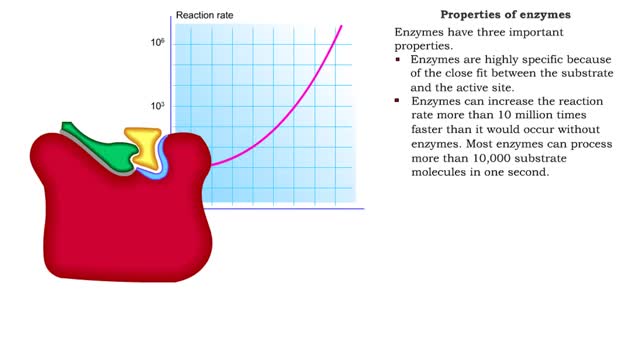
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11121
â– Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. â– Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. â– Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. â– Coenzymes often come from vitamins. â– Cofactors affect the shape of...
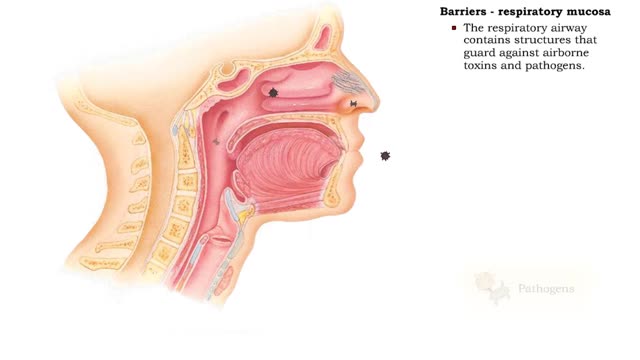
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11441
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. â€...
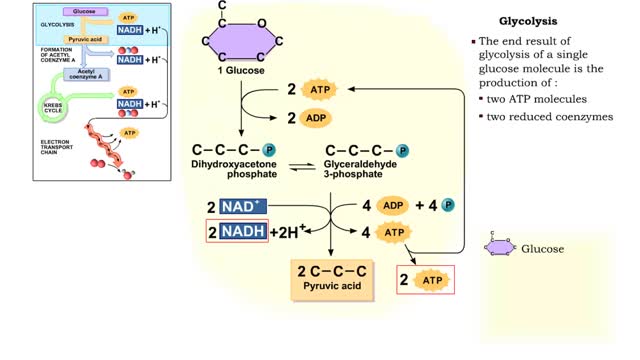
By: HWC, Views: 11491
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Advertisement